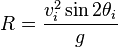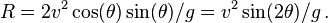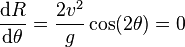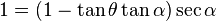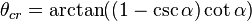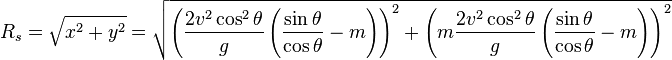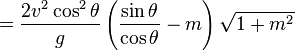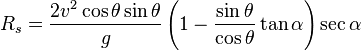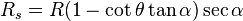Trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that a moving object follows through space as a function of time. The object might be a projectile or a satellite, for example. It thus includes the meaning of orbit—the path of a planet, an asteroid or a comet as it travels around a central mass. A trajectory can be described mathematically either by the geometry of the path, or as the position of the object over time.
In control theory a trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system (see e.g. Poincaré map). In discrete mathematics, a trajectory is a sequence
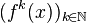 of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping
of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping
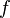 to an element
to an element 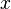 of its source.
of its source.
Physics of trajectories
A familiar example of a trajectory is the path of a projectile such as a thrown ball or rock. In a greatly simplified model the object moves only under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field. This can be a good approximation for a rock that is thrown for short distances for example, at the surface of the moon. In this simple approximation the trajectory takes the shape of a parabola. Generally, when determining trajectories it may be necessary to account for nonuniform gravitational forces and air resistance (drag and aerodynamics). This is the focus of the discipline of ballistics.
One of the remarkable achievements of Newtonian mechanics was the derivation of the laws of Kepler. In the gravitational field of a point mass or a spherically-symmetrical extended mass (such as the Sun), the trajectory of a moving object is a conic section, usually an ellipse or a hyperbola.[lower-alpha 1] This agrees with the observed orbits of planets, comets, and artificial spacecraft, to a reasonably good approximation, although if a comet passes close to the Sun, then it is also influenced by other forces, such as the solar wind and radiation pressure, which modify the orbit, and cause the comet to eject material into space.
Newton's theory later developed into the branch of theoretical physics known as classical mechanics. It employs the mathematics of differential calculus (which was, in fact, also initiated by Newton, in his youth). Over the centuries, countless scientists contributed to the development of these two disciplines. Classical mechanics became a most prominent demonstration of the power of rational thought, i.e. reason, in science as well as technology. It helps to understand and predict an enormous range of phenomena. Trajectories are but one example.
Consider a particle of mass 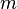 , moving in a potential field
, moving in a potential field 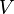 . Physically speaking, mass represents inertia, and the field
. Physically speaking, mass represents inertia, and the field 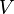 represents external forces, of a particular kind known as "conservative". That is, given
represents external forces, of a particular kind known as "conservative". That is, given 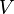 at every relevant position, there is a way to infer the associated force that would act at that position, say from gravity. Not all forces can be expressed in this way, however.
at every relevant position, there is a way to infer the associated force that would act at that position, say from gravity. Not all forces can be expressed in this way, however.
The motion of the particle is described by the second-order differential equation
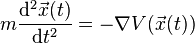 with
with 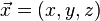
On the right-hand side, the force is given in terms of 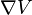 , the gradient of the potential, taken at positions along the trajectory. This is the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion: force equals mass times acceleration, for such situations.
, the gradient of the potential, taken at positions along the trajectory. This is the mathematical form of Newton's second law of motion: force equals mass times acceleration, for such situations.
Examples
Uniform gravity, no drag or wind

The ideal case of motion of a projectile in a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of other forces (such as air drag), was first investigated by Galileo Galilei. To neglect the action of the atmosphere, in shaping a trajectory, would have been considered a futile hypothesis by practical minded investigators, all through the Middle Ages in Europe. Nevertheless, by anticipating the existence of the vacuum, later to be demonstrated on Earth by his collaborator Evangelista Torricelli, Galileo was able to initiate the future science of mechanics. And in a near vacuum, as it turns out for instance on the Moon, his simplified parabolic trajectory proves essentially correct.
In the analysis that follows we derive the equation of motion of a projectile as measured from an inertial frame, at rest with respect to the ground, to which frame is associated a right-hand co-ordinate system - the origin of which coincides with the point of launch of the projectile. The x-axis is parallel to the ground and the y axis perpendicular to it ( parallel to the gravitational field lines ). Let 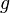 be the acceleration of gravity. Relative to the flat terrain, let the initial horizontal speed be
be the acceleration of gravity. Relative to the flat terrain, let the initial horizontal speed be  and the initial vertical speed be
and the initial vertical speed be 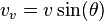 . It will also be shown that, the range is
. It will also be shown that, the range is 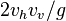 , and the maximum altitude is
, and the maximum altitude is 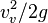 ; The maximum range, for a given initial speed
; The maximum range, for a given initial speed 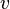 , is obtained when
, is obtained when  , i.e. the initial angle is 45 degrees. This range is
, i.e. the initial angle is 45 degrees. This range is 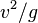 , and the maximum altitude at the maximum range is a quarter of that.
, and the maximum altitude at the maximum range is a quarter of that.
Derivation of the equation of motion
Assume the motion of the projectile is being measured from a Free fall frame which happens to be at (x,y)=(0,0) at t=0. The equation of motion of the projectile in this frame (by the principle of equivalence) would be  . The co-ordinates of this free-fall frame, with respect to our inertial frame would be
. The co-ordinates of this free-fall frame, with respect to our inertial frame would be 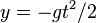 . That is,
. That is, 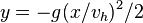 .
.
Now translating back to the inertial frame the co-ordinates of the projectile becomes 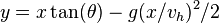 That is:
That is:
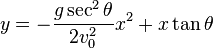 ,
,
(where v0 is the initial velocity, 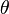 is the angle of elevation, and g is the acceleration due to gravity).
is the angle of elevation, and g is the acceleration due to gravity).
Range and height

The range, R, is the greatest distance the object travels along the x-axis in the I sector. The initial velocity, vi, is the speed at which said object is launched from the point of origin. The initial angle, θi, is the angle at which said object is released. The g is the respective gravitational pull on the object within a null-medium.
The height, h, is the greatest parabolic height said object reaches within its trajectory
Angle of elevation
In terms of angle of elevation 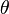 and initial speed
and initial speed 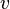 :
:
giving the range as
This equation can be rearranged to find the angle for a required range
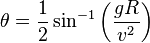 (Equation II: angle of projectile launch)
(Equation II: angle of projectile launch)
Note that the sine function is such that there are two solutions for 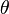 for a given range
for a given range 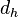 . The angle
. The angle 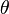 giving the maximum range can be found by considering the derivative or
giving the maximum range can be found by considering the derivative or 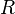 with respect to
with respect to 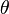 and setting it to zero.
and setting it to zero.
which has a nontrivial solution at 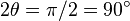 , or
, or 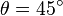 .
The maximum range is then
.
The maximum range is then 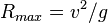 . At this angle
. At this angle  , so the maximum height obtained is
, so the maximum height obtained is 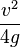 .
.
To find the angle giving the maximum height for a given speed calculate the derivative of the maximum height 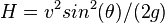 with respect to
with respect to 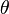 , that is
, that is
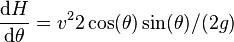 which is zero when
which is zero when  . So the maximum height
. So the maximum height 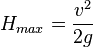 is obtained when the projectile is fired straight up.
is obtained when the projectile is fired straight up.
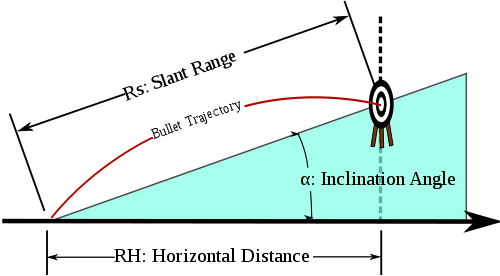
Uphill/downhill in uniform gravity in a vacuum
Given a hill angle 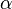 and launch angle
and launch angle 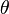 as before, it can be shown that the range along the hill
as before, it can be shown that the range along the hill 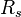 forms a ratio with the original range
forms a ratio with the original range 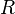 along the imaginary horizontal, such that:
along the imaginary horizontal, such that:
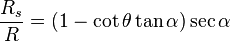 (Equation 11)
(Equation 11)
In this equation, downhill occurs when 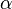 is between 0 and -90 degrees. For this range of
is between 0 and -90 degrees. For this range of 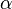 we know:
we know: 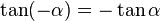 and
and  . Thus for this range of
. Thus for this range of 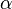 ,
,
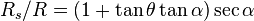 . Thus
. Thus  is a positive value meaning the range downhill is always further than along level terrain. The lower level of terrain causes the projectile to remain in the air longer, allowing it to travel further horizontally before hitting the ground.
is a positive value meaning the range downhill is always further than along level terrain. The lower level of terrain causes the projectile to remain in the air longer, allowing it to travel further horizontally before hitting the ground.
While the same equation applies to projectiles fired uphill, the interpretation is more complex as sometimes the uphill range may be shorter or longer than the equivalent range along level terrain. Equation 11 may be set to 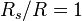 (i.e. the slant range is equal to the level terrain range) and solving for the "critical angle"
(i.e. the slant range is equal to the level terrain range) and solving for the "critical angle" 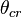 :
:
Equation 11 may also be used to develop the "rifleman's rule" for small values of 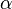 and
and 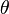 (i.e. close to horizontal firing, which is the case for many firearm situations). For small values, both
(i.e. close to horizontal firing, which is the case for many firearm situations). For small values, both 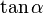 and
and 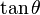 have a small value and thus when multiplied together (as in equation 11), the result is almost zero. Thus equation 11 may be approximated as:
have a small value and thus when multiplied together (as in equation 11), the result is almost zero. Thus equation 11 may be approximated as:
And solving for level terrain range, 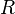
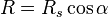 "Rifleman's rule"
"Rifleman's rule"
Thus if the shooter attempts to hit the level distance R, s/he will actually hit the slant target. "In other words, pretend that the inclined target is at a horizontal distance equal to the slant range distance multiplied by the cosine of the inclination angle, and aim as if the target were really at that horizontal position."
Derivation based on equations of a parabola
The intersect of the projectile trajectory with a hill may most easily be derived using the trajectory in parabolic form in Cartesian coordinates (Equation 10) intersecting the hill of slope 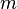 in standard linear form at coordinates
in standard linear form at coordinates 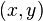 :
:
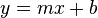 (Equation 12) where in this case,
(Equation 12) where in this case, 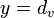 ,
,  and
and 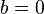
Substituting the value of  into Equation 10:
into Equation 10:
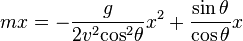
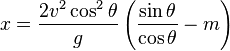 (Solving above x)
(Solving above x)
This value of x may be substituted back into the linear equation 12 to get the corresponding y coordinate at the intercept:
Now the slant range 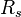 is the distance of the intercept from the origin, which is just the hypotenuse of x and y:
is the distance of the intercept from the origin, which is just the hypotenuse of x and y:
Now 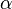 is defined as the angle of the hill, so by definition of tangent,
is defined as the angle of the hill, so by definition of tangent, 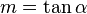 . This can be substituted into the equation for
. This can be substituted into the equation for 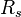 :
:
Now this can be refactored and the trigonometric identity for 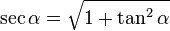 may be used:
may be used:
Now the flat range  by the previously used trigonometric identity and
by the previously used trigonometric identity and  so:
so:
Orbiting objects
If instead of a uniform downwards gravitational force we consider two bodies orbiting with the mutual gravitation between them, we obtain Kepler's laws of planetary motion. The derivation of these was one of the major works of Isaac Newton and provided much of the motivation for the development of differential calculus.
Catching balls
If a projectile, such as a baseball or cricket ball, travels in a parabolic path, with negligible air resistance, and if a player is positioned so as to catch it as it descends, he sees its angle of elevation increasing continuously throughout its flight. The tangent of the angle of elevation is proportional to the time since the ball was sent into the air, usually by being struck with a bat. Even when the ball is really descending, near the end of its flight, its angle of elevation seen by the player continues to increase. The player therefore sees it as if it were ascending vertically at constant speed. Finding the place from which the ball appears to rise steadily helps the player to position himself correctly to make the catch. If he is too close to the batsman who has hit the ball, it will appear to rise at an accelerating rate. If he is too far from the batsman, it will appear to slow rapidly, and then to descend.
Notes
- ↑ It is theoretically possible for an orbit to be a radial straight line, a circle, or a parabola. These are limiting cases which have zero probability of occurring in reality.
See also
- Aft-crossing trajectory
- Orbit (dynamics)
- Orbit (group theory)
- Planetary orbit
- Porkchop plot
- Range of a projectile
- Rigid body
- Trajectory of a projectile
External links
| The Wikibook High school physics has a page on the topic of: Projectile motion |
- Projectile Motion Flash Applet
- Trajectory calculator
- An interactive simulation on projectile motion
- Projectile Motion Simulator, java applet
- Projectile Lab, JavaScript trajectory simulator
- Parabolic Projectile Motion: Shooting a Harmless Tranquilizer Dart at a Falling Monkey by Roberto Castilla-Meléndez, Roxana Ramírez-Herrera, and José Luis Gómez-Muñoz, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Trajectory, ScienceWorld.
- Java projectile-motion simulation, with first-order air resistance.
- Java projectile-motion simulation; targeting solutions, parabola of safety.