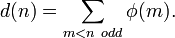Tonality diamond

In music theory and tuning, a tonality diamond is a two-dimensional diagram of ratios in which one dimension is the Otonality and one the Utonality.[1] Thus the n-limit tonality diamond is an arrangement in diamond-shape of the set of rational numbers r, 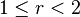 , such that the odd part of both the numerator and the denominator of r, when reduced to lowest terms, is less than or equal to the fixed odd number n. Equivalently, the diamond may be considered as a set of pitch classes, where a pitch class is an equivalence class of pitches under octave equivalence. The tonality diamond is often regarded as comprising the set of consonances of the n-limit. Although originally invented by Max Friedrich Meyer,[2] the tonality diamond is now most associated with Harry Partch.
, such that the odd part of both the numerator and the denominator of r, when reduced to lowest terms, is less than or equal to the fixed odd number n. Equivalently, the diamond may be considered as a set of pitch classes, where a pitch class is an equivalence class of pitches under octave equivalence. The tonality diamond is often regarded as comprising the set of consonances of the n-limit. Although originally invented by Max Friedrich Meyer,[2] the tonality diamond is now most associated with Harry Partch.
The diamond arrangement
Partch arranged the elements of the tonality diamond in the shape of a rhombus, and subdivided into (n+1)2/4 smaller rhombuses. Along the upper left side of the rhombus are placed the odd numbers from 1 to n, each reduced to the octave (divided by the minimum power of 2 such that 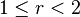 ). These intervals are then arranged in ascending order. Along the lower left side are placed the corresponding reciprocals, 1 to 1/n, also reduced to the octave (here, multiplied by the minimum power of 2 such that
). These intervals are then arranged in ascending order. Along the lower left side are placed the corresponding reciprocals, 1 to 1/n, also reduced to the octave (here, multiplied by the minimum power of 2 such that 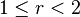 ). These are placed in descending order. At all other locations are placed the product of the diagonally upper- and lower-left intervals, reduced to the octave. This gives all the elements of the tonality diamond, with some repetition. Diagonals sloping in one direction form Otonalities and the diagonals in the other direction form Utonalities. One of Partch's instruments, the diamond marimba, is arranged according to the tonality diamond.
). These are placed in descending order. At all other locations are placed the product of the diagonally upper- and lower-left intervals, reduced to the octave. This gives all the elements of the tonality diamond, with some repetition. Diagonals sloping in one direction form Otonalities and the diagonals in the other direction form Utonalities. One of Partch's instruments, the diamond marimba, is arranged according to the tonality diamond.
5-limit
| 3/2 | |||||
| 5/4 | 6/5 | ||||
| 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | |||
| 8/5 | 5/3 | ||||
| 4/3 |
This diamond contains three identities (1, 3, 5).
7-limit
| 7/4 | ||||||
| 3/2 | 7/5 | |||||
| 5/4 | 6/5 | 7/6 | ||||
| 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | |||
| 8/5 | 5/3 | 12/7 | ||||
| 4/3 | 10/7 | |||||
| 8/7 |
This diamond contains four identities (1, 3, 5, 7).
11-limit

This diamond contains six identities (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11). Harry Partch used the 11-limit tonality diamond, but flipped it 90 degrees.
15-limit
15/8
7/4 5/3
13/8 14/9 3/2
3/2 13/9 7/5 15/11
11/8 4/3 13/10 14/11 5/4
5/4 11/9 6/5 13/11 7/6 15/13
9/8 10/9 11/10 12/11 13/12 14/13 15/14
1/1 1/1 1/1 1/1 1/1 1/1 1/1 1/1
16/9 9/5 20/11 11/6 24/13 13/7 28/15
8/5 18/11 5/3 22/13 12/7 26/15
16/11 3/2 20/13 11/7 8/5
4/3 18/13 10/7 22/15
16/13 9/7 4/3
8/7 6/5
16/15
This diamond contains eight identities (1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15).

Geometry of the tonality diamond
The five- and seven-limit tonality diamonds exhibit a highly regular geometry within the modulatory space, meaning all non-unison elements of the diamond are only one unit from the unison. The five-limit diamond then becomes a regular hexagon surrounding the unison, and the seven-limit diamond a cuboctahedron surrounding the unison.
Properties of the tonality diamond
Three properties of the tonality diamond and the ratios contained:
- All ratios between neighboring ratios are superparticular ratios, those with a difference of 1 between numerator and denominator.[3]
- Ratios with relatively lower numbers have more space between them than ratios with higher numbers.[3]
- The system, including the ratios between ratios, is symmetrical within the octave when measured in cents not in ratios.[3]
For example:
| 5-limit tonality diamond, ordered least to greatest | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio | 1/1 | 6/5 | 5/4 | 4/3 | 3/2 | 8/5 | 5/3 | 2/1 | ||||||||
| Cents | 0 | 315.64 | 386.31 | 498.04 | 701.96 | 813.69 | 884.36 | 1200 | ||||||||
| Width | 315.64 | 70.67 | 111.73 | 203.91 | 111.73 | 70.67 | 315.64 | |||||||||
- The ratio between 6/5 and 5/4 (and 8/5 and 5/3) is 25/24.
- The ratios with relatively low numbers 4/3 and 3/2 are 203.91 cents apart, while the ratios with relatively high numbers 6/5 and 5/4 are 70.67 cents apart.
- The ratio between the lowest and 2nd lowest and the highest and 2nd highest ratios are the same, and so on.
Size of the tonality diamond
If φ(n) is Euler's totient function, which gives the number of positive integers less than n and relatively prime to n, that is, it counts the integers less than n which share no common factor with n, and if d(n) denotes the size of the n-limit tonality diamond, we have the formula
From this we can conclude that the rate of growth of the tonality diamond is asymptotically equal to 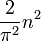 . The first few values are the important ones, and the fact that the size of the diamond grows as the square of the size of the odd limit tells us that it becomes large fairly quickly. There are seven members to the 5-limit diamond, 13 to the 7-limit diamond, 19 to the 9-limit diamond, 29 to the 11-limit diamond, 41 to the 13-limit diamond, and 49 to the 15-limit diamond; these suffice for most purposes.
. The first few values are the important ones, and the fact that the size of the diamond grows as the square of the size of the odd limit tells us that it becomes large fairly quickly. There are seven members to the 5-limit diamond, 13 to the 7-limit diamond, 19 to the 9-limit diamond, 29 to the 11-limit diamond, 41 to the 13-limit diamond, and 49 to the 15-limit diamond; these suffice for most purposes.
Translation to string length ratios
Yuri Landman rewrites Partch's diamond to clarify its theoretical relationship to string lengths (as Partch used in his Kitharas) and his Moodswinger instrument. Landman flips the ratios (5/4 becomes 4/5) and takes the complement string part (1/5 instead of 4/5) to make them easier to understand.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Rasch, Rudolph (2000). "A Word or Two on the Tunings of Harry Partch", Harry Partch: An Anthology of Critical Perspectives, p.28. Dunn, David, ed. ISBN 90-5755-065-2.
- ↑ "Musical Mathematics: Meyer's Diamond", Chrysalis-Foundation.org.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Rasch (2000), p.30.
- ↑ "Partch's Tonality Diamond Related to my Moodswinger Color Schedule", Hypercustom.com.
| ||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||