Tommaso Laureti

Tommaso Laureti, often called Tommaso Laureti Siciliano (c. 1530 — 22 September 1602),[1] was an Italian painter from Sicily who trained in the atelier of the aged Sebastiano del Piombo and worked in Bologna. From 1582, he worked for papal patrons in Rome in a Michelangelo-inspired style with special skill in illusionistic perspective that in his Roman work avoided all but traces of Mannerism (Freedberg 1993:654).
Laureti was born in Palermo. After his master's death in 1547, he settled in Bologna, introducing illusionistic perspective paintings on ceilings to the city, notably an Alexander the Great ceiling with a painted architectural setting in Palazzo Vizzani.[2] He painted a Transportation of the body of Saint Augustine for San Giacomo Maggiore. The Mannerist structural elements of the marble and bronze Fountain of Neptune in Bologna, which is surmounted by Giambologna's Neptune, completed in 1566, were based on a 1563 drawing by Laureti. This commission from Pope Pius IV is undoubtedly Laureti's most familiar public work (illustration, left below).
In the Church of Santa Susanna, Rome, Laureti's painting of the Death of Saint Susanna is above the High Altar. His frescoes in the Sala dei Capitani in Michelangelo's Palazzo dei Conservatori on the Campidoglio, painted in 1587-94, depicted episodes from Roman history: The Justice of Brutus; Horatius Cocles defending the Pons Sublicius; Victory at Lake Regillus; Mucius Scaevola before Lars Porsena.

In 1582, the administration of Pope Gregory XIII commissioned Laureti to execute a series of frescoes on a post-Council of Trent triumphalist theme, The Triumph of the Christian religion on the newly vaulted ceiling of the Sala di Costantino or Hall of Constantine, where the walls had been frescoed by the school of Raphael earlier in the century. The central theme is surrounded by allegorical female figures representing the Italian provinces. The ceiling was completed under the pontificate of Sixtus V, which had grown discontent with the dilatory performance of Laureti. The rigorous illusionistic perspectives represent a lifetime's fascination with the art of perspective. Baglione states Laureti was assisted by the painter Antonio Scalvati.[3]
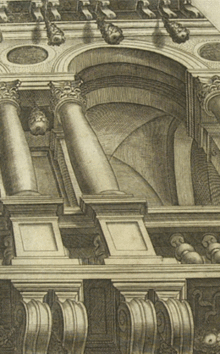
Laureti's illusionistic perspective design for a portion of an illusionistic ceiling, seen as di sotto in su or 'from below to above', was engraved for Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola's, Le due regole della prospettiva pratica., 1583 (illustration, right).[4]
In the Basilica of San Prospero in Reggio Emilia, his altarpiece of the Assumption was completed by Ludovico Carracci in 1602.
Laureti was the second principe or director of the Accademia di San Luca or the artists' academy in Rome, succeeding Federico Zuccari in 1595. His commemorative portrait by Orazio Borgianni, dated 1603, is in the Accademia di San Luca, Rome.[5]
Sources
- Filippo Titi, Descrizione delle Pitture, Sculture e Architetture esposte in Roma, 1763
- (Getty Museum) "the Geometry of Seeing" 2002
- Laueti and the Sala di Costantino
- Roberto Piperno, "Chiesa di Santa Susanna" G. Vasi's description, 1761.
- Freedberg, Sydney J. (1993). Pelican History of Art, ed. Painting in Italy, 1500-1600. Penguin Books Ltd. pp. 654–55.
Notes
- ↑ G. Baglione, Le vite dei pittore (Rome) 1642:
- ↑ An engraved detail is dated 1562, according to Ebria Feinblatt, "Contributions to Girolamo Curti" The Burlington Magazine 117 No. 867 (June 1975, pp. 342+344-353) p. 349.
- ↑ Patrons of the Arts in the Vatican Museums, webpage on Hall of Constantine.
- ↑ An example was included in the Getty Museum exhibition "The Geometry of Seeing", 2002.
- ↑ Harold E. Wethey, "Orazio Borgianni in Italy and in Spain" The Burlington Magazine 106 No. 733 (April 1964, pp. 146-159), pp 148f, 152, fig. 6, 154.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tommaso Laureti. |