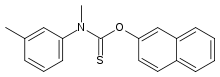
Tolnaftate
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| O-2-naphthyl methyl(3-methylphenyl)thiocarbamate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Tinactin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682617 |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
2398-96-1 | |
| D01AE18 | |
| PubChem | CID 5510 |
| DrugBank |
DB00525 |
| ChemSpider |
5309 |
| UNII |
06KB629TKV |
| KEGG |
D00381 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:9620 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL83668 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H17NOS |
| 307.41 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| Physical data | |
| Melting point | 110 to 111.5 °C (230.0 to 232.7 °F) |
| | |
Tolnaftate is a synthetic thiocarbamate used as an anti-fungal agent that may be sold without medical prescription in most jurisdictions. It is supplied as a cream, powder, spray, and liquid aerosol. Tolnaftate is used to treat fungal conditions such as jock itch, athlete's foot and ringworm. It is sold under several brand names, including Absorbine, Aftate, Genaspor, Lamisil AF, Mycil (Reckitt Benckiser), NP 27, Odor Eaters (Combe Incorporated), Scholl, Tinactin (Bayer), Tinaderm, and Ting.
Synthesis
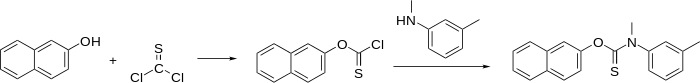
Equimolar amounts of 2-naphthol and thiophosgene are combined to make a monosubstituted product of thiophosgene.
The synthesis of tolnaftate is a three-step process first involving 2-napthol with a base, to deprotonate the acidic phenol hydrogen. NaH, NaNH2 are commonly used. Other common bases may also be used with the same effect. Treatment of N-methyl-m-toluidine with CS2 and CH3Br results in a thiocarbamate intermediate that reacts with the negatively charged oxygen on the deprotonated 2-napthol, displacing the -SCH3 group and forming the final product.
Mechanism
Although the exact mechanism of action is not entirely known, it is believed to inhibit squalene epoxidase,[2] an important enzyme in the biosynthetic pathway of ergosterol (a key component of the fungal membrane) in a similar way to allylamines.[3]
Uses
Tolnaftate has been found to be generally slightly less effective than azoles when used to treat tinea pedis (athlete's foot). It is, however, useful when dealing with ringworm, especially when passed from pets to humans.[4]
References
- ↑ Noguchi, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Miyazaki, K.; Kaji, A.; J. Pharm. Soc. Japan 1968, 88, 335
- ↑ Ryder NS, Frank I, Dupont MC (May 1986). "Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition by the thiocarbamate antifungal agents tolnaftate and tolciclate". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 29 (5): 858–60. doi:10.1128/aac.29.5.858. PMC 284167. PMID 3524433.
- ↑ "antifung". Retrieved 2008-07-09.
- ↑ Crawford F, Hart R, Bell-Syer S, Torgerson D, Young P, Russell I. Topical treatments for fungal infections of the skin and nails of the foot (Cochrane Review). In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 1, 2003. Oxford: Update Software.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||