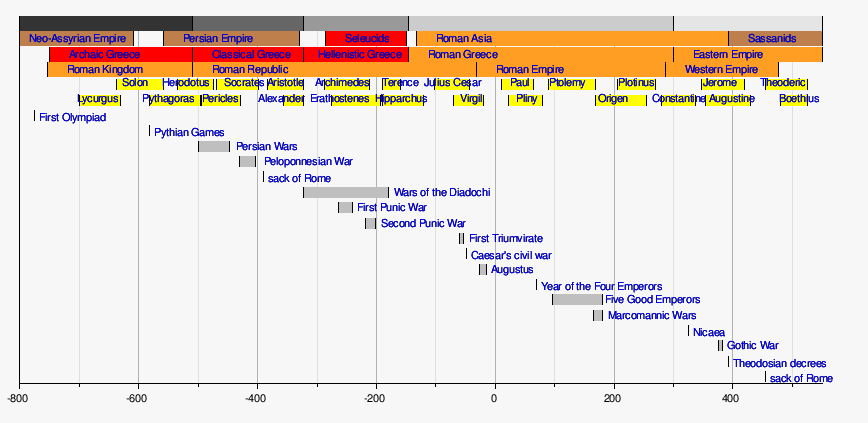
Timeline of ancient Rome
This is a timeline of events concerning ancient Rome, from the city foundation until the last attempt of the Eastern Roman Empire to re-conquer Rome.
7th century BCE
6th century BCE
 |
A graphical timeline is available at
Timeline of the Roman Republic |
ROMAN REPUBLIC
- expulsion of Tarquinius Superbus
- first consuls are Lucius Junius Brutus and Lucius Tarquinius Collatinus
- First Plebeian (commoner) senators appointed (conscripti) to fill vacancies created by the overthrow of the monarchy
- possible siege of Rome : Roman-Etruscan Wars
- 508 BCE: office of pontifex maximus (high priest) created when these powers are stripped from the consuls; possible second siege of Rome by Etruscans : Roman-Etruscan Wars
- 504 BCE: Consul Publius Valerius Publicola grants due process rights to all Roman citizens, criminalizes all future attempts to plot to seize a tyranny
- 501 BCE: Offices of Roman Dictator and Master of the Horse created
5th century BCE
4th century BCE
- 396 BCE
- 394 BCE: Office of consul replaces Tribuni militum consulari potestate.
- 391 BCE: Office of Tribuni militum consulari potestate replaces office of consul.
- 390 BCE: Gauls defeat Roman army : battle of the Allia
- sack of Rome by the Gauls
- 375/371 BCE: Anarchy years: no magistrates elected
- 367 BCE: Office of consul replaces Tribuni militum consulari potestate for last time.
- 366 BCE: Patricians agree to allow Plebeian Consuls to be elected (the first being Lucius Sextius Sextinus). By this, Plebeians acquire de facto right to be elected Censor or appointed Dictator. As a concession, the Plebeians allow the Patricians to create the offices of Praetor and Curule Aedile, and allow only Patricians to run for these offices.
- 351 BCE: Elected : first non-patrician Dictator
- 351 BCE: Elected : first non-patrician censor
- 343 BCE: Rome captures Campania and Capua : First Samnite War
- 342 BCE
- Battle of Mount Gaurus.
- Lex Genucia passed:
- no man can hold the same office before 10 years have elapsed from the first election
- Second law passed, disallowing any man from holding two offices at once.
- 341 BCE: Rome withdraws from the conflict with the Samnites. End of First Samnite War.
- 340 BCE: Latin League pushes for independence : Latin War
- 339 BCE: Law passed (the lex Publilia) which requires the election of one Plebeian censor for each five-year term.
- 338 BCE: Latin League dissolved and Rome controls territory : Latin War Ends.
- 337 BCE: Elected the first non-patrician Praetor (Q. Publilius Philo).
- 326 BCE: Second Samnite War begins
- Samnites attack Campagnia
- 321 BCE: Battle of the Caudine Forks.
- 316 BCE: Battle of Lautulae.
- 311 BCE: Etruscans join the Samnites against Rome.
- 310 BCE: Battle of Lake Vadimo between Rome and the Etruscans.
- 308 BCE: Second Samnite war escalates as Umbrians, Picentini, and Marsians join against Rome.
- 306 BCE: The Hernici revolt against Rome (Livy ix. 42).
- 305 BCE: Samnite forces broken : Battle of Bovianum
- 304 BCE
- Aequi defeated.
- Rome conquers Central and Southern Italy
- Second Samnite War ends
- 300 BCE: Lex Ogulnia passed: priesthoods opened to plebeians
3rd century BCE
- 298 BCE: Third Samnite War begins
- 298 BCE: Rome captures Samnite cities Taurasia, Bovianum Vetus and Aufidena.
- 297 BCE: consul Fabius Maximus Rullianus defeats the Samnites near Tifernum (Liv. 10.14).
- 295 BCE: Battle of Sentinum.
- 294 BCE: Samnite victory at Luceria.
- 293 BCE: Battle of Aquilonia.
- 291 BCE: The Romans storm the Samnite city of Venusia.
- 290 BCE: Rome dominates Italian Peninsula : Third Samnite War ends.
- 287 BCE
- 283 BCE: Rome defeats the Etruscans and the Boii (a Gallic tribe) in the Battle of Lake Vadimo
- 281 BCE: Mounting tensions between Rome and Tarentum. Tarentum appeals to Pyrrhus of Epirus for aid.
- 280 BCE
- 267 BCE: Number of quaestors raised from 4 to 6
- 264/241 BCE: Conquest of Sicily, First Punic War against Carthage
- 242 BCE: Office of Praetor peregrinus created
- 241 BCE: Sicily becomes the first Roman province : First Punic War Ends
- 238 BCE: Sardinia and Corsica become Roman Provinces in the "Truceless War" with Carthage
- 229 BCE: Adriatic Control : First Illyrian War begins.
- 227 BCE
- Queen Teuta surrenders : First Illyrian War ends
- Number of quaestors raised from 6 to 8
- number of praetors raised from 2 to 4
- 224 BCE: Rome defeats Gaul invasion : Battle of Telamon
- 222 BCE: Rome defeats Gauls : Cisalpine Gaul
- 220 BCE: Adriatic Control : Second Illyrian War begins.
- 219 BCE: Demetrius defeated : Second Illyrian War ends.
- 218/201 BCE: Conquest Western Mediterranean : Second Punic War against Carthage. Rome is defeated at the Battle of the River Trebia.
- 216 BCE: Hannibal defeats Roman forces : Battle of Cannae
- 214/205 BCE: Stalemate : First Macedonian War
- 213/211 BCE: Rome captures Syracuse : Siege of Syracuse
- 204/202 BCE: Scipio Africanus Major invades Africa, Hannibal recalled and defeated : Battle of Zama
- 202/196 BCE: Philip V of Macedon defeated : Second Macedonian War
2nd century BCE
1st century BCE
 |
A graphical timeline is available at
Timeline of the Roman Empire |
- 91/88 BCE– Social War, the last rebellion of the Italian nations against Rome
- 88 BCE– Sulla crosses the pomerium with his legions and invades Rome
- 88/85 BCE– First Mithridatic War against Mithridates VI of Pontus
- 83/82 BCE– First Roman civil war, between Sulla and the popular faction; Sulla wins and becomes dictator; censor office abolished (to be recreated in 70 BCE)
- 83/82 BCE– Second Mithridatic War; Sulla returns to Rome and is nominated dictator
- 82/72 BCE– Sertorius, the last Marian general continues the civil war in Hispania
- 74/66 BCE– Third Mithridatic War, eventually won by Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, aka Pompey
- 73/71 BCE- Servile War led by Spartacus
- 67 BCE– Pompey clears the Mediterranean of pirates
- 63 BCE
- 60/54 BCE– An informal coalition is formed by Gāius Jūlius Caesar, Pompey and Marcus Licinius Crassus to govern the Roman republic. This coalition is often referred to as the First triumvirate, even though it did not have the official sanction of law required for a legal triumvirate.
- 58/50 BCE– Caesar fights the Gallic Wars, acquiring the province of Gallia Comata
- 54/53 BCE– First campaign against the Parthian Empire; Crassus utterly defeated and killed
- 49 BCE– Caesar crosses the Rubicon (alea iacta est) and begins the Second Roman civil war against the Optimates, the conservative faction of the Senate, led by Pompey
- 48/45 BCE– Caesar pursues and defeats the Optimates in Greece and Africa
- 44 BCE– Caesar is assassinated on the Ides of March
- 44/42 BCE– Third Roman civil war, between the assassins of Caesar (led by Cassius and Brutus) and Caesar's heirs, Octavian and Mark Antony
- 43 BCE– Octavian, Antony and Lepidus form the second triumvirate
- 36 BCE– Antony's Parthian campaign ends in failure
- 32 BCE– End of peaceful relations between Octavian and Antony
- 31 BCE– In the battle of Actium, Octavian decisively defeats Antony and Cleopatra
- 30 BCE– Antony and Cleopatra commit suicide; Egypt becomes a Roman province
ROMAN EMPIRE
==1st century CE
March– Inauguration of the '"Colosseum'"
- 81– Titus dies suddenly; his brother Domitian becomes emperor
- 85– King Decebalus of Dacia rebels and invades Moesia
- 89– Rebellions in Germania Inferior and Pannonia force peace with Decebalus of Dacia
- 96– Domitian assassinated– end of Flavian dynasty; succeeded by Nerva, the first of the Five good emperors
- 98– Trajan becomes emperor
2nd century
- 101/102– First Dacian War
- 105/106– Second Dacian War; king Decebalus commits suicide and Dacia becomes a province
- 106– Building of Trajan's Forum and construction of Trajan's column
- 113/117– Trajan's successful campaigns against the Parthian Empire
- 115/117– Jewish rebellion that started in Egypt (Kitos War)
- 117– Hadrian becomes emperor
- 121/125– Hadrian travels through the Northern Empire
- 122– construction of Hadrian's Wall begins
- 128/132– Hadrian travels through Africa and the Eastern Empire
- 131/135 - Jewish Bar Kokhba revolt
- 138– Antoninus Pius becomes emperor
- 140/143– After a rebellion Antoninus conquers Scotland; construction of Antonine Wall begins
- 150/163– rebellions in Scotland, Antonine Wall is abandoned and reoccupied several times
- 161– Marcus Aurelius becomes emperor
- 162/166– Lucius Verus successful campaigns against the Parthian Empire
- 167– The tribe of the Marcomanni crosses the Danube and invades Dacia
- 168/175– Marcus Aurelius' campaigns against the Marcomanni
- 180– Death of Marcus Aurelius, the last of the Five good emperors; Commodus becomes emperor
- 184– Antonine Wall abandoned for the last time
- 193– Commodus is murdered. After the short reigns of Pertinax and Didius Julianus, Septimius Severus becomes emperor. There is opposition from first Pescennius Niger and then Clodius Albinus
- 197– Septimius Severus secures the empire after the battle of Lugdunum
- 198– Septimius Severus invades Parthia
3rd century
- 208/211– Severus campaigns against the Caledonians
- 211– Severus dies. His sons Caracalla and Geta become joint emperors. Caracalla has Geta murdered shortly thereafter.
- 217– Caracalla assassinated; Macrinus becomes emperor
- 218– Macrinus deposed and executed, Elagabalus is installed on the throne
- 222– Elagabalus is murdered. Alexander Severus becomes emperor
- 231-33– War against Persia
- 235– Alexander killed in a soldier mutiny. Maximinus Thrax becomes emperor.
- 238– Year of the Six Emperors. The Senate supports a revolt of Gordian I and Gordian II in Africa. These two are defeated by an ally of Thrax, and the Senate appoints Balbinus and Pupienus as co-emperors. They are soon assassinated, and Thrax is killed in a mutiny. The young Gordian III becomes emperor.
- 241– Victory over the Persians at Resaina.
- 244– Romans defeated at Misiche. Philip the Arab becomes emperor.
- 249– Decius usurps the throne with support from the Danubian legions. He names his son Herennius co-emperor.
- 251– Decius and Herennius defeated and slain by Cniva, king of the Goths. Another son of Decius, Hostilian, is briefly emperor, but dies in a plague outbreak. Gallus and his son Volusianus become emperors.
- 252– King Shapur I of Persia defeats the Romans at Barbalissos.
- 253– Aemilianus becomes emperor after leading a revolt and Gallus and Volusianus are slain by their own troops. Valerian and his son Gallienus become emperors after Aemilianus is killed by his own soldiers. Shapur captures Antioch.
- 257– Valerian retakes Antioch. The Franks invade Gaul and Hispania. The Alemanni invades Italy but are defeated at Milan.
- 258– Goths invade Asia Minor
- 260– Valerian is taken captive by the Persians. Retreating Persian army attacked by Odaenathus of Palmyra. Postumus proclaimed emperor in Gaul. He is also supported in Hispania and Britain.
- 267– Odaenathus assassinated. His widow Zenobia takes control of Palmyra
- 268– Gallienus defeats Gothic invasion, but is later assassinated. Claudius II becomes emperor.
- 269– Postumus is killed. Victorinus proclaimed emperor in Gaul and Britain. The Palmyrenes takes Egypt and Syria. Claudius defeats the Goths at Naissus in Moesia.
- 270– Claudius dies of plague. After a brief rule by Claudius' brother Quintillus, Aurelian becomes emperor.
- 271– Aurelian campaigns against the Vandals, Juthungi and the Sarmatians. Victorinus is murdered and his soldiers proclaim Tetricus I emperor
- 272– Aurelian defeats Zenobia at Antioch and Emesa and takes Palmyra. Zenobia is captured. The province of Dacia is abandoned.
- 273– Palmyra revolts. The city is destroyed by Aurelian.
- 274– Aurelian defeats the army of Tericus at the Catalaunian fields.
- 275– Aurelian is murdered. Tacitus becomes emperor.
- 276– Tacitus dies. After the brief reign and assassination of Florianus, Probus becomes emperor.
- 277– The Burgundians, Longiones, Alemanni and Franks defeated.
- 279– Probus campaigns against the Vandals in Illyricum.
- 282– Carus proclaimed emperor. Probus killed by his own troops.
- 283– Carus dies during an invasion of Persia. His sons Carinus and Numerian become emperors.
- 284– Numerian dies. Diocletian proclaimed emperor and marches against Carinus.
- 285– Carinus dies in battle against Diocletian. Diocletian splits the empire into two halves and appoints Maximian emperor of the Western portion while Diocletian rules the East.
- 286– Carausius revolts in Britain.
- 293– Diocletian appoints Constantius I and Galerius as caesars. Carausius murdered by Allectus who proclaims himself emperor.
- 296– Allectus defeated and slain.
- 299– Galerius defeats the Sarmatians and the Carpi
4th century
- 301– Diocletian issues the Edict on Maximum Prices.
- 303– Diocletian orders the persecution of Christians.
- 305– Diocletian and Maximian abdicate. Constantius and Galerius becomes Augusti. Maximinus is appointed Caesar in the east and Severus in the west.
- 306– Constantius dies at York. His son Constantine I proclaimed emperor. Maxentius, son of Maximian, proclaims himself emperor in Rome.
- 307– Maxentius reinvests his father Maximian as emperor. Severus is put to death. Galerius lays siege to Rome.
- 308– Conference of Carnuntum. Diocletian convinces Maximian to step down. Licinius appointed Caesar in the East.
- 310– Maximian again proclaims himself emperor, but is captured by Constantine. He commits suicide.
- 311– Galerius dies at Sardica. Maximinus and Licinius split his realm between them.
- 312– Constantine defeats and kills Maxentius at the Milvian Bridge. Licinius marries Constantine's sister Constantia. Constantine converts to Christianity.
- 313– Licinus defeats Maximinus twice. Maximinus dies at Tarsus.
- Constantine issues Edict of Milan, ending persecution of Christians and establishing religious toleration throughout the Empire.
- 314– Constantine defeats Licinius at Cibalae
- 317– Constantine defeats Licinius on the Campus Ardiensis. Licinius forced to cede all his European provinces except Thrace.
- 318– Excommunication of Arius.
- 324– Constantine defeats Licinius at the Hebrus River and at Chrysopolis. Licinius abdicates.
- 325– The Ecumenical Council of Nicaea.
- 326– Constantine orders the death of his oldest son, Crispus.
- 330– Constantine makes Constantinople the capital.
- 332– Constantine campaigns against the Goths.
- 334– Constantine campaigns against the Sarmatians.
- 337– Constantine dies at Nicomedia. His three sons, Constantine II, Constantius II and Constans become emperors.
- 338– Constantine II defeats the Alemanni. War with Persia.
- 340– Constantine II invades Italy. He is ambushed and slain by Constans at Aquileia.
- 341– Constans and Constantius II issue a ban against pagan sacrifice.
- 347– The Donatists revolt in Africa.
- 348– Constantius defeats the Persians at the Siege of Singara.
- 350– Magnentius usurps the throne in the west. Constans is captured and killed. Nepotianus attacks Rome with a band of gladiators
- 351– Constantius appoints his cousin Constantius Gallus as Caesar. Magnentius is defeated at Mursa.
- 353– Constantius defeats Magnentius at Mons Seleuci. Magnentius commits suicide.
- 354– Constantius Gallus is put to death.
- 355– Julian is appointed Caesar in Gaul.
- 357– Julian defeats the Franks at Strasbourg.
- 360– With a Persian war imminent, Constantius orders Julian to send several legions east. The troops mutiny and proclaim Julian Augustus.
- 361– Constantius dies of illness, naming Julian his successor. Julian openly declares himself a pagan, but his attempt at rejuvenating paganism in the empire fails.
- 363– Julian invades Persia, but forced to retreat, he is mortally wounded during a skirmish and dies. Jovian is proclaimed emperor.
- 364– Jovien dies of accidental asphyxiation. Valentinian I becomes emperor and splits the empire with his brother Valens.
- 375– Valentinian dies and is succeeded by Gratian as Western emperor.
- 378– Valens is defeated and killed by the Goths at the Battle of Adrianople. Theodosius I succeeds him as Eastern emperor.
- 380- Edict of Thessalonica issued by Theodosius I makes Christianity the State church of the Roman Empire
- 384– Gratian is murdered, Valentinian II becomes emperor.
- 392– Valentinian II dies of apparent suicide, though murder by Arbogast is more likely. Arbogast installs the puppet Eugenius on the Western throne, but Theodosius refuses to recognize the usurper.
- 394– Eugenius and Arbogast are deposed and killed by Theodosius, who briefly reunites the empire for the last time.
- 395– Theodosius I dies, leaving the Western empire to his son Honorius and the Eastern empire to his son Arcadius.
5th century
- 410– Rome is sacked by Alaric I
- 423– After a long and disastrous reign, Honorius dies; succeeded by the usurper Joannes
- 425– Valentinian III becomes Western emperor
- 447– Eastern Rome loses to Attila the Hun
- 452– Attila the Hun is turned away from Rome by Pope Leo I.
- 455– Valentinian III is assassinated and succeeded by Petronius Maximus as emperor. Rome is plundered by the Vandals, and Maximus is killed during mob violence. Avitus becomes emperor of the west.
- 457– Avitus is deposed by the magister militum Ricimer and killed. Majorian is installed as Western emperor.
- 461– Majorian is deposed by Ricimer. Libius Severus becomes Western emperor.
- 465– Libius Severus dies, possibly poisoned by Ricimer.
- 467– Anthemius becomes western emperor with the support of Leo I.
- 468– War against the Vandals by the joint forces of both empires. Naval expedition ends in failure.
- 472– Ricimer kills Anthemius and makes Olybrius new western emperor. Both Ricimer and Olybrius die of natural causes. Gundobad becomes magister militum in Italy.
- 473– Gundobad makes Glycerius new western emperor.
- 474– Gundobad leaves Italy to take part in a succession struggle among the Burgundians. Glycerius is deposed by Julius Nepos who proclaims himself western emperor.
- 475– Julius Nepos forced to flee to Dalmatia by his magister militum Orestes. Orestes proclaims his own son Romulus Augustulus as western emperor.
- 476– Germanic general Odoacer kills Orestes, forces Romulus Augustus to abdicate and proclaims himself King of Italy. Traditional date for the fall of the western Roman Empire. The Eastern Roman Empire (later known as the Byzantine Empire) continues on.
- 480– Julius Nepos, still claiming to be emperor, is killed in Dalmatia.
6th century and beyond
- 533– Justinian I begins to restore the empire in the west; Belisarius defeats the Vandals at the Battle of Ad Decimum and the Battle of Tricamarum
- 536– Belisarius recaptures Rome from the Ostrogoths
- 552– Narses defeats the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Taginae
- 553– Narses defeats the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Mons Lactarius
- 568– The Lombards invade Italy; no further attempts to restore the empire
- 607– Emperor Phocas donates The Pantheon to the Pope and has a column erected in the Forum.
- 640- The Roman legion of the East Roman army is disbanded, and the theme systems is introduced.
- 663– Constans II is the last emperor to visit Rome, and the city gradually slips out of imperial control
- 976- Basil II effectively becomes Emperor of the Romans after the death of John I Tzimiskes.
- 1014-Basil crushes Bulgarian forces in the battle of kliedion, and he is called the "Father of the army" by his troops.
- 1025-The eastern Roman empire is at its peak in the eleventh century, regaining its foothold in the Balkans and southern Italy. Yet marks the death of Basil II.
- 1071- The battle of manzikert devastated Byzantine forces in Anatolia losing the themata and tagmata to the Seljuk Turks.
- 1204– Crusaders sack Constantinople and establish the Latin Empire of Constantinople.
- 1261– Michael VIII Palaiologos recovers Constantinople from the Latin Empire.
- 1453– Constantinople falls to the Ottoman Turks. End of the Byzantine/eastern Roman Empire.
- 1461– Trebizond falls to the Ottoman Turks. End of the Empire of Trebizond and of the last remnant of the Roman Empire.
See also