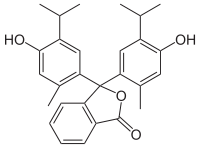
Thymolphthalein
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,3-bis(4-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-propan-2-ylphenyl)-2-benzofuran-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 125-20-2 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL587849 |
| ChemSpider | 29054 |
| EC number | 204-729-7 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 31316 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C28H30O4 |
| Molar mass | 430.54 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 248 to 252 °C (478 to 486 °F; 521 to 525 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | 4, 10 |
| S-phrases | S22 S24/25 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Thymolphthalein is an acid-base (pH) indicator. Its transition range is around pH 9.3-10.5. Below this pH, it is colorless; above, it is blue. The molar extinction coefficient for the blue thymolphthalein dianion is 38000 M−1cm−1 at 595 nm.[1]
| Thymolphthalein (pH indicator) | ||
| below pH 9.3 | above pH 10.5 | |
| 9.3 | ⇌ | 10.5 |
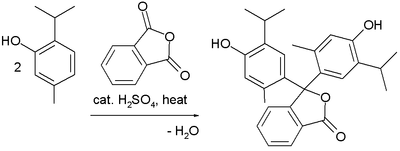
Preparation
Thymolphthalein can be synthesized from thymol and phthalic anhydride by Friedel-Crafts alkylation:
References
- ↑ Hahn HH, Cheuk SF, Elfenbein S, Wood WB (April 1970). "Studies on the Pathogenesis of Fever: Xix. Localization of Pyrogen in Granulocytes" (PDF). J. Exp. Med. 131 (4): 701–9. doi:10.1084/jem.131.4.701. PMC 2138774. PMID 5430784.