Thiocarlide
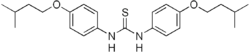 | |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
| 1,3-bis[4-(3-methylbutoxy)phenyl]thiourea | |
| Clinical data | |
| Identifiers | |
|
910-86-1 | |
| J04AD02 | |
| PubChem | CID 3001386 |
| ChemSpider |
2272774 |
| UNII |
43M23X81Y2 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL214920 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C23H32N2O2S |
| 400.578 g/mol | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Thiocarlide (or tiocarlide or isoxyl) is a thiourea drug used in the treatment of tuberculosis, inhibiting synthesis of oleic acid and tuberculostearic acid.[1]
Thiocarlide has considerable antimycobacterial activity in vitro and is effective against multi-drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[2] Isoxyl inhibits M. bovis with six hours of exposure, which is similar to isoniazid and ethionamide, two other prominent anti-TB drugs. Unlike these two drugs, however, isoxyl also partially inhibits the synthesis of fatty acids.
Thiocarlide was developed by a Belgian company, Continental Pharma S.A. Belgo-Canadienne in Brussels, Belgium. The head researcher was Professor N. P. Buu-Hoi, head of Continental Pharma's Research Division.
References
- ↑ Phetsuksiri B, Jackson M, Scherman H et al. (December 2003). "Unique mechanism of action of the thiourea drug isoxyl on Mycobacterium tuberculosis". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (52): 53123–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311209200. PMID 14559907.
- ↑ Phetsuksiri B, Baulard AR, Cooper AM et al. (May 1999). "Antimycobacterial activities of isoxyl and new derivatives through the inhibition of mycolic acid synthesis". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43 (5): 1042–51. PMC 89109. PMID 10223912.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||