The Avenues (gang)
|
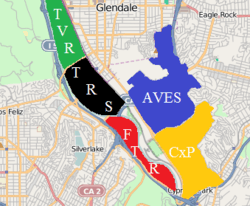
The Avenues (AVES) depicted in blue among other North-East Los Angeles gangs | |
| Founded | 1940s |
|---|---|
| Founding location | Los Angeles |
| Years active | 1940s – Present Day |
| Territory | Mainly in Los Angeles, Highland Park, Cypress Park, Glassell Park, and Eagle Rock[1] |
| Ethnicity | Hispanic |
| Membership | 800–1000.[2] |
| Criminal activities | Murder,[3] Assault, Arms trafficking, Drug trafficking,[4] extortion, hate crimes,[5] kidnapping, Racketeering, Motor vehicle theft, Robbery, Burglary, Vandalism, Witness intimidation and human trafficking[6] |
| Allies | Sureños, Mexican Mafia |
| Rivals | Cypress Park, Thee Rascals, Highland Park, 18th Street, Tooner Ville Rifa 13, some Sureño sets, Crips, MS-13, Bloods |
The Avenues, also known as Avenidas or AVE's, is a Mexican/Mexican American criminal street gang mostly in Los Angeles County, California. They originally started as a social club for local Hispanic youths to protect themselves from other violent youths. The Avenues, like most Mexican gangs in Los Angeles, are under the direct control of the Mexican Mafia when sent to State, County, or Federal prisons. They have a long history, but not all of it is riddled with violence and hate.
History
The Avenues were not always violent when they started and rarely engaged in illegal activities. They were started by the Flores brothers in the 1940s, but little is known about the brothers. The greatest of their crimes during the 1940s were simple assaults. As time progressed and their numbers increased, they became more violent and started to act more like a criminal street gang and less like a social club. In the late 1960s, when heroin started to flood the streets, they turned for the worse and would be forevermore labeled a criminal street gang. They increasingly took part in the illegal drug trade and these actions have continued to the present day. By the time the 1970's rolled around the Avenues had grown from a neighborhood social club into a highly organized gang who's territory stretched nearly 6 miles. By the late-70's the Avenue's hood began to shrink in size as two new gangs, Cypress Park and Highland Park, established themselves in Avenue territory. At first, it was common for rival gang members to fight one another to settle scores, but once cocaine hit the streets, gangs noticed that huge amounts of money can be generated from it's distribution and shootings/stabbings became more prevalent. In the 1990's the main drug of choice in the Avenue's hood switched from cocaine to methamphetamine due to the establishment of industrial-sized meth laboratories in central-Mexico as well as the increased scarcity of cocaine after the fall of the Medellin cartel. During this period of time drug-addiction and violent crime became an everyday fact of life in northeast Los Angeles as rival gangs began fighting over drug turf. The Avenues attempted to expand operations southward along Fletcher Drive but were confronted by the smaller yet equally-vicious Rascals gang. In the last half of the 1990s northeast Los Angeles had more homicides than any other part of the city with 500 gang-related shootings. The Avenues Gang are well known for their hatred of and hate crimes committed against African-American residents of their neighborhoods.[7] Reflecting their hate-filled attitudes, they tried to keep even non-gang affiliated African-Americans from moving into the Highland Park area.
Location
The Avenues are located in Cypress Park, Glassell Park, Highland Park and Eagle Rock. Each of the Avenues cliques claims a gang territory based on where gang members live. The four main cliques are 43rd Aves, Avenues 57, Cypress Avenues, and Drew Street, all centered on the streets for which they are named. Their barrio once covered almost 6 square miles.[8] Members of the 43rd Aves were prosecuted by the U.S. Attorney's Office in 2006 for hate-crime charges for harassing, attacking and murdering African Americans in Highland Park. Many gang members have relocated to San Bernardino and Riverside counties – and other areas of Los Angeles County – due to the gang injunctions from the LAPD. Increased housing and rental prices in many east side neighborhoods have meant that former gang members have moved as rentals and home prices became too expensive. Even through all of this, the Avenues gang that rule Drew Street have survived countless convictions, injunctions, evictions and deportations. Police have desperately tried to break the gang for decades. Major successes came with raids and later the demolition of an Avenues bastion on Drew Street in Glassell Park.[9][10]
Culture
The Avenues have a long history of involvement with the Mexican Mafia. Gang members are secretive and their code of silence is taken seriously and violations have lethal consequences. Respect and loyalty are considered to be very important. They challenge anyone and enforce the borders of their territory with deadly accuracy. Avenues gang members tattoos are known by a skull with a fedora and a bullet hole in the skull, or the letters LA, AVES, A and Avenidos. The Avenues are one of LA's most violent gangs. They are so violent that even President Bill Clinton spoke out against them in 1995.
Criminal activity
The Avenues gained national attention in 1995, when several members opened fire on a car that made a wrong turn into a Cypress Park alley, killing 3-year-old Stephanie Kuhen. Gang members were also accused of the August 2008 killing of Los Angeles County Deputy Sheriff Abel Escalante, 27, who worked at the Men's Central Jail guarding some of the county's most dangerous inmates. Escalante was gunned down outside his parents' Cypress Park home as he prepared to go to work.[11] The Avenues are notorious for their participation in hate crimes against black inhabitants of their neighborhoods. [12] Some have called their actions a campaign of ethnic cleansing.[13] Aside from their participation in hate related crimes, their main source of income is from illegal narcotics and human trafficking.[14] The Avenues, as with most other Sureño sets, are well connected with Mexican drug cartels, specifically the Sinaloa cartel. Methamphetamine, cocaine, black-tar heroin, and marijuana is sold by street dealers who operate out of numerous hidden "trap-houses" where the product is stored and processed into smaller quantities. The Avenues also sell an arsenal of illegal/stolen firearms, ranging from handguns to assault rifles, as well as knives, clubs, etc. They are responsible for over 100 murders in the last 20 years alone, specifically rival gang members.
See also
- Surenos
- Mexican Mafia
References
- ↑ Boxall, B. (2012). "Avenues gang has a long, violent history in Los Angeles | Street Gangs Resource Center". streetgangs.com. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- ↑ "how many murders is the notorious avenues gang responsible for?". askville.amazon.com. 2011. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ↑ "Historic Highland Park Neighborhood Council –". historichighlandpark.org. 2011. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ↑ Quinones, S. (2010, February 8). Former shot-caller is now spilling gang's secrets. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved from http://articles.latimes.com/2010/feb/08/local/la-me-drew-street9-2010feb09
- ↑ Peleski, C. (2005, July 14). Avenues of death. Retrieved from http://www.streetgangs.com/topics/2005/071405ave.html
- ↑ Arnold, M. (2011). "The Arroyo Seco Journal: Avenues Gang Leader Sentenced for Human Smuggling". arroyosecojournal.blogspot.com. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ↑ Pelisek, C. (2006, August 2). Avenues gang members meet the end of the road. Los Angeles Weekly. Retrieved from http://www.laweekly.com/2006-08-03/news/avenues-gang-members-meet-the-end-of-the-road/
- ↑ Hewlitt, R. (Director) (2009). Highway to hell [Television series episode]. In Pearman, V. (Executive Producer), Gangland: Season 4, Episode 1. Los Angeles, CA: The History Channel.
- ↑ Rubin, J. (2009). "Massive raid in Glassell Park nabs 44 Avenues gang members; Los Angeles Times". latimes.com.
- ↑ Quinones, S. (2009). "Avenues gang bastion is demolished; Los Angeles Times". latimes.com.
- ↑ Boxell, B. (2011). "Avenues gang has a long, violent history in Los Angeles | Street Gangs Resource Center". streetgangs.com. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ↑ Deverell, W., & Hise, G. (2010). A companion to los angeles. (p. 83). Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing
- ↑ Mock, B. (2011). "L.A. Blackout | Southern Poverty Law Center". splcenter.org. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ↑ Williams, S. (2011). "DEA, Partners Attack Notorious L.A. Avenues Gang | Black Radio Networ...". blackradionetwork.com. Retrieved December 25, 2011.