Texas river cooter
| Texas river cooter |
| |
|
| Scientific classification |
| Kingdom: |
Animalia |
| Phylum: |
Chordata |
| Class: |
Reptilia |
| Subclass: |
Anapsida |
| Order: |
Testudines |
| Suborder: |
Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: |
Testudinoidea |
| Family: |
Emydidae |
| Subfamily: |
Deirochelyinae |
| Genus: |
Pseudemys |
| Species: |
P. texana |
| Binomial name |
Pseudemys texana
Baur, 1893 |
|
| Synonyms[1] |
- Pseudemys texana Baur, 1893
- Chrysemys texana Ditmars, 1907
- Pseudemys floridana texana Carr, 1938
- Pseudemys concinna texana Conant, 1958
- Chrysemys concinna texana Smith & Taylor, 1966
- Chrysemys concinna texaba Gosławski & Hryniewicz, 1993 (ex errore)
|
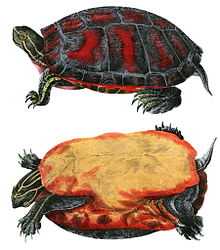
The Texas river cooter (Pseudemys texana) is a species of freshwater turtle native to creeks, rivers, and lakes of the US state of Texas. They are found in the river basins of the Colorado, Brazos, Guadalupe, and San Antonio Rivers. It is one of two species of cooter native to the state, the other being the Eastern River Cooter.
Description
The Texas River Cooter is a relatively large turtle, capable of growing to a shell length of 12+ inches (30.5 cm). They are green in color, with yellow and black markings that fade with age. Males can be distinguished from females by their longer tails, longer claws, and overall smaller size.
Taxonomy
The Texas Cooter was once reclassified to a subspecies of the Eastern Cooter, Pseudemys concinna, but was given full species status in 1991.
Similar species
The Red-eared slider (Trachemys scripta elegans) shares its range and habits, but can easily be distinguished from the Texas Cooter by red patches on either side of its head. Various species of map turtle can also look much like juvenile Texas Cooters.
References
|
|---|
| | | | Suborder | |
|---|
| | Cryptodira | | |
|---|
| | | Carettinae | |
|---|
| |
- Chelonia
- Eretmochelys
- Natator
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | Pleurodira | | | Chelinae | |
|---|
| Chelodininae | |
|---|
| Hydromedusinae | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | |
|---|
| | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
| |
|