For the 5th-century Cornish saint also known as Teth, see
Saint Tetha.
| Teth |
|---|
|

|
|
ט | |
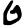
| |
ܛ | |
ط |
|
| Phonemic representation |
tˤ |
|---|
| Position in alphabet |
9 |
|---|
| Numerical value |
9 |
|---|
| Alphabetic derivatives of the Phoenician |
|---|
|
|
Teth, also written as Ṭēth or Tet, is the ninth letter of many Semitic abjads (vowel-less alphabets) including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Tet ט, Syriac ܛ, and Arabic Ṭāʾ ط. It is 16th in modern Arabic order. The Persian Ța is pronounced as a hard "t" sound and is the 19th letter in the modern Persian alphabet. The Phoenician letter also gave rise to the Greek theta (Θ), originally an aspirated voiceless alveolar stop but now used for the voiceless dental fricative.
The sound value of Teth is /tˤ/, one of the Semitic emphatic consonants.
Origins
The Phoenician letter name ṭēth means "wheel", but the letter possibly (according to Brian Colless) continues a Middle Bronze Age glyph named ṭab "good", Tav in Aramaic and Tov טוב in Hebrew, ṭayyib طَيّب in modern Arabic, based on the nfr "good" hieroglyph:
Jewish scripture books about the "holy letters" from the 10th century and on discuss the connection or origin of the letter Teth with the word Tov,[1] and the Bible uses the word 'Tov' in alphabetic chapters to depict the letter.[2]
Hebrew Tet
The Hebrew spelling of name of the letter: טֵית
Hebrew pronunciation
In Modern Hebrew, Tet represents a voiceless alveolar plosive /t/, although this can be pharyngealized to produce [tˤ] in traditional Temani and Sephardi pronunciation.
Significance
In gematria, Tet represents the number nine. When followed by an apostrophe, it means 9,000. The most common example of this usage is in the numbers of the Hebrew years (e.g., ט'תשנד in numbers would be the date 9754).
As well, in gematria, the number 15 is written with Tet and Vav, (9+6) to avoid the normal construction Yud and Hei (10+5) which spells a name of God. Similarly, 16 is written with Tet and Zayin (9+7) instead of Yud and Vav (10+6) to avoid spelling part of the Tetragrammaton.
Tet is also one of the seven letters which receive special crowns (called tagin) when written in a Sefer Torah. See Shin, Ayin, Gimmel, Nun, Zayin, and Tzadi.
Arabic Ṭāʾ
The letter is named Ṭāʾ ; Modern Standard Arabic pronunciation: /tˤ/.
| Position in word: |
Isolated |
Final |
Medial |
Initial |
| Glyph form: |
ط |
ـط |
ـطـ |
طـ |
Similar symbols
A symbol similar to the Phoenician teth is used for the tensor product, as 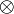 , but this is presumably an independent development, by modification of the multiplication sign ×. The Hebrew ט is also visually similar to the letter Ʋ.
, but this is presumably an independent development, by modification of the multiplication sign ×. The Hebrew ט is also visually similar to the letter Ʋ.
Character encodings
| Character | ט | ط | ܛ | ࠈ |
| Unicode name | HEBREW LETTER TET | ARABIC LETTER TAH | SYRIAC LETTER TETH | SAMARITAN LETTER TIT |
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 1496 | U+05D8 | 1591 | U+0637 | 1819 | U+071B | 2056 | U+0808 |
| UTF-8 | 215 152 | D7 98 | 216 183 | D8 B7 | 220 155 | DC 9B | 224 160 136 | E0 A0 88 |
| Numeric character reference | ט | ט | ط | ط | ܛ | ܛ | ࠈ | ࠈ |
| Character | 𐎉 | 𐡈 | 𐤈 |
| Unicode name | UGARITIC LETTER TET | IMPERIAL ARAMAIC LETTER TETH | PHOENICIAN LETTER TET |
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 66441 | U+10389 | 67656 | U+10848 | 67848 | U+10908 |
| UTF-8 | 240 144 142 137 | F0 90 8E 89 | 240 144 161 136 | F0 90 A1 88 | 240 144 164 136 | F0 90 A4 88 |
| UTF-16 | 55296 57225 | D800 DF89 | 55298 56392 | D802 DC48 | 55298 56584 | D802 DD08 |
| Numeric character reference | 𐎉 | 𐎉 | 𐡈 | 𐡈 | 𐤈 | 𐤈 |
References
- ↑ This was especially emphasized ever since the late 1600s after the Baal Shem Tov became influential, since the letter Teth was in his Acronym standing for Tov, and goodness was part of his philosophy.
- ↑ i.e. Psalms 119: 65-72. and many more.
The Northwest Semitic abjad |
|---|
| | | |
|
 , but this is presumably an independent development, by modification of the multiplication sign ×. The Hebrew ט is also visually similar to the letter Ʋ.
, but this is presumably an independent development, by modification of the multiplication sign ×. The Hebrew ט is also visually similar to the letter Ʋ.