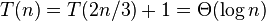Ternary search
A ternary search algorithm is a technique in computer science for finding the minimum or maximum of an increasing or decreasing function. A ternary search determines either that the minimum or maximum cannot be in the first third of the domain or that it cannot be in the last third of the domain, then repeats on the remaining two-thirds. A ternary search is an example of a divide and conquer algorithm (see search algorithm).
The function
Assume we are looking for a maximum of f(x) and that we know the maximum lies somewhere between A and B. For the algorithm to be applicable, there must be some value x such that
- for all a,b with A ≤ a < b ≤ x, we have f(a) < f(b), and
- for all a,b with x ≤ a < b ≤ B, we have f(a) > f(b).
Algorithm
Let a unimodal function f(x) on some interval [l; r]. Take any two points m1 and m2 in this segment: l < m1 < m2 < r. Then there are three possibilities:
- if f(m1) < f(m2), then the required maximum can not be located on the left side - [l; m1]. It means that the maximum further makes sense to look only in the interval (m1;r]
- if f(m1) > f(m2), that the situation is similar to the previous, up to symmetry. Now, the required maximum can not be in the right side - [m2; r], so go to the segment [l; m2]
- if f(m1) = f(m2), then the search should be conducted in [m1; m2], but this case can be attributed to any of the previous two (in order to simplify the code). Sooner or later the length of the segment will be a little less than a predetermined constant, and the process can be stopped.
choice points m1 and m2:
- m1 = l + (r-l)/3
- m2 = r - (r-l)/3
def ternarySearch(f, left, right, absolutePrecision): """ Find maximum of unimodal function f() within [left, right] To find the minimum, revert the if/else statement or revert the comparison. """ while True: #left and right are the current bounds; the maximum is between them if abs(right - left) < absolutePrecision: return (left + right)/2 leftThird = left + (right - left)/3 rightThird = right - (right - left)/3 if f(leftThird) < f(rightThird): left = leftThird else: right = rightThird
Run time order
Recursive algorithm
def ternarySearch(f, left, right, absolutePrecision): #left and right are the current bounds; the maximum is between them if abs(right - left) < absolutePrecision: return (left + right)/2 leftThird = (2*left + right)/3 rightThird = (left + 2*right)/3 if f(leftThird) < f(rightThird): return ternarySearch(f, leftThird, right, absolutePrecision) else: return ternarySearch(f, left, rightThird, absolutePrecision)
See also
- Newton's method in optimization (can be used to search for where the derivative is zero)
- Golden section search (similar to ternary search, useful if evaluating f takes most of the time per iteration)
- Binary search (can be used to search for where the derivative changes in sign)
- Interpolation search
- Exponential search
- Linear search