Temple of Garni
| Temple of Garni | |
|---|---|
|
The temple in 2013 | |
 Location within Armenia | |
| General information | |
| Status |
Museum (as part of a larger protected area) neopagan shrine |
| Type | Pagan temple or tomb[1] |
| Architectural style | Ancient Greek, Greco-Roman, Armenian influence |
| Location | Garni, Kotayk Province, Armenia |
| Coordinates | 40°06′45″N 44°43′49″E / 40.112421°N 44.730277°ECoordinates: 40°06′45″N 44°43′49″E / 40.112421°N 44.730277°E |
| Elevation | 1,396 m (4,580 ft)[2] |
| Completed | First or second century AD[1] |
| Owner | Armenian Ministry of Culture |
The Temple of Garni (Armenian: Գառնիի հեթանոսական տաճար, Gařnii het’anosakan tačar)[upper-alpha 1] is a reconstructed classical Hellenistic temple near Garni, Armenia. It is the only Greco-Roman colonnaded building in Armenia and the former Soviet Union.[3]
It is the best-known structure and symbol of pre-Christian Armenia. It was probably built by king Tiridates I in the first century AD as a temple to the sun god Mithra (known as Mihr in Armenian). After Armenia's conversion to Christianity in the early fourth century, it was converted into a royal summer house of Khosrovidukht, the sister of Tiridates III. According to some scholars it was not a temple but a tomb and thus survived the universal destruction of pagan structures. It collapsed in a 1679 earthquake. Renewed interest in the 19th century led to its eventual reconstruction between 1969 and 1975. It is one of the main tourist attractions in Armenia and the central shrine of Armenian neopaganism.
Location
The temple is situated at the edge of a triangular cliff and is part of the fortress of Garni (Armenian: Գառնիի ամրոց, Gařnii amrots or Գառնու ամրոց, Gařnu amrots). One of the oldest fortresses in Armenia,[4] it is mentioned as Gorneas in the first-century Annals of Tacitus.[5] The site is located near the village of Garni, in Armenia's Kotayk Province and is officially known as the Garni Historical and Cultural Museum Reserve (Armenian: «Գառնի» պատմա-մշակութային արգելոց-թանգարան), which includes the temple, a bath complex, a royal summer palace, the seventh century church of St. Sion and several other minor structures, including medieval khachkars. In total, the list of intangible historical and cultural monuments approved by the government of Armenia includes 11 items.[6] It occupies 3.5 hectares and is supervised by the Service for the Protection of Historical Environment and Cultural Museum Reservations, an agency attached to the Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Armenia.[7]
History
The precise date of construction of the temple is unknown and is subject to debate. The dominant view[upper-alpha 2] is that it was built in 77 AD, during the eleventh year of reign of king Tiridates I. In 1945 the prominent Armenian painter Martiros Saryan discovered a Greek inscription,[upper-alpha 3] which named Tiridates the Sun ("Helios") the founder of the temple.[9] Medieval historian Movses Khorenatsi attributed the inscription to Tiridates III.[10] The inscription reads: "The Sun God Tiridates, uncontested king of Great Armenia built the temple and the impregnable fortress in the eleventh year of his reign when Mennieay was hazarapet [thousander, chiliarch] and Amateay was sparapet [general, commander]."[11] Most scholars now attribute the inscription to Tiridates I and considering that the inscription says the temple was built in the eleventh year of reign of Tiridates I (i.e. 66 AD), the temple is believed to have been completed in 77 AD.[10] This date was proposed by Alexander Sahinian[12] and has since gained general acceptance in Armenia.[13] The date is primarily linked to the visit of Tiridates I to Rome in 66 AD, where he was coronated by Roman emperor Nero.[upper-alpha 4] To rebuilt the city of Artaxata (Artashat)—destroyed by the Roman general Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo—Nero gave Tiridates 50 million drachmas and provided him with Roman craftsmen. Upon his return to Armenia Tiridates began a major project of reconstruction, which included rebuilding the fortified city of Garni. It is during this period that the temple is thought to have been built.[16] The temple is believed to have been dedicated to Mihr (Mithra),[17][18][upper-alpha 5] the sun god in the Zoroastrian-influenced Armenian mythology. Tiridates, like other Armenian monarchs, considered Mihr their patron. Some scholars have argued that the historical context during which the temple was built, i.e. after returning from Rome as king, it is natural that Tiridates dedicated the temple to his patron god.[16]
According to a different interpretation of the extant literary testimonia and the evidence provided by coinage, the erection of the temple started in 115 AD. The pretext for its construction would have been the declaration of Armenia as a Roman province[10] and the temple would have housed the imperial effigy of Trajan.[20]
A newer alternative theory proposed by Wilkinson (1982) suggests that the building is a tomb, probably constructed circa 175 AD. This theory is based on a comparison to Graeco-Roman buildings of western Asia Minor (e.g. Nereid Monument, Belevi Mausoleum, Mausoleum at Halicarnassus),[5] the discovery of nearby graves that date to about that time, the discovery of a few marble pieces of the Asiatic sarcophagus style, and other arguments such as the unlikelihood that a pagan temple would survive destruction during Armenia's conversion to Christianity when all other such temples were destroyed. If it is the case that the building is a tomb of that era, then it might be the tomb of an Armeno-Roman ruler such as Sohaemus or possibly Aurelius Pacorus (Bakur).[21]
Decline
In the early fourth century[upper-alpha 6] when Armenian King Tiridates III adopted Christianity as a state religion virtually all known pagan places of worship were destroyed.[27] The Temple of Garni is the only pagan[upper-alpha 7] and Hellenistic[17][31] structure to have survived the widespread destruction. It remains unknown why the temple was exempted from destruction, but philosopher Grigor Tananyan argues that its status as a "masterpiece of art" possibly saved it from destruction. He suggests that the temple was perceived to be a "quintessence of an entire culture."[32] Robert H. Hewsen suggested that the reason why it was not destroyed is because it was not a temple, but a tomb of a Roman-appointed king of Armenia. He also noted that in the seventh century a church was built immediately next to it and not in its place.[4]

According to Movses Khorenatsi the temple was at the time converted into the summer house of Khosrovidukht, the sister of Tiridates III.[30] As its purpose changed the temple underwent some changes. The sacrificial altars in the outside of the temple and the cult statue in the cella were removed. The opening in the roof for skylight was closed. The stone structures for removal of water from the roof were also removed, while the entrance of the temple was transformed and adjusted for residence.[32] Almost nothing is known about the subsequent history of the temple.

Destruction and reconstruction
The temple was destroyed in a devastating 1679 earthquake, the epicenter of which was, according to many scholars,[35] located in gorge of Garni.[36] Most of the original building blocks remained scattered at the site, allowing the building to be reconstructed.
European travelers mentioned the temple in their works as early as the 17th century.[1] Jean Chardin (who visited Armenia before the earthquake) and James Justinian Morier both incorrectly described it through local informants since they never actually visited the site.[5] Upon Robert Ker Porter's visit the temple was called "Takht-i Tiridates" ("Throne of Tiridates") by the locals. Ker Porter described what he saw as follows: "a confused pile beautiful fragments; columns, architraves, capitals, friezes, all mingled together in broken disorder."[5] Another European to visit and document the ruins of the temple was Dubois de Montpereux,[5] who referred to the temple as "Takh Terdat".[5] In his 1839 book he proposed a reconstruction plan.[5]
The first known proposal to reconstruct the temple was made by the archaeologist Aleksey Uvarov at the fifth All-Russian Archaeological Congress in 1880. He proposed its stones be moved to Tiflis (in Georgia) and be reconstructed there according to de Montpereux's plan.[37] The governor of Erivan, citing technical difficulties, did not implement the plan.[38] Lori Khatchadourian suggests that the plan "could be read as an attempt at co-opting Armenia's Roman past to the glory of Russia through the relocation of its most iconic monument to the nearest administrative center."[37]
In the subsequent decades scholars such as Nikoghayos Buniatian (arm), Babken Arakelyan, and Nikolay Tokarsky (rus) studied the temple.[32] In 1909–11, during an excavation led by Nicholas Marr, the temple ruins were uncovered. Buniatian sought to reconstruct the temple in the 1930s.[38]
In 1949 the Armenian Academy of Sciences began major excavations of the site led by Babken Arakelyan. Architectural historian Alexander Sahinian focused on the temple itself. It was not until almost twenty years later, on December 10, 1968, that the Soviet Armenian government approved the reconstruction plan of the temple. A group led by Sahinian began reconstruction works in January 1969. It was completed by 1975, almost 300 years after it was destroyed in an earthquake.[17][39] The temple was almost entirely rebuilt using its original stones, except the missing pieces which were filled with unprocessed stones and are easily noticeable.[38] A monument dedicated to Sahinian was erected in 1978 not far from the temple.[39]
Architecture
Overview
The temple imitates the typical style of classical Ancient Greek architecture, which began developing in the seventh century BC.[40] Scholars have variously described the structure as "Greek", "Roman" or "Greco-Roman" and have usually linked it to Hellenistic art, almost always pointing out its distinct features and local Armenian influence.[41] Some scholars have emphasized the Armenian influence on its architecture, calling it "Armenian-Hellenic" (Sahinian), while others have completely dismissed this view, calling it a "foreign structure on Armenian soil".[42] Toros Toramanian, for instance, stressed the singularity of the temple as a Roman-style building on the Armenian Highlands and "remarked that the Garni construction essentially had no influence on contemporary or subsequent Armenian architecture."[43]
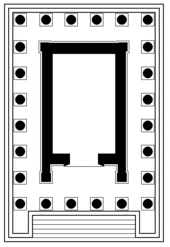
More specifically, it is a peripteros (a temple surrounded by a portico with columns) built on an elevated podium.[44][38] It is constructed of gray basalt quarried locally.[44][5] The temple is composed of a portico (pronaos) and a cella (naos). The temple is supported by a total of twenty-four 6.54 m high columns of the Ionic order: six in the front and back and eight on the sides (the corner columns are listed twice).[44][40] Based on a comparative analysis Sahinian proposed that the columns of the temple of Garni have their origins in Asia Minor.[45]
Exterior

The triangular pediment depicts sculptures of plants and geometrical figures.[46] The staircase has nine[38] unusually high steps—30 cm high around twice as high as the average height of stairs.[46] Tananyan suggests that the unusually high stairs compel a person ascending the staircase to feel humbled and make physical effort to reach the altar.[46] On the both sides of the staircase there are roughly square pedestals. Atlas, the Greek mythological Titan who held up the earth, is sculpted on both pedestals in a way seemingly trying to hold the entire temple on its shoulders. It is assumed that, originally, pedestals held up altars (sacrificial tables).[46]
The exterior of the temple is richly decorated. The frieze depicts a continuous line of acanthus. Furthermore, there are ornaments on the capital, architrave, and soffit. The stones in the front cornice depict sculptures of lion heads.[47] One of the lion heads from the architrave was removed by a Captain J Buchan Telfer in the late nineteenth century and bequeathed by him to the British Museum in 1907.[48]

Cella
The cella of the temple is 7.132 m high, 7.98 m long, and 5.05 m wide.[46] Due to the relatively small size of the cella, it has been proposed that a statue once stood inside (and the ceremonies were held in the outside). Furthermore, white marble sculptures of bull hooves have been discovered some twenty meters from the temple which could possibly be the remains of a sculpture of the god Mihr, who was often portrayed in a fight with a bull.[47]
The cello is lighten from two sources. The unproportionally large entrance (2.29 × 4.68 m) and the opening in the roof (1.74 × 1.26 m) provide more than sufficient lighting.[49]
Current status and use
.png)
The Temple of Garni, along with the nearby medieval monastery of Geghard, is one of the main tourist attraction sites in Armenia.[51] The two sites are collectively known as Garni-Geghard (Գառնի-Գեղարդ).[52] In 2013 some 200,000 people visited the temple.[7] In recent years many notable individuals have visited the temple, such as Cypriot President Demetris Christofias,[53] Polish First Lady Anna Komorowska,[54] Austrian President Heinz Fischer,[55] Spanish opera singer Montserrat Caballé,[56] and Greek President Karolos Papoulias.[57]
The temple and the fortress are part of the Garni Historical and Cultural Museum Reserve, which is supervised by the Service for the Protection of Historical Environment and Cultural Museum Reservations, a government agency attached to the Armenian Ministry of Culture.[7] In a 2006 survey the state of conservation of Garni was rated by over three-quarters of the visitors as "good" or "very good".[58] In 2011 UNESCO awarded the Museum-Reservation of Garni the Melina Mercouri International Prize for the Safeguarding and Management of Cultural Landscapes for "measures taken to preserve its cultural vestiges, and the emphasis placed on efforts to interpret and open the site for national and international visitors."[59]
Since 1990, the temple has been the central shrine[60] of the small number of followers of Armenian neopaganism who hold annual ceremonies at the temple,[61] especially on March 21—the pagan New Year.[62][63] Celebrations by neopagans are also held during the summer festival of Vardavar.[50][64]
The square in front of the temple is a site of occasional concerts. One such concert was held on July 2, 2004 by the National Chamber Orchestra of Armenia, conducted by Aram Gharabekian.[65] The orchestra played the works of Aram Khachaturian, Komitas, Edvard Mirzoyan, Strauss, Mozart, and other composers.[66]
Incidents
On September 25, 2014 Maksim Nikitenko, a Russian tourist in his early 20s, defaced the temple[67] by spray painting "В мире идол ничто" (literally translating to "In the world, idol is nothing".[68][69] The painting was cleaned days later.[70]
Gallery
-
-

-

Ornaments in the ceiling
-
Ornaments in the ceiling
-

Side view
-

-

-
Opening in the roof
-

Folk dancers in front of the temple
-
The Greek inscription of Tiridates I
-
Monument-foundation dedicated to the reconstruction by Sahinian (1978)
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Literally translates to "pagan temple of Garni". Also known as Գառնիի տաճար Gařnii tačar or Գառնու տաճար Gařnu tačar, both meaning "Garni temple".
- ↑ Khatchadourian writes that the "structure is most commonly regarded as a temple to the god Mihr".[5]
- ↑ "on a block of basalt 165 cm long, 50 cm high, and 79–80 cm thick; the letters are about 5 x 5.5 cm in size.[8]
- ↑ After the Roman–Parthian War over Armenia (58–63) a peace treaty was signed according to which Tiridates would be coronated by Nero and thus became an ally of Rome.[14] In exchange, Rome recognized Armenia's independence.[15]
- ↑ James R. Russell find the view of the structure being a temple of Mithra baseless.[19]
- ↑ The traditional date is 301 AD,[22] first calculated by historian Mikayel Chamchian.[23] A growing number of authors argue that the correct date is 314 by citing the Edict of Milan.[24][25] Elizabeth Redgate writes that "the scholarly consensus is to prefer c. 314."[26]
- ↑ "The monuments of Garni are the only vestiges of the pagan architecture of Armenia known to us. [...] The most important ruins are those of the temple"[28]
"Armenia's only remaining pagan temple, at Garni"[29]
"Գառնիի ճարտարապետական համալիրի անգին զարդն է տաճարը՝ հեթանոս հայության ճարտարապետական ժառանգությունից պահպանված միակ հիշատակարանը"[30]
"The obliteration of pagan vestiges was so complete that almost no architectural remains or temple records have survived ... The only exception is the Temple of Garni"[27]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Khatchadourian 2008, p. 251.
- ↑ "Garni, Armenia". elevationmap.net.
- ↑ Smith, Adam T. (2012). "'Yerevan, My Ancient Erebuni': Archaeological Repertoires, Public Assemblages, and the Manufacture of a (Post-)Soviet Nation". In Charles W. Hartley, G. Bike Yazicioğlu, Adam T. Smith. The Archaeology of Power and Politics in Eurasia: Regimes and Revolutions. Cambridge University Press. p. 65. ISBN 9781107016521.
the unique temple-tomb at Garni, just east of Yerevan – the only Greco-Roman colonnaded building anywhere in the Soviet Union.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hewsen, Robert H. (2001). Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 62. ISBN 0-226-33228-4.
a large Ionic building usually taken for a temple but whose survival, and the fact that in the seventh century a church was built next to it rather than in its place, suggests that it was more likely the tomb of one of the Roman-appointed kings of Armenia, perhaps Tiridates I (51–60; 63-p. 75) or Sohaimos of Emesa (140–160).
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 Khatchadourian 2008, p. 252.
- ↑ "Հայաստանի Հանրապետության Կոտայքի մարզի պատմության և մշակույթի անշարժ հուշարձանների պետական ցուցակ". arlis.am (in Armenian). Armenian Legal Information System. 24 December 2003. Archived from the original on 12 January 2015.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Petrosyan, Sara (21 February 2014). "Crime of Culture: Government Neglect and New Café Ensure that Garni Will Never Become a UNESCO World Heritage Site". Hetq Online.
- ↑ Russell 1987, p. 269.
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, pp. 31–32.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Nersessian 2001, p. 101.
- ↑ Ananian, Poghos (1994). "Garnii Yunaren ardzanagrut'iwne [The Greek inscription of Garni]". Bazmavep (in Armenian) 152: 111. cited in Nersessian 2001, p. 103
- ↑ Sahinian, Alexander (1983). Գառնիի անտիկ կառույցների ճարտարապետությունը [Architecture of antique constructions of Garni] (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian SSR Academy of Sciences Publishing.
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, pp. 33–34.
- ↑ Dando-Collins, Stephen (2010). The Great Fire of Rome: The Fall of the Emperor Nero and His City. Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press. p. 15. ISBN 978-0306818905.
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, p. 34.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Tananyan 2014, p. 35.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Petrosyan, Hamlet (2001). "Symbols of Armenian Identity: The Temple". In Abrahamian, Levon; Sweezy, Nancy. Armenian Folk Arts, Culture, and Identity. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. p. 43. ISBN 9780253337047.
The only surviving Hellenistic temple, the wonderful ionic-columned temple of Garni was built in the 1st century AD and dedicated to the sun god, Mithra (Mihr in Armenian).
- ↑ Bauer-Manndorff 1981, p. 72: "Only the temple of Mihr, in the fortress of Garni..."
- ↑ Russell 1987, p. 270: "Although Arm. scholars such as Arakelyan insist that the colonnaded building at Garni was a temple of Mithra, there is no evidence to support this save the inscription—and one cannot be certain that the inscription refers to it."
- ↑ Report by Kamilla Trever cited in Field, Henry; Price, Kathleen (1950). "Archaeological News, Russia". American Journal of Archaeology 54 (4): 427. doi:10.2307/501010.
- ↑ Wilkinson, R. D. (1982). "A Fresh Look at the Ionic Building at Garni". Revue des Études Arméniennes (XVI): 221–244. cited in Anne Elizabeth Redgate, The Armenians Blackwell Publishing, 2000, p. 102, footnote 39, ISBN 978-0-631-22037-4
- ↑ Balakian, Peter (2009). The Burning Tigris. New York: HarperCollins. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-06-186017-1.
- ↑ Panossian 2006, p. 106.
- ↑ Panossian 2006, p. 42.
- ↑ Hastings, Adrian; Mason, Alistair; Pyper, Hugh, ed. (2000). The Oxford Companion to Christian Thought. Oxford University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-19-860024-4.
- ↑ Redgate, A. E. (2000). The Armenians. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 314. ISBN 9780631220374.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Hacikyan, Agop Jack; Basmajian, Gabriel; Franchuk, Edward S.; Ouzounian, Nourhan (2000). The Heritage of Armenian Literature: From the Oral Tradition to the Golden Age. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. p. 80. ISBN 9780814328156.
The obliteration of pagan vestiges was so complete that almost no architectural remains or temple records have survived ... The only exception is the Temple of Garni...
- ↑ Der Nersessian, Sirarpie (1969). The Armenians. New York: Praeger. p. 99.
The monuments of Garni are the only vestiges of the pagan architecture of Armenia known to us. [...] The most important ruins are those of the temple built during the reign of Trdat I, shortly after ad 66, and which had survived until it was destroyed by an earthquake in 1679.
- ↑ Berman, Michael (2008). The Shamanic Themes in Armenian Folktales. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 34. ISBN 9781847186218.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 Tananyan 2014, p. 31.
- ↑ Nersessian 2001, p. 100: "The pagan temple of Garni, dedicated to the god Mihr (Mithra), is the only surviving Hellenistic building built by King Trdat I about 77 BC."
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Tananyan 2014, p. 32.
- ↑ Porter, Robert Ker (1821). Travels in Georgia, Persia, Armenia, ancient Babylonia, &c. &c. Volume 1. London: Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown. p. 624.
- ↑ Strzygowski, Josef (1918). Die Baukunst der Armenier und Europa [The Architecture of the Armenians and of Europe] Volume 1 (in German). Vienna: Kunstverlag Anton Schroll & Co. p. 13. Color pictures from before reconstruction can be found here.
- ↑ Guidoboni, E.; Haroutiunian, R.; Karakhanian, A. (2003). "The Garni (Armenia) large earthquake on 14 June 1679: a new analysis". Journal of Seismology (Kluwer Academic Publishers) 7 (3): 302. doi:10.1023/A:1024561622879.
- ↑ Hasrat'yan, Mourad (1995). "The medieval earthquakes of the Armenian Plateau and the historic towns of Ayrarat and Shirak (Dvin, Ani, Erevan)". Annali di Geofisica (Italian National Institute of Geophysics) 38 (5–6): 721.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 Khatchadourian 2008, p. 256.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 38.3 38.4 Tananyan 2014, p. 33.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 ""Գառնի" պատմա- մշակութային արգելոց-թանգարան ["Garni" Historical-Cultural Museum-Reservation]". hushardzan.am (in Armenian) (Service for the Protection of Historical Environment and Cultural Museum-Reservations, Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Armenia).
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Tananyan 2014, p. 37.
- ↑ Bauer-Manndorff 1981, p. 65: "Although at first glance the temple of Garni would seem alien to Armenian architecture, it is not purely Hellenistic for it also follows ancient local traditions."
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, pp. 41–42.
- ↑ Khatchadourian 2008, p. 272.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 Arakelyan, Babken (1968). "Excavations at Garni, 1949–1950". In Alekseyev, Valery. Contributions to the archaeology of Armenia. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Peabody Museum of Archaeology and Ethnology. p. 22.
The temple is peripteral, built on a high podium, with 24 Ionic columns, 6 in front and back and 8 at each side; the corner columns are listed twice. It is constructed of gray basalt quarried at Garni.
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, p. 41.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 46.4 Tananyan 2014, p. 38.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Tananyan 2014, p. 39.
- ↑ "Fragment of a carved black basalt frieze". British Museum.
- ↑ Tananyan 2014, pp. 38–39.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Krikorian, Onnik (26 July 2007). "Armenian Festival Combines Paganism and Nationalism". eurasianet.org (Open Society Institute).
- ↑ "The number of foreign tourists visiting Armenia expected to surge to one million". ARKA News Agency. 30 June 2014.
Foreign tourists usually visit the pagan temple of Garni, Geghard Monastery, Holy Etchmiadzin and Lake Sevan.
- ↑ "Գառնի-Գեղարդ. Հայաստանի մարգարիտները՝ իրենց գույներով". azatutyun.am (in Armenian). Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 16 May 2012.
- ↑ "With warm feelings and bright impressions". Hayastani Hanrapetutyun. 8 July 2009.
- ↑ "Rita Sargsyan and First Lady of Poland Anna Komarowska visited Garni". president.am (Office to the President of the Republic of Armenia). 28 July 2011.
- ↑ Mehrabyan, Tigran (27 June 2012). "Ավստրիայի նախագահ Հեյնց Ֆիշերի այցը Գառնու տաճար և Գեղարդի վանք" (in Armenian). PanARMENIAN.Net.
- ↑ Ghazanchyan, Siranush (12 June 2013). "Montserrat Caballe visits Garni Temple and Geghard Monastery". Public Radio of Armenia.
- ↑ "Greek President arriving in Armenia on state visit". ArmeniaNow. 29 September 2014.
- ↑ Alberini, Anna; Longo, Alberto (2006). "Combining the travel cost and contingent behavior methods to value cultural heritage sites: Evidence from Armenia". Journal of Cultural Economics (Springer Science+Business Media) 30 (4): 293.
- ↑ "Armenian and Palestinian sites share 2011 cultural landscape prize". unesco.org. UNESCOPRESS. 12 May 2011.
- ↑ Aitamurto, Kaarina; Simpson, Scott (2014). "Sacred Landscapes". Modern Pagan and Native Faith Movements in Central and Eastern Europe. Routledge. ISBN 978-1844656622.
- ↑ Antonyan, Yulia (2010). ""Reconstituting" Religion: Neo-Paganism in Armenia. Summary". Laboratorium: Russian Review of Social Research (Saint Petersburg) (1). ISSN 2078-1938.
- ↑ "Ամանորը և Վահագնի ծնունդը՝ մարտի 21-ին". Aravot (in Armenian). 19 March 2011.
Արորդիների ուխտը 1990–ից ի վեր Ամանորն ավանդաբար տոնում է Գառնիի տաճարում: Այս տարի նույնպես Ամանորի ծիսակատարությունը կսկսվի մարտի 21-ի կեսօրին՝ Գառնիում:
- ↑ "Վահագնի ծնունդը Գառնիի տաճարում". religions.am (in Armenian). 21 March 2014. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ↑ "Vardavar Celebrations in Garni". Hetq Online. 8 July 2013.
- ↑ Abrahamyan, Gayane (2 July 2004). "Nature Worship: Sounds and sights make a special night in Garni". ArmeniaNow.
- ↑ "Բացօթյա համերգ Գառնիում". Aravot (in Armenian). 26 June 2004.
Կկատարվի Արամ Խաչատրյան, Կոմիտաս-Ասլամազյան, Էդվարդ Միրզոյան, Շտրաուս, Մոցարտ եւ այլն:
- ↑ "Iravunk: Investigation into Russian tourist case continues". aysor.am. 3 October 2010.
- ↑ Турист из Москвы исписал языческий храм в Армении. Gazeta.ru (in Russian). 26 September 2014.
- ↑ ՌԴ քաղաքացին պղծել է Գառնու տաճարը. A1plus (in Armenian). 26 September 2014.
- ↑ Գառնիի տաճարի վրա ռուս զբոսաշրջիկի գրառումը մաքրվել է. Tert.am (in Armenian). 1 October 2014.
Bibliography
- Khatchadourian, Lori (2008). "Making Nations from the Ground up: Traditions of Classical Archaeology in the South Caucasus". American Journal of Archaeology 112 (2): 247–278. doi:10.3764/aja.112.2.247.
- Tananyan, Grigor (2014). "Գառնի պատմամշակութային կոթողը (տաճարի վերականգման 40-ամյակի առթիվ) [The Historic & Cultural Monument of Garni (to the 40th anniversary of the restoration of the temple)]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (2): 25–45.
- Panossian, Razmik (2006). The Armenians: From Kings and Priests to Merchants and Commissars. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231139267.
- Nersessian, Vrej (2001). Treasures from the Ark: 1700 Years of Armenian Christian Art. Los Angeles: J. Paul Getty Museum. ISBN 9780892366392.
- Bauer-Manndorff, Elisabeth (1981). Armenia: Past and Present. Lucerne: Reich Verlag.
- Russell, James R. (1987). Zoroastrianism in Armenia. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-96850-6.
Further reading
- Bartikian, Hrach (1965). "Գառնիի հունարեն անձանագրությունը և Մովսես Խորենացին [The Greek Inscription of Garni and Movses Khorenatsi]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (3): 229–234.
- Mouradian, G. S. (1981). "Греческая надпись Трдата I, найденная в Гарни [Tiridates I's Greek Inscription Discovered in Garni]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Russian) (3): 81–94.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1979). "Գառնիի անտիկ տաճարի կառուցման ժամանակը [The Time of the Construction of the Antique Temple of Garny]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (3): 165–181.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1979). "Գառնիի անտիկ տաճարի վերակազմության գիտական հիմունքները [Scientific Foundations of the Reconstruction of the Ancient Temple of Garny]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (4): 135–155.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1979). "Գառնիի անտիկ տաճարի վերականգնումը [The Reconstruction of the Ancient Temple of Garni]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian) (10): 59–74. ISSN 0320-8117.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1979). "Գառնիի անտիկ տաճարի համաչափական համակարգը [Proportional System of the Ancient Temple of Garni]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian) (12): 76–92. ISSN 0320-8117.
- Sargsian, Harma (1982). "Գառնիի հեթանոսական տաճարի վերականգնման ճարտարագիտական հարցերը [Engineering questions of the restoration of paganish temple of Garni]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian) (12): 70–76. ISSN 0320-8117.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1983). Գառնիի անտիկ կառույցների ճարտարապետությունը [Architecture of ancient structures of Garni] (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian SSR Academy of Sciences Publishing.
- Sahinian, Alexander (1988). Архитектура античных сооружений Гарни [Architecture of ancient structures of Garni] (in Russian). Yerevan: Sovetakan Grogh.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Temple of Garni. |




