Tax increment financing
Tax increment financing, or TIF, is a public financing method that is used as a subsidy for redevelopment, infrastructure, and other community-improvement projects in many countries, including the United States. Similar or related value capture strategies are used around the world.
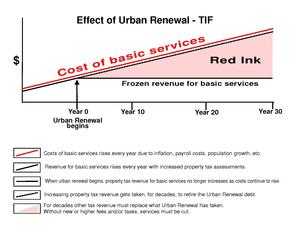
TIF is a method to use future gains in taxes to subsidize current improvements, which are projected to create the conditions for gains above the routine yearly increases which often occur without the improvements. To provide the needed subsidy, the urban renewal district, or TIF district, is essentially always drawn around 100s or 1000s of acres of additional real estate (beyond the project site) to provide the needed borrowing capacity for the project or projects. The borrowing capacity is established by committing all of normal yearly future real estate tax increases from every parcel in the TIF district (for 20–25 years, or more) along with the anticipated new tax revenue eventually coming from the project or projects themselves. If the projects are public improvements paying no real estate taxes all of the repayment will come from the adjacent properties within the TIF district. Although questioned, it is often presumed that even public improvements trigger gains in taxes above what occurs, or would have occurred in the district without the investment. In many jurisdictions yearly property tax increases are restricted and cannot exceed what would otherwise have occurred. The completion of a public or private project can at times result in an increase in the value of surrounding real estate, which generates additional tax revenue. Sales-tax revenue may also increase, and jobs may be added, although these factors and their multipliers usually do not influence the structure of TIF.
The routine yearly increases district wide along with any increase in site value from the public and private investment generates an increase in tax revenues. This is the "tax increment." Tax increment financing dedicates tax increments within a certain defined district to finance the debt that is issued to pay for the project. TIF was designed to channel funding toward improvements in distressed, underdeveloped, or underutilized parts of a jurisdiction where development might otherwise not occur. TIF creates funding for public or private projects by borrowing against the future increase in these property-tax revenues.[1]
Although the TIF method has been discontinued in the state it began in, California, thousands of TIF districts still currently operate nationwide in the US, from small and mid-sized cities, to the State of California which will be paying off debt on old TIFs for years to come. As of 2008, California had over four hundred TIF districts with an aggregate of over $10 billion per year in revenues, over $28 billion of long-term debt, and over $674 billion of assessed land valuation.[2] TIF began in California in 1952, but the state has currently discontinued the use of them due to a couple of lawsuits.[3][4]
With the exception of Arizona, every state and the District of Columbia has enabled legislation for tax increment financing.[5] Some states, such as Illinois, have used TIF for decades, but others have only recently embraced TIF.[6] The state of Maine has a program named TIF; however, this title refers to a process very different than in most states.[7]
Since the 1970s, the following factors have led local governments (cities, townships, etc.) to consider tax increment financing: lobbying by developers, a reduction in federal funding for redevelopment-related activities (including spending increases), restrictions on municipal bonds (which are tax-exempt bonds), the transfer of urban policy to local governments, State-imposed caps on municipal property tax collections, and State-imposed limits on the amounts and types of city expenditures. Considering these factors, many local governments have chosen TIF as a way to strengthen their tax bases, attract private investment, and increase economic activity.
Criticism
TIF districts have attracted much criticism. Some question whether TIF districts actually serve their resident populations. An organization called Municipal Officials for Redevelopment Reform (MORR) holds regular conferences on redevelopment abuse.[8]
Here are further claims made by TIF opponents:
- as investment in an area increases, it is not uncommon for real estate values to rise and for gentrification to occur.
- Although generally sold to legislatures as a tool to redevelop blighted areas, some districts are drawn up where development would happen anyway, such as ideal development areas at the edges of cities. California has passed legislation designed to curb this abuse.[9][10]
- The designation of urban areas as "blighted," essential to most TIF implementation, can allow governmental condemnation of property through eminent domain laws. The famous Kelo v. City of New London United States Supreme Court case, where homes were condemned for a private development, arose over actions within a TIF district.
- The TIF process arguably leads to favoratism for politically connected developers, implementing attorneys, economic development officials, and others involved in the processes.
- In some cases, school districts within communities using TIF are experiencing larger increases in state aid than districts not in such communities. This may be creating an incentive for governments to "over-TIF," consequently taking on riskier development projects. Local governments are under no obligation to recognize when TIF designation would adversely affect a school district's financial condition, and consequently the quality of some schools can be compromised.
- Normal inflationary increases in property values can be captured with districts in poorly written TIFs, representing money that would have gone into the public coffers even without the financed improvements.
- Districts can be drawn excessively large thus capturing revenue from areas that would have appreciated in value regardless of TIF designation.
- Approval of districts can sometimes capture one entity's future taxes without its official input, i.e. a school districts taxes will be frozen on action of a city.
- Capturing the full tax increment and directing it to repay the development bonds ignores the fact that the incremental increase in property value likely requires an increase in the provision of public services, which will now have to be funded from elsewhere (often from subsidies from less economically thriving areas). For example, the use of tax increment financing to create a large residential development means that public services from schools to public safety will need to be expanded, yet if the full tax increment is captured to repay the development bonds, other money will have to be used.[11]
Examples
Chicago
The city of Chicago, in Cook County, Illinois, has a significant number of TIF districts and has become a prime location for examining the benefits and disadvantages of TIF districts. The city runs 131 districts with tax receipts totaling upwards of $500 million for 2006.[12] Lori Healey, appointed commissioner of the city's Planning and Development department in 2005 was instrumental in the process of approving TIF districts as first deputy commissioner.
The Chicago Reader, a Chicago alternative newspaper published weekly, has published articles regarding tax increment financing districts in and around Chicago. Written by staff writer Ben Joravsky, the articles are critical of tax increment financing districts as implemented in Chicago.[13]
Cook County Clerk David Orr, in order to bring transparency to Chicago and Cook County tax increment financing districts, began to feature information regarding Chicago area districts on his office's website.[14] The information featured includes City of Chicago TIF revenue by year, maps of Chicago and Cook County suburban municipalities' TIF districts.
The Neighborhood Capital Budget Group of Chicago, Illinois, a non-profit organization, advocated for area resident participation in capital programs. The group also researched and analyzed the expansion of Chicago's TIF districts. Though the organization closed on February 1, 2007, their research will be available on their website for six months.[15]
In April 2009, the “TIF Sunshine Ordinance” introduced by Alderman Scott Waguespack and Alderman Manuel Flores (then 1st Ward Alderman) passed City Council. The ordinance made all TIF Redevelopment Agreements and attachments available on the City’s website in a searchable electronic format. The proposal intended to improve the overall transparency of TIF Agreements, thereby facilitating significantly increased public accountability.[16]
Albuquerque
Currently, the 2nd largest TIF project in America is located in Albuquerque, New Mexico: the $500 million Mesa del Sol development. Mesa del Sol is controversial in that the proposed development would be built upon a "green field" that presently generates little tax revenue and any increase in tax revenue would be diverted into a tax increment financing fund. This "increment" thus would leave governmental bodies without funding from the developed area that is necessary for the governmental bodies' operation.
Detroit
In July 2014, Detroit's Downtown Development Authority announced TIF financing for the new Red Wings hockey stadium. The total project cost, including additional private investments in retail and housing, is estimated at $650 million, of which $250 million will be financed using TIF capture to repay 30-year tax exempt bonds purchased by the Michigan Strategic Fund, the state's economic development arm.
Alameda, California
In 2009, SunCal Companies, an Irvine, California based developer, introduced a ballot initiative that embodied a redevelopment plan for the former Naval Air Station Alameda and a financial plan based in part on roughly $200 million worth of tax increment financing to pay for public amenities. SunCal structured the initiative so that the provision of public amenities was contingent on receiving tax increment financing, and on the creation of a community facilities (Mello-Roos) district, which would levy a special (extra) tax on property owners within the development.[17] Since Alameda City Council did not extend the Exclusive Negotiation Agreement with Suncal, this project will not move forward. In California, Community Redevelopment Law governs the use of tax increment financing by public agencies.[18]
Applications and administration
Cities use TIF to finance public infrastructure, land acquisition, demolition, utilities and planning costs, and other improvements including sewer expansion and repair, curb and sidewalk work, storm drainage, traffic control, street construction and expansion, street lighting, water supply, landscaping, park improvements, environmental remediation, bridge construction and repair, and parking structures.
State enabling legislation gives local governments the authority to designate tax increment financing districts. The district usually lasts 20 years, or enough time to pay back the bonds issued to fund the improvements. While arrangements vary, it is common to have a city government assuming the administrative role, making decisions about how and where the tool is applied.[19]
Most jurisdictions only allow bonds to be floated based upon a portion (usually capped at 50%) of the assumed increase in tax revenues. For example, if a $5,000,000 annual tax increment is expected in a development, which would cover the financing costs of a $50,000,000 bond, only a $25,000,000 bond would be typically allowed. If the project is moderately successful, this would mean that a good portion of the expected annual tax revenues (in this case over $2,000,000) would be dedicated to other public purposes other than paying off the bond.
See also
References
- ↑ Various, (2001). Tax Increment Financing and Economic Development, Uses, Structures and Impact. Edited by Craig L. Johnson and Joyce Y. Man. State University of New York Press.
- ↑ California State Controller's Annual Report on Redevelopment Agencies, 2007-2008
- ↑ "Urban Renewal Dead in California," The Antiplanner, Thoreau Institute (2 January 2012).
- ↑ See California Redevelopment Association v. Ana Matosantos.
- ↑ Council of Development Finance Agencies 2008 TIF State-By-State Report accessed 2014-3-21.
- ↑ Arkansas (2000), Washington (2001), New Jersey (2002), Delaware (2003), Louisiana (2003), North Carolina (2005), and New Mexico (2006).
- ↑ http://www.pressherald.com/2013/05/26/tif-helps-communities-that-dont-need-it_2013-05-26/
- ↑ "Redevelopment.com website". Retrieved 2009-12-04.
- ↑ "Redevelopment: The unknown government". Coalition for Redevelopment Reform. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
- ↑ "Subsidizing Redevelopment in California". Public Policy Institute of California. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
- ↑ See Richard Dye and David Merriman, "The Effects of Tax-Increment Financing on Economic Development," 47 Journal of Urban Economics, no. 2 (2000) pp. 306-328
- ↑ "City of Chicago TIF Revenue Totals by Year 1986-2013" (PDF). Cook County Clerk's Office. Retrieved 2014-08-19.
- ↑ "articles by Reader staff writer Ben Joravsky on Chicago's TIF (tax increment financing) districts". Chicago Reader. Retrieved 2008-05-29.
- ↑ "TIFs 101: A taxpayer's primer for understanding TIFs". Cook County Clerk's Office. Retrieved 2008-05-29.
- ↑ "Research". Neighborhood Capital Budget Group of Chicago, Illinois. Retrieved 2008-05-29.
- ↑ "Research". 32ND WARD SERVICE OFFICE. Retrieved 2014-45-29. Check date values in:
|accessdate=(help) - ↑ "Alameda Point Development Initiative Election Report Executive Summary Part I" (PDF). City of Alameda. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
- ↑ "California Community Redevelopment Law". Retrieved 2009-12-05.
- ↑ "Growth Within Bounds: Report of the Commission on Local Governance for the 21st Century" (PDF). State of California. Retrieved 2009-12-04.
External links
- Tax Increment Financing: Imagining Urban Futures - Research on the circulation of the Tax Increment Financing model across North America and the UK by Professor Kevin Ward (University of Manchester)
- Michael Dardia "Subsidizing Redevelopment in California" (1998). Written for the Public Policy Institute of California.
- Nathan A. Benefield's academic paper titled "The Effects of Tax Increment Financing on Home Values in the City of Chicago" (2003). Benefield's paper was prepared for presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwest Political Science Association.
- Swenson & Eathington's "Do Tax Increment Finance Districts in Iowa Spur Regional Economic and Demographic Growth?" (2002).
- Scott, Brendan S., 2013 "Factors that Influence the Size of Tax Increment Financing Districts in Texas" Applied Research Project, Texas State University.
- "How to Grow Your Real Estate Portfolio Tax Free."
- An abstract of Weber's Equity and Entrepreneurialism: The Impact of Tax Increment Financing on School Finance (2003).
- An abstract of Weber, et al.'s "Does Tax Increment Financing Raise Urban Industrial Property Values?" (2003).
- An abstract of Robinson's "Hunger Discipline and Social Parasites: The Political Economy of the Living Wage" (2004).
- "Creative Success Alliance show you how to invest in real estate".
- Hubbell & Eaton's "Tax Increment Financing in the State of Missouri" (University of Missouri-Kansas City, 1997).
- Wood & Hughes' report for Center on Wisconsin Strategy (at University of Wisconsin–Madison) titled "From Stumps to Dumps: Wisconsin's Anti-Environmental Subsidies" (2001).
- Matthew Mayrl's report for Center on Wisconsin Strategy (at University of Wisconsin–Madison) titled "Refocusing Wisconsin’s TIF System On Urban Redevelopment: Three Reforms" (2005) and the Executive Summary.