Tavush Province
| Tavush Տավուշ | |
|---|---|
| Province | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 40°53′N 45°8′E / 40.883°N 45.133°ECoordinates: 40°53′N 45°8′E / 40.883°N 45.133°E | |
| Country | Armenia |
| Capital | Ijevan |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Armen Ghularyan |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,704 km2 (1,044 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 4th |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 128,609 |
| • Rank | 10th |
| • Density | 48/km2 (120/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+04 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+05 (UTC) |
| Postal code | 3901–4216 |
| ISO 3166 code | AM.TV |
| FIPS 10-4 | AM09 |
| Website | tavush.gov.am |
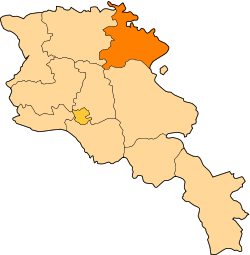
Tavush (Armenian: Տավուշ, Armenian pronunciation: [tɑˈvuʃ]) is a province (marz) of Armenia. The marz of Tavush is located in the north of Armenia and borders on Georgia and Azerbaijan.
It is well known for its mountains. The most part of its territory is situated 800-1,000 m above sea level. The territory relief consists of rocky hillsides covered with the bright green carpet of Alpine meadows; Tavush is sometimes referred to as a little Armenian Switzerland.
Tavush is also famous for the abundance of rivers and other water resources. The largest river of the marz is the Agstev with the inflows – the Getik, the Voskepar, and the Sarnadzhur. The Akhum, the Tavush and the Khndzorot originate in the Miapor Mountains and flow across the beautiful valleys. In Tavush there are a number of mountain springs, mineral water springs and small lakes; the most known of them is Lake Parz of extraordinary beauty. The pure watered lake rounded with thick woods is situated near the city of Dilijan.
And, finally, the woods – another treasure of Tavush. In fact a half of its territory is covered by fine virgin woods which grow high on mountains slopes inhabited by various representatives of fauna. Tavush woods are especially attractive in autumn when trees are dressed in multi-colored attires.
In a word, Tavush is a great recreation area with picturesque river valleys, deep gorges, crystal curative springs and lakes reflecting the azure sky and surrounding woods. Dilizhan alone is similar to an Alpine resort known far beyond the borders of Armenia.
Tavush received its name after the historical area of Armenia – Tavush gavar – a part of Great Armenia – which included the most part of modern Tavush. The surviving medieval settlements, fortresse and monasteries confirm the ancient history of Tavush and prove that the territory was extensively populated in the early Middle Ages.
The main places of interest of Tavush marz are monastic complexes Goshavank (12th – 13th centuries), Agartsin (11th – 13th centuries), Makaravank (11th – 13th century), Voskepar (6th – 7th centuries), Mshavank (12th century), Nor Varagavank (12th – 13th centuries), Khoranagat (13th century) and others were constructed either amidst thick woods or at such heights that at times they are obscured by the clouds descending from the mountains.
Mountainous and forested, Tavush is home to many historic Armenian monasteries, churches, castles, forts, and khachkars. The noteworthy Goshavank, Makaravank, and the Haghartsin monasteries are all located in this region. Haghartsin was built between the 10th and 14th centuries while Goshavank was founded by Mkhitar Gosh, an Armenian scholar and priest who wrote the civil and canon law.
Tavush borders the following marzer:
- Gegharkunik – south
- Kotayk – southwest
- Lori – west
Communities
| Part of a series on |
| Armenia Հայաստան |
|---|
  |
| Culture |
| History |
| Demographics |
| Administrative divisions |
|
| Armenia portal |
The province of Tavush consists of the following 62 communities (hamaynkner), of which 5 are considered urban and 57 are considered rural.[1]
Towns or urban communities
| Image | City (town) | Province | Founded | Land area (km2) | Population (2011 est.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Ayrum | Tavush | 1937 | 1.6 | 2,400 |
| Berd | Tavush | 10th century | 3.5 | 8,500 | |
.jpg) | Dilijan | Tavush | 1544 | 13 | 15,600 |
 | Ijevan | Tavush | 1780s | 4.6 | 20,700 |
 | Noyemberyan | Tavush | 13th century (first settled) | 3.6 | 5,500 |
Villages or rural communities
Non-community villages
- Chermakavan, belongs to the Khachardzan community.
- Geghatap, belongs to the Khachardzan community.
- Kayan, belongs to the Aygehovit community.
References
- Report of the results of the 2001 Armenian Census, National Statistical Service of the Republic of Armenia
- ↑ "RA Tavush Marz" (PDF). Marzes of the Republic of Armenia in Figures, 2002–2006. National Statistical Service of the Republic of Armenia. 2007.
External links
| ||||||||||||




