TRNA (carboxymethyluridine34-5-O)-methyltransferase
| TRNA (carboxymethyluridine34-5-O)-methyltransferase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 2.1.1.229 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
TRNA (carboxymethyluridine34-5-O)-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.229, ALKBH8, ABH8, Trm9, tRNA methyltransferase 9) is an enzyme with system name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:tRNA (carboxymethyluridine34-5-O)-methyltransferase.[1][2][3] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- S-adenosyl-L-methionine + carboxymethyluridine34 in tRNA
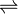 S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 5-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)uridine34 in tRNA
S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + 5-(2-methoxy-2-oxoethyl)uridine34 in tRNA
The enzyme catalyses the posttranslational modification of uridine residues at the wobble position 34 of the anticodon loop of tRNA.
References
- ↑ Fu, D., Brophy, J.A., Chan, C.T., Atmore, K.A., Begley, U., Paules, R.S., Dedon, P.C., Begley, T.J. and Samson, L.D. (2010). "Human AlkB homolog ABH8 Is a tRNA methyltransferase required for wobble uridine modification and DNA damage survival". Mol. Cell. Biol. 30 (10): 2449–2459. doi:10.1128/MCB.01604-09. PMID 20308323.
- ↑ Songe-Møller, L., van den Born, E., Leihne, V., Vågbø, C.B., Kristoffersen, T., Krokan, H.E., Kirpekar, F., Falnes, P.Ø. and Klungland, A. (2010). "Mammalian ALKBH8 possesses tRNA methyltransferase activity required for the biogenesis of multiple wobble uridine modifications implicated in translational decoding". Mol. Cell. Biol. 30 (7): 1814–1827. doi:10.1128/MCB.01602-09. PMID 20123966.
- ↑ Kalhor, H.R. and Clarke, S. (2003). "Novel methyltransferase for modified uridine residues at the wobble position of tRNA". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (24): 9283–9292. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.24.9283-9292.2003. PMID 14645538.
External links
- TRNA (carboxymethyluridine34-5-O)-methyltransferase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)