TERF2
Telomeric repeat-binding factor 2 is a protein that is also known as TRF2 and TRBF2. It is in humans encoded by the TERF2 gene.[1][2]
Function
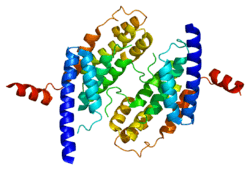
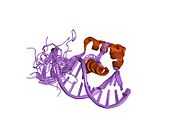
This gene encodes a telomere specific protein, TERF2, which is a component of the shelterin nucleoprotein complex. This protein is present at telomeres in metaphase of the cell cycle, is a second negative regulator of telomere length and plays a key role in the protective activity of telomeres. While having similar telomere binding activity and domain organization, TERF2 differs from TERF1 in that its N terminus is basic rather than acidic.[3]
Interactions
TERF2 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ↑ Broccoli D, Smogorzewska A, Chong L, de Lange T (November 1997). "Human telomeres contain two distinct Myb-related proteins, TRF1 and TRF2". Nat. Genet. 17 (2): 231–5. doi:10.1038/ng1097-231. PMID 9326950.
- ↑ Sakaguchi AY, Padalecki SS, Mattern V, Rodriguez A, Leach RJ, McGill JR et al. (May 1999). "Chromosomal sublocalization of the transcribed human telomere repeat binding factor 2 gene and comparative mapping in the mouse". Somat. Cell Mol. Genet. 24 (3): 157–63. doi:10.1023/B:SCAM.0000007118.47691.d7. PMID 10226653. Check date values in:
|year= / |date= mismatch(help) - ↑ "Entrez Gene: TERF2 telomeric repeat binding factor 2".
- ↑ Song K, Jung D, Jung Y, Lee SG, Lee I (September 2000). "Interaction of human Ku70 with TRF2". FEBS Lett. 481 (1): 81–5. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01958-x. PMID 10984620.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Zhu XD, Küster B, Mann M, Petrini JH, de Lange T (July 2000). "Cell-cycle-regulated association of RAD50/MRE11/NBS1 with TRF2 and human telomeres". Nat. Genet. 25 (3): 347–52. doi:10.1038/77139. PMID 10888888. Vancouver style error (help)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 O'Connor MS, Safari A, Liu D, Qin J, Songyang Z (July 2004). "The human Rap1 protein complex and modulation of telomere length". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (27): 28585–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.M312913200. PMID 15100233.
- ↑ Li B, Oestreich S, de Lange T (May 2000). "Identification of human Rap1: implications for telomere evolution". Cell 101 (5): 471–83. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80858-2. PMID 10850490.
- ↑ Opresko PL, von Kobbe C, Laine JP, Harrigan J, Hickson ID, Bohr VA (October 2002). "Telomere-binding protein TRF2 binds to and stimulates the Werner and Bloom syndrome helicases". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (43): 41110–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205396200. PMID 12181313.
Further reading
- Bilaud T, Koering CE, Binet-Brasselet E, Ancelin K, Pollice A, Gasser SM et al. (1996). "The telobox, a Myb-related telomeric DNA binding motif found in proteins from yeast, plants and human". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (7): 1294–303. doi:10.1093/nar/24.7.1294. PMC 145771. PMID 8614633.
- Bilaud T, Brun C, Ancelin K, Koering CE, Laroche T, Gilson E (1997). "Telomeric localization of TRF2, a novel human telobox protein". Nat. Genet. 17 (2): 236–9. doi:10.1038/ng1097-236. PMID 9326951.
- van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T (1998). "TRF2 protects human telomeres from end-to-end fusions". Cell 92 (3): 401–13. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80932-0. PMID 9476899.
- Griffith JD, Comeau L, Rosenfield S, Stansel RM, Bianchi A, Moss H et al. (1999). "Mammalian telomeres end in a large duplex loop". Cell 97 (4): 503–14. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80760-6. PMID 10338214.
- Teichmann M, Wang Z, Martinez E, Tjernberg A, Zhang D, Vollmer F et al. (1999). "Human TATA-binding protein-related factor-2 (hTRF2) stably associates with hTFIIA in HeLa cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (24): 13720–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.24.13720. PMC 24131. PMID 10570139.
- Smogorzewska A, van Steensel B, Bianchi A, Oelmann S, Schaefer MR, Schnapp G et al. (2000). "Control of human telomere length by TRF1 and TRF2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (5): 1659–68. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.5.1659-1668.2000. PMC 85349. PMID 10669743.
- Li B, Oestreich S, de Lange T (2000). "Identification of human Rap1: implications for telomere evolution". Cell 101 (5): 471–83. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80858-2. PMID 10850490.
- Zhu XD, Küster B, Mann M, Petrini JH, de Lange T (2000). "Cell-cycle-regulated association of RAD50/MRE11/NBS1 with TRF2 and human telomeres". Nat. Genet. 25 (3): 347–52. doi:10.1038/77139. PMID 10888888. Vancouver style error (help)
- Song K, Jung D, Jung Y, Lee SG, Lee I (2000). "Interaction of human Ku70 with TRF2". FEBS Lett. 481 (1): 81–5. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01958-X. PMID 10984620.
- Song K, Jung Y, Jung D, Lee I (2001). "Human Ku70 interacts with heterochromatin protein 1alpha". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (11): 8321–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008779200. PMID 11112778.
- Fairall L, Chapman L, Moss H, de Lange T, Rhodes D (2001). "Structure of the TRFH dimerization domain of the human telomeric proteins TRF1 and TRF2". Mol. Cell 8 (2): 351–61. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00321-5. PMID 11545737.
- Bailey SM, Cornforth MN, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ, Goodwin EH (2001). "Strand-specific postreplicative processing of mammalian telomeres". Science 293 (5539): 2462–5. doi:10.1126/science.1062560. PMID 11577237.
- Karlseder J, Smogorzewska A, de Lange T (2002). "Senescence induced by altered telomere state, not telomere loss". Science 295 (5564): 2446–9. doi:10.1126/science.1069523. PMID 11923537.
- Mignon-Ravix C, Depetris D, Delobel B, Croquette MF, Mattei MG (2002). "A human interstitial telomere associates in vivo with specific TRF2 and TIN2 proteins". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 10 (2): 107–12. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200775. PMID 11938440.
- Ancelin K, Brunori M, Bauwens S, Koering CE, Brun C, Ricoul M et al. (2002). "Targeting assay to study the cis functions of human telomeric proteins: evidence for inhibition of telomerase by TRF1 and for activation of telomere degradation by TRF2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 22 (10): 3474–87. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.10.3474-3487.2002. PMC 133804. PMID 11971978.
- Opresko PL, von Kobbe C, Laine JP, Harrigan J, Hickson ID, Bohr VA (2002). "Telomere-binding protein TRF2 binds to and stimulates the Werner and Bloom syndrome helicases". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (43): 41110–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205396200. PMID 12181313.
- Chagnon P, Michaud J, Mitchell G, Mercier J, Marion JF, Drouin E et al. (2002). "A missense mutation (R565W) in cirhin (FLJ14728) in North American Indian childhood cirrhosis". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71 (6): 1443–9. doi:10.1086/344580. PMC 378590. PMID 12417987.
| |||||||||||||||||