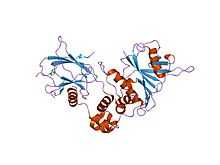
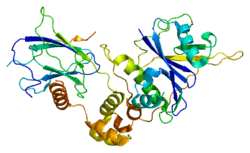TCEB1
Transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCEB1 gene.[1][2]
Function
This gene encodes the protein elongin C, which is a subunit of the transcription factor B (SIII) complex. The SIII complex is composed of elongins A/A2, B and C. It activates elongation by RNA polymerase II by suppressing transient pausing of the polymerase at many sites within transcription units. Elongin A functions as the transcriptionally active component of the SIII complex, whereas elongins B and C are regulatory subunits. Elongin A2 is specifically expressed in the testis, and capable of forming a stable complex with elongins B and C. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein binds to elongins B and C, and thereby inhibits transcription elongation.[3]
Interactions
TCEB1 has been shown to interact with:
References
- ↑ Garrett KP, Haque D, Conaway RC, Conaway JW (Feb 1995). "A human cDNA encoding the small subunit of RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII". Gene 150 (2): 413–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90467-7. PMID 7821821.
- ↑ Duan DR, Pause A, Burgess WH, Aso T, Chen DY, Garrett KP et al. (Oct 1995). "Inhibition of transcription elongation by the VHL tumor suppressor protein". Science 269 (5229): 1402–6. doi:10.1126/science.7660122. PMID 7660122.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: TCEB1 transcription elongation factor B (SIII), polypeptide 1 (15kDa, elongin C)".
- ↑ Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N et al. (Oct 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Ohh M, Takagi Y, Aso T, Stebbins CE, Pavletich NP, Zbar B et al. (Dec 1999). "Synthetic peptides define critical contacts between elongin C, elongin B, and the von Hippel-Lindau protein". J. Clin. Invest. 104 (11): 1583–91. doi:10.1172/JCI8161. PMC 481054. PMID 10587522.
- ↑ Krumm A, Groudine M (Sep 1995). "Tumor suppression and transcription elongation: the dire consequences of changing partners". Science 269 (5229): 1400–1. doi:10.1126/science.7660121. PMID 7660121.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Li Z, Na X, Wang D, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (Feb 2002). "Ubiquitination of a novel deubiquitinating enzyme requires direct binding to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (7): 4656–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108269200. PMID 11739384.
- ↑ Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S et al. "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- ↑ Tsuchiya H, Iseda T, Hino O (Jul 1996). "Identification of a novel protein (VBP-1) binding to the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor gene product". Cancer Res. 56 (13): 2881–5. PMID 8674032.
- ↑ Min JH, Yang H, Ivan M, Gertler F, Kaelin WG, Pavletich NP (Jun 2002). "Structure of an HIF-1alpha -pVHL complex: hydroxyproline recognition in signaling". Science 296 (5574): 1886–9. doi:10.1126/science.1073440. PMID 12004076.
- ↑ Hacker KE, Lee CM, Rathmell WK. Zhang B, ed. "VHL type 2B mutations retain VBC complex form and function". PLoS ONE 3 (11): e3801. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0003801. PMC 2583047. PMID 19030229.
- ↑ Kim BY, Kim H, Cho EJ, Youn HD (Feb 2008). "Nur77 upregulates HIF-alpha by inhibiting pVHL-mediated degradation". Exp. Mol. Med. 40 (1): 71–83. doi:10.3858/emm.2008.40.1.71. PMC 2679322. PMID 18305400.
Further reading
- Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC (1995). "Elongin (SIII): a multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II". Science 269 (5229): 1439–43. doi:10.1126/science.7660129. PMID 7660129.
- Kibel A, Iliopoulos O, DeCaprio JA, Kaelin WG (1995). "Binding of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein to Elongin B and C". Science 269 (5229): 1444–6. doi:10.1126/science.7660130. PMID 7660130.
- Bradsher JN, Jackson KW, Conaway RC, Conaway JW (1994). "RNA polymerase II transcription factor SIII. I. Identification, purification, and properties". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (34): 25587–93. PMID 8244996.
- Pause A, Lee S, Worrell RA, Chen DY, Burgess WH, Linehan WM et al. (1997). "The von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor gene product forms a stable complex with human CUL-2, a member of the Cdc53 family of proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (6): 2156–61. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.6.2156. PMC 20057. PMID 9122164.
- Lonergan KM, Iliopoulos O, Ohh M, Kamura T, Conaway RC, Conaway JW et al. (1998). "Regulation of hypoxia-inducible mRNAs by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein requires binding to complexes containing elongins B/C and Cul2". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (2): 732–41. PMC 108784. PMID 9447969.
- Zhang JG, Farley A, Nicholson SE, Willson TA, Zugaro LM, Simpson RJ et al. (1999). "The conserved SOCS box motif in suppressors of cytokine signaling binds to elongins B and C and may couple bound proteins to proteasomal degradation". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (5): 2071–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.5.2071. PMC 26738. PMID 10051596.
- Stebbins CE, Kaelin WG, Pavletich NP (1999). "Structure of the VHL-ElonginC-ElonginB complex: implications for VHL tumor suppressor function". Science 284 (5413): 455–61. doi:10.1126/science.284.5413.455. PMID 10205047.
- Pause A, Peterson B, Schaffar G, Stearman R, Klausner RD (1999). "Studying interactions of four proteins in the yeast two-hybrid system: structural resemblance of the pVHL/elongin BC/hCUL-2 complex with the ubiquitin ligase complex SKP1/cullin/F-box protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (17): 9533–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.17.9533. PMC 22243. PMID 10449727.
- Iwai K, Yamanaka K, Kamura T, Minato N, Conaway RC, Conaway JW et al. (1999). "Identification of the von Hippel-lindau tumor-suppressor protein as part of an active E3 ubiquitin ligase complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (22): 12436–41. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.22.12436. PMC 22941. PMID 10535940.
- Ohh M, Takagi Y, Aso T, Stebbins CE, Pavletich NP, Zbar B et al. (2000). "Synthetic peptides define critical contacts between elongin C, elongin B, and the von Hippel-Lindau protein". J. Clin. Invest. 104 (11): 1583–91. doi:10.1172/JCI8161. PMC 481054. PMID 10587522.
- Aso T, Yamazaki K, Amimoto K, Kuroiwa A, Higashi H, Matsuda Y et al. (2000). "Identification and characterization of Elongin A2, a new member of the Elongin family of transcription elongation factors, specifically expressed in the testis". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (9): 6546–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6546. PMID 10692460.
- Adryan B, Decker HJ, Papas TS, Hsu T (2000). "Tracheal development and the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor homolog in Drosophila". Oncogene 19 (24): 2803–11. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203611. PMID 10851083.
- Kamura T, Sato S, Iwai K, Czyzyk-Krzeska M, Conaway RC, Conaway JW (2000). "Activation of HIF1alpha ubiquitination by a reconstituted von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (19): 10430–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.190332597. PMC 27041. PMID 10973499.
- Aso T, Yamazaki K, Aigaki T, Kitajima S (2000). "Drosophila von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor complex possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 276 (1): 355–61. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3451. PMID 11006129.
- Kamura T, Burian D, Yan Q, Schmidt SL, Lane WS, Querido E et al. (2001). "Muf1, a novel Elongin BC-interacting leucine-rich repeat protein that can assemble with Cul5 and Rbx1 to reconstitute a ubiquitin ligase". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (32): 29748–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103093200. PMID 11384984.
- Li Z, Na X, Wang D, Schoen SR, Messing EM, Wu G (2002). "Ubiquitination of a novel deubiquitinating enzyme requires direct binding to von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (7): 4656–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108269200. PMID 11739384.
- Yamazaki K, Guo L, Sugahara K, Zhang C, Enzan H, Nakabeppu Y et al. (2002). "Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel transcription elongation factor, Elongin A3". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 26444–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202859200. PMID 11994304.
- Porkka K, Saramäki O, Tanner M, Visakorpi T (2002). "Amplification and overexpression of Elongin C gene discovered in prostate cancer by cDNA microarrays". Lab. Invest. 82 (5): 629–37. doi:10.1038/labinvest.3780457. PMID 12004003. Vancouver style error (help)
| |||||||||||||||||||