T-54/55 operators and variants
| T-54/55 | |
|---|---|
|
US Army recognition poster | |
| Type | Main battle tank |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1947–present |
| Production history | |
| Designer |
Morozov (T-54), OKB-520 (T-54A and later) |
| Designed | 1945 |
| Manufacturer |
KhPZ, UVZ (USSR), Bumar-Łabędy (Pol.), ZTS Martin (Czech.) |
| Produced |
1946–81 (USSR) 1956–79 (Pol.) 1957–83 (Czech.) |
| Number built | 86,000–100,000 est. |
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The T-54/55 tank series is the most widely used tank in the world and it has seen service in over 50 countries. It also served as the platform for a wide variety of specialty armored vehicles.[1][2]
List of operators
-
 Abkhazia – A number of T-55s in service at the beginning of the 1992-1993 War in Abkhazia, all of which were lost in the first four months of the fighting at which point Abhazian forces had 8 T-55s captured from the Georgians.[3] At peak there were 100 T-55s and T-72s in service.[4] More than 50 T-55s and T-72s were in service in 2004.[5] 87 T-55s and T-72s were in service before the 2008 South Ossetia war.[6] Between 50 and 60 T-55s and T-72s are currently in service.
Abkhazia – A number of T-55s in service at the beginning of the 1992-1993 War in Abkhazia, all of which were lost in the first four months of the fighting at which point Abhazian forces had 8 T-55s captured from the Georgians.[3] At peak there were 100 T-55s and T-72s in service.[4] More than 50 T-55s and T-72s were in service in 2004.[5] 87 T-55s and T-72s were in service before the 2008 South Ossetia war.[6] Between 50 and 60 T-55s and T-72s are currently in service. -
 Afghanistan – 50 T-54s and 50 T-55s were ordered in 1961 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1962 and 1964 (T-54s were previously in Soviet service). 200 T-54s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1978 and 1979 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 705 T-55s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1978 and 1991 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 1,000 T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and PT-76s were in service on 1 April 1992.[8] Currently 600 T-55s are in service and are to be replaced with M60 Pattons.
Afghanistan – 50 T-54s and 50 T-55s were ordered in 1961 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1962 and 1964 (T-54s were previously in Soviet service). 200 T-54s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1978 and 1979 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 705 T-55s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1978 and 1991 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 1,000 T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and PT-76s were in service on 1 April 1992.[8] Currently 600 T-55s are in service and are to be replaced with M60 Pattons. -
 Algeria – 40 T-54s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1963 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 25 T-54s and 25 T-55s were ordered in 1965 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1966 (T-54s were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-54s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1966 and 1967 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1967. 50 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] 324 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001[8] and 320 in early 2003[9] and 2004[5] and 270 in 2006.[10]
Algeria – 40 T-54s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1963 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 25 T-54s and 25 T-55s were ordered in 1965 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1966 (T-54s were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-54s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1966 and 1967 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1967. 50 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] 324 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001[8] and 320 in early 2003[9] and 2004[5] and 270 in 2006.[10] -
 Angola – 150 T-54s and possibly T-55s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1975 and 1978 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1987 and 1988 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service). 30 T-55s were received between 1993 and 1994 from Russia (20 in 1993 and 10 in 1994).[11] 62 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 1999 from Belarus and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 31 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service). 205 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1999 from Slovakia with 150 being delivered in 1999 and 55 in 2000 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Slovakian service).[7][12] 90 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2000.[13] Around 560 T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[8] 400 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004[14] and around 200 in 2005[5] and 2006.[10]
Angola – 150 T-54s and possibly T-55s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1975 and 1978 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1987 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1987 and 1988 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service). 30 T-55s were received between 1993 and 1994 from Russia (20 in 1993 and 10 in 1994).[11] 62 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 1999 from Belarus and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 31 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service). 205 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1999 from Slovakia with 150 being delivered in 1999 and 55 in 2000 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Slovakian service).[7][12] 90 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2000.[13] Around 560 T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[8] 400 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004[14] and around 200 in 2005[5] and 2006.[10] -
 Bangladesh – 15 T-54s were ordered in 1973 from Egypt and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service). 15 T-55s were ordered in 1975 from Egypt and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Egypt service).[7] 240 T-54s, T-55s, Type 59s and Type 62s were in service in early 2001[15] and 180 in early 2003.[16] 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] 122 modernized T-54s and T-55s with laser rangefinders and improved armor protection are currently in service.
Bangladesh – 15 T-54s were ordered in 1973 from Egypt and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service). 15 T-55s were ordered in 1975 from Egypt and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Egypt service).[7] 240 T-54s, T-55s, Type 59s and Type 62s were in service in early 2001[15] and 180 in early 2003.[16] 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] 122 modernized T-54s and T-55s with laser rangefinders and improved armor protection are currently in service. -
 Bosnia and Herzegovina – [17] 10 T-55s were ordered in 1997 from Egypt and delivered in 1997 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service).[7] 170 T-34s, T-55s, M60A3s and AMX-30s were in service in early 2001.[15] 192 T-34s, T-54s T-55s, M60A3s, M-84s and AMX-30s were in service in early 2003. Currently, the military of Bosnia Herzegovina operates 180 T-55s.[16] 80 T-55s were in service in 2004,[18] 69 T-55s and 13 T-54s in 2005[5] and 75 T-55s in 2006.[10]
Bosnia and Herzegovina – [17] 10 T-55s were ordered in 1997 from Egypt and delivered in 1997 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service).[7] 170 T-34s, T-55s, M60A3s and AMX-30s were in service in early 2001.[15] 192 T-34s, T-54s T-55s, M60A3s, M-84s and AMX-30s were in service in early 2003. Currently, the military of Bosnia Herzegovina operates 180 T-55s.[16] 80 T-55s were in service in 2004,[18] 69 T-55s and 13 T-54s in 2005[5] and 75 T-55s in 2006.[10] -
 Cambodia – 10 T-54s were ordered in 1983 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1988 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1989 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service, the vehicles could be supplied by Vietnam). 15 T-55s were ordered in 1990 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1990. 40 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1994 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 50 T-55AM2BPs were ordered in 1994 from Poland and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service).[7] 150 T-55s, Type 59s and PT-76s were in service in early 2001[19] and 170 in early 2003.[20] More than 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] 103 T-54s are currently in service 2007.Cambodia has purchased 50 T-55A main battle tank from eastern Europe that arrive on September 20, 2010. Cambodia's Armoured cavalry has 220 T-54/T-55 in service in 2011 .[21]
Cambodia – 10 T-54s were ordered in 1983 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1988 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1989 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service, the vehicles could be supplied by Vietnam). 15 T-55s were ordered in 1990 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1990. 40 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1994 from Czech Republic and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 50 T-55AM2BPs were ordered in 1994 from Poland and delivered in 1994 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service).[7] 150 T-55s, Type 59s and PT-76s were in service in early 2001[19] and 170 in early 2003.[20] More than 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] 103 T-54s are currently in service 2007.Cambodia has purchased 50 T-55A main battle tank from eastern Europe that arrive on September 20, 2010. Cambodia's Armoured cavalry has 220 T-54/T-55 in service in 2011 .[21] -
 Chad – 60 T-55s were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][22][23] Currently 60 T-55s are in service.[24]
Chad – 60 T-55s were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][22][23] Currently 60 T-55s are in service.[24] -
 People's Republic of China – 6,000 Type 59s were in service in 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000, 5,000 in 2003 and 2005 and around 5,000 in 2010.
People's Republic of China – 6,000 Type 59s were in service in 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000, 5,000 in 2003 and 2005 and around 5,000 in 2010. -
 Central African Republic – 4 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Libya and delivered in 1982 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Libyan service).[7] 4 T-55s were in service in early 2001[25] and 3 in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][26]
Central African Republic – 4 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Libya and delivered in 1982 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Libyan service).[7] 4 T-55s were in service in early 2001[25] and 3 in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][26] -
 Democratic Republic of the Congo – [27] 20 T-55s were ordered in 2005 from Ukraine and delivered in 2006 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service).[7][11] 20 T-55s were in service in 2006.[10]
Democratic Republic of the Congo – [27] 20 T-55s were ordered in 2005 from Ukraine and delivered in 2006 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service).[7][11] 20 T-55s were in service in 2006.[10] -
 Republic of the Congo – 25 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1982 from an unknown supplier and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were probably second-hand).[7] 25 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 25 T-54s and T-55s are in service.
Republic of the Congo – 25 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1982 from an unknown supplier and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were probably second-hand).[7] 25 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 25 T-54s and T-55s are in service. -
 Ivory Coast – 10 T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][20]
Ivory Coast – 10 T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][20] -
 Cuba – 100 T-55s were received in 1963 from the Soviet Union as aid (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 1,200 T-55s were ordered in 1964 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1975. 25 T-55s and T-54-based ARVs were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] Currently Cuba possesses 1,100 T-55s, most of which are in storage or used as Artillery Propeller and SPAAG with SA-3 and SA-2 missiles mounted . 120 T-55s are modernized to T-55M standard and 20 more to T-55AM.[28]
Cuba – 100 T-55s were received in 1963 from the Soviet Union as aid (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 1,200 T-55s were ordered in 1964 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1975. 25 T-55s and T-54-based ARVs were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] Currently Cuba possesses 1,100 T-55s, most of which are in storage or used as Artillery Propeller and SPAAG with SA-3 and SA-2 missiles mounted . 120 T-55s are modernized to T-55M standard and 20 more to T-55AM.[28] -
 Egypt – 350 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1961 and 1966 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line). 150 T-55s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1966. Egypt lost 820 vehicles in the Six Day War including 82 T-55s.[3] 800 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1972 (some of the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian and/or Poland production line). 550 T-55s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1973. 50 T-54s were ordered in 1972 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1973 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 895 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003 and 2004.[5][29] 840 T-54s and T-55s were in storage in 2006.[10] 260 Ramses IIs were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5]
Egypt – 350 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1961 and 1966 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line). 150 T-55s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1966. Egypt lost 820 vehicles in the Six Day War including 82 T-55s.[3] 800 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1972 (some of the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian and/or Poland production line). 550 T-55s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1973. 50 T-54s were ordered in 1972 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1973 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 895 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003 and 2004.[5][29] 840 T-54s and T-55s were in storage in 2006.[10] 260 Ramses IIs were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5] -
 Eritrea – 120 T-55As were ordered in 2004 from Bulgaria and delivered in 2005 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service).[7][11] 150 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][30]
Eritrea – 120 T-55As were ordered in 2004 from Bulgaria and delivered in 2005 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service).[7][11] 150 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][30] -
 Ethiopia – 200 T-54s and 200 T-55s were ordered in 1977 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978 (the T-54s were previously in Soviet service while the T-55s were possibly previously in Soviet service). 60 T-54s were ordered in 1978 from East Germany and delivered between 1979 and 1980 (the vehicles were previously in East German service). 700 T-55s were ordered in 1980 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1980 and 1988 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line). 90 T-55s were ordered in 1983 from Libya and delivered in 1984 (the vehicles were previously in Libyan service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1989 from East Germany and delivered in 1989 (the vehicles were previously in East German service, more were ordered but the order was canceled). 40 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Belarus and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Belorussian service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, some may have been ex-Ukrainian and/or ex-Romanian vehicles sold through Bulgaria). 140 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered between 1999 and 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, some may have been ex-Ukrainian and/or ex-Romanian vehicles sold through Bulgaria, the delivery of last 40 vehicles was suspended between 2000 and 2001 due to UN embargo).[7] Around 160 T-55s and T-62s were in service in early 2001[31] and more than 270 in early 2003.[30] More than 250 T-54s, T-55s and T-62s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Ethiopia – 200 T-54s and 200 T-55s were ordered in 1977 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978 (the T-54s were previously in Soviet service while the T-55s were possibly previously in Soviet service). 60 T-54s were ordered in 1978 from East Germany and delivered between 1979 and 1980 (the vehicles were previously in East German service). 700 T-55s were ordered in 1980 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1980 and 1988 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line). 90 T-55s were ordered in 1983 from Libya and delivered in 1984 (the vehicles were previously in Libyan service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1989 from East Germany and delivered in 1989 (the vehicles were previously in East German service, more were ordered but the order was canceled). 40 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Belarus and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Belorussian service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, some may have been ex-Ukrainian and/or ex-Romanian vehicles sold through Bulgaria). 140 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered between 1999 and 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, some may have been ex-Ukrainian and/or ex-Romanian vehicles sold through Bulgaria, the delivery of last 40 vehicles was suspended between 2000 and 2001 due to UN embargo).[7] Around 160 T-55s and T-62s were in service in early 2001[31] and more than 270 in early 2003.[30] More than 250 T-54s, T-55s and T-62s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Equatorial Guinea – 3
Equatorial Guinea – 3 -
 Georgia – 120 T-55AM2s and T-54s were ordered in 1998 from Czech Republic with 10 T-55AM2s being delivered in 2000 and the rest in 2001 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service).[7][12] 108 T-55Ms were in service at the beginning of the 1992-1993 War in Abhazia.[3] Around 40 T-55s were in service in 1992 and 1995, 48 in 2000, 59 in 2002, 55 in 2004,[5] 2005 and 2006[10] and 23 T-55s and 3 T-54s in 2008 and 2010.[32]
Georgia – 120 T-55AM2s and T-54s were ordered in 1998 from Czech Republic with 10 T-55AM2s being delivered in 2000 and the rest in 2001 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service).[7][12] 108 T-55Ms were in service at the beginning of the 1992-1993 War in Abhazia.[3] Around 40 T-55s were in service in 1992 and 1995, 48 in 2000, 59 in 2002, 55 in 2004,[5] 2005 and 2006[10] and 23 T-55s and 3 T-54s in 2008 and 2010.[32] -
 Guinea – 8 T-54s were ordered in 1974 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1974 (the vehicles were probably second-hand).[7] 8 T-54s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 8 T-54s are in service.
Guinea – 8 T-54s were ordered in 1974 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1974 (the vehicles were probably second-hand).[7] 8 T-54s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 8 T-54s are in service. -
 Iran – 60 T-54s and 65 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from Libya and delivered in 1981 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Libyan service). 120 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Syria and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7] Iran also bought a number of Tirans from Israel during the Iraq-Iran War.[33] Some vehicles were captured from Iraq during the Iraq–Iran War. 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 1990, 110 in 1995, 500 in 2000 and around 250 in 2002. 540 T-54s, T-55s and Type 59s were in service in 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2008.[5][10][34] 200 T-54s, T-55s and Type 59s have been upgraded to Safir-74 (also known as T-72Z although it should not be confused with Iraqi modernization of the same name) standard (20 could possibly be Sudanese vehicles modernized for Sudan).[7]
Iran – 60 T-54s and 65 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from Libya and delivered in 1981 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Libyan service). 120 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Syria and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7] Iran also bought a number of Tirans from Israel during the Iraq-Iran War.[33] Some vehicles were captured from Iraq during the Iraq–Iran War. 100 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 1990, 110 in 1995, 500 in 2000 and around 250 in 2002. 540 T-54s, T-55s and Type 59s were in service in 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2008.[5][10][34] 200 T-54s, T-55s and Type 59s have been upgraded to Safir-74 (also known as T-72Z although it should not be confused with Iraqi modernization of the same name) standard (20 could possibly be Sudanese vehicles modernized for Sudan).[7] -
 Iraq – 250 T-54s were ordered in 1958 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1959 and 1965. 50 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1968.[7] Between 80 and 120 T-54s were lost during the Yom Kippur War.[3] 300 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975. 50 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1980 from East Germany and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were previously in East German service). 400 T-55s and T-54s were ordered in 1980 from Poland and delivered between 1981 and 1982 (the vehicles were probably previously in Polish service). 250 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from Egypt and delivered between 1981 and 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service). 150 TR-580s were ordered in 1981 from Romania and delivered between 1981 and 1984 (the vehicles were delivered via Egypt). 400 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1982 and 1985 (the vehicles were from the Czechoslovakian production line).[7] Around 200 T-54s and T-55s were upgraded to T-72Z standard (not to be confused with Iranian T-54/55/Type 59 modernization Safir-74 also known as T-72Z).[35] 1,500 T-54s, T-55s and TR-580s were in service with the Iraqi Regular Army in 1990 and 500 in 1995, 2000 and 2002.[36] 406 T-54 and T-55 were in service with Iraqi Regular Army in 2003. All destroyed or scrapped except for 4 T-55s which are now in service with the New Iraqi Army.[36] 76 T-55s are in service with New Iraqi Army since 2004.[37] 4 VT-55As were ordered in 2005 from Hungary and delivered in 2005 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Hungarian service).[7] Iraq also received 2 JVBT-55As in 2005 from Hungary.[11]
Iraq – 250 T-54s were ordered in 1958 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1959 and 1965. 50 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1968.[7] Between 80 and 120 T-54s were lost during the Yom Kippur War.[3] 300 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975. 50 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1980 from East Germany and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were previously in East German service). 400 T-55s and T-54s were ordered in 1980 from Poland and delivered between 1981 and 1982 (the vehicles were probably previously in Polish service). 250 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from Egypt and delivered between 1981 and 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service). 150 TR-580s were ordered in 1981 from Romania and delivered between 1981 and 1984 (the vehicles were delivered via Egypt). 400 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1982 and 1985 (the vehicles were from the Czechoslovakian production line).[7] Around 200 T-54s and T-55s were upgraded to T-72Z standard (not to be confused with Iranian T-54/55/Type 59 modernization Safir-74 also known as T-72Z).[35] 1,500 T-54s, T-55s and TR-580s were in service with the Iraqi Regular Army in 1990 and 500 in 1995, 2000 and 2002.[36] 406 T-54 and T-55 were in service with Iraqi Regular Army in 2003. All destroyed or scrapped except for 4 T-55s which are now in service with the New Iraqi Army.[36] 76 T-55s are in service with New Iraqi Army since 2004.[37] 4 VT-55As were ordered in 2005 from Hungary and delivered in 2005 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Hungarian service).[7] Iraq also received 2 JVBT-55As in 2005 from Hungary.[11] -
 Iraqi Kurdistan – 250-300 T-54s, T-55s and Type-59s captured from former Iraqi army. Not all are operational. 95 in active service as of 2011, and 120 in reserve. The fate of the rest of the captured tanks is unknown.[38]
Iraqi Kurdistan – 250-300 T-54s, T-55s and Type-59s captured from former Iraqi army. Not all are operational. 95 in active service as of 2011, and 120 in reserve. The fate of the rest of the captured tanks is unknown.[38] -
 Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant operates small numbers captured from Syrian and possibly Iraqi stocks.[39]
Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant operates small numbers captured from Syrian and possibly Iraqi stocks.[39] -
 North Korea – 400 T-54s and 250 T-55s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1970. 300 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1974 (the vehicles were probably produced or assembled in North Korea). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1970 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1972 and 1973. 500 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1975 and 1979 (The supplier may have been PRC in which case the vehicles wouldn't be T-55s but Type 59s).[7] 19 T-55s were ordered from Russia and delivered in 1992 (the vehicles were delivered through Belarus).[11][12] There were 1,600 T-54s in service in 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000.[40] There were 3,500 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and Type 59s in early 2001,[19] around 3,500 in early 2003[20] and 2004[5] and more than 3,500 in 2006.[10]
North Korea – 400 T-54s and 250 T-55s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1970. 300 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1974 (the vehicles were probably produced or assembled in North Korea). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1970 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1972 and 1973. 500 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1975 and 1979 (The supplier may have been PRC in which case the vehicles wouldn't be T-55s but Type 59s).[7] 19 T-55s were ordered from Russia and delivered in 1992 (the vehicles were delivered through Belarus).[11][12] There were 1,600 T-54s in service in 1985, 1990, 1995 and 2000.[40] There were 3,500 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and Type 59s in early 2001,[19] around 3,500 in early 2003[20] and 2004[5] and more than 3,500 in 2006.[10] -
 Laos – 15 T-54s and 15 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] 15 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Laos – 15 T-54s and 15 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (aid, the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] 15 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Latvia – 5 T-55AMs Mérida were donated by Poland in 1999. 3 T-55AMs were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][41][42] Currently 3 T-55AM2s are in service.
Latvia – 5 T-55AMs Mérida were donated by Poland in 1999. 3 T-55AMs were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][41][42] Currently 3 T-55AM2s are in service. -
 Lebanon – 180 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1991 from Syria and delivered between 1992 and 1993 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7]
Lebanon – 180 T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1991 from Syria and delivered between 1992 and 1993 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7] -
 Libya – 100 T-54s and 100 T-55s were ordered in 1970 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1971 (the T-54s were probably previously in Soviet service). 150 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1974. 500 T-54s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1976 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 200 T-54s were ordered in 1976 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1976 and 1977 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 2,000 T-55s were ordered in 1976 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978.[7] Around 2,200 T-55s were in service in 1986.[43] 1,600 T-54s and T-55s were in service and in storage in early 2001, 500 in service in early 2003,[41][42] 500 in service and around 1,040 in storage in 2004[5] and 2006.[10] 210 T-54s and T-55s are currently in service.[44]
Libya – 100 T-54s and 100 T-55s were ordered in 1970 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1971 (the T-54s were probably previously in Soviet service). 150 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1974. 500 T-54s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1976 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 200 T-54s were ordered in 1976 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1976 and 1977 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 2,000 T-55s were ordered in 1976 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1977 and 1978.[7] Around 2,200 T-55s were in service in 1986.[43] 1,600 T-54s and T-55s were in service and in storage in early 2001, 500 in service in early 2003,[41][42] 500 in service and around 1,040 in storage in 2004[5] and 2006.[10] 210 T-54s and T-55s are currently in service.[44] -
 Mali – 21 T-34s, T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001,[45] 33 in early 2003.[46] 12 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004[5] and 2006.[10]
Mali – 21 T-34s, T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001,[45] 33 in early 2003.[46] 12 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004[5] and 2006.[10] -
 Mauritania – 35 T-55s were ordered in 1990 from Soviet Union and delivered in 1991 (the vehicles were second-hand). 16 T-55s were ordered in 2001 from Poland and delivered in 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service).[7] 35 T-55s were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][45][46] Currently 35 T-55s are in service.
Mauritania – 35 T-55s were ordered in 1990 from Soviet Union and delivered in 1991 (the vehicles were second-hand). 16 T-55s were ordered in 2001 from Poland and delivered in 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Polish service).[7] 35 T-55s were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][45][46] Currently 35 T-55s are in service. -
 Mongolia – 250 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1961 and 1964. 250 T-55s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1967.[7] 650 T-54s, T-55s and T-62s were in service in early 2001 and 370 in early 2003.[45][46] 370 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 370 T-54s and T-55s are in service.
Mongolia – 250 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1961 and 1964. 250 T-55s were ordered in 1963 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1964 and 1967.[7] 650 T-54s, T-55s and T-62s were in service in early 2001 and 370 in early 2003.[45][46] 370 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 370 T-54s and T-55s are in service. -
 Mozambique – 60 T-54s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 60 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1985 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] Around 60 T-54s were in service in 2005 and more than 60 in 2006.[5][10]
Mozambique – 60 T-54s were ordered in 1981 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1983 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 60 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1983 and 1985 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] Around 60 T-54s were in service in 2005 and more than 60 in 2006.[5][10] -
 Namibia – Up to 20 T-34s and T-55s were in service in early 2001 and a few in early 2003.[47][48] Some T-34s, T-54s and T-55s in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Namibia – Up to 20 T-34s and T-55s were in service in early 2001 and a few in early 2003.[47][48] Some T-34s, T-54s and T-55s in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Nicaragua – 20 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from an unknown supplier and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Libyan service). 66 T-55s were ordered in 1984 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1984 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 20 T-54s were ordered in 1984 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1985 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1986 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1987 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 127 T-55s were in service and in storage in early 2001 and early 2003 and 62 in service and 65 in storage in 2004 and 2006.[5][10][47][48] Currently 31 T-55s are in service.
Nicaragua – 20 T-55s were ordered in 1981 from an unknown supplier and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were possibly previously in Libyan service). 66 T-55s were ordered in 1984 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1984 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 20 T-54s were ordered in 1984 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1985 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 50 T-55s were ordered in 1986 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1987 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service).[7] 127 T-55s were in service and in storage in early 2001 and early 2003 and 62 in service and 65 in storage in 2004 and 2006.[5][10][47][48] Currently 31 T-55s are in service. -
 Nigeria – Between 50 and 100 T-55s were ordered in 1979 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] Around 200 T-55s and Vickers Mk. IIIs were in service in early 2001 and around 250 in early 2003.[47][48] 100 T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 50 T-55s are in service and are 50% serviceable.[49]
Nigeria – Between 50 and 100 T-55s were ordered in 1979 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service).[7] Around 200 T-55s and Vickers Mk. IIIs were in service in early 2001 and around 250 in early 2003.[47][48] 100 T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] Currently 50 T-55s are in service and are 50% serviceable.[49] -
 Federal State of Novorossiya – 1 T-54 was acquired from an open-air museum in July 2014, with hopes of restoring the tank to combat-ready status.[50] It is unknown if the tank is currently operational.
Federal State of Novorossiya – 1 T-54 was acquired from an open-air museum in July 2014, with hopes of restoring the tank to combat-ready status.[50] It is unknown if the tank is currently operational. -
 Peru – 24 T-54s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1973. 250 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975.[7] At peak there were 375 T-54s and T-55s in service. 300 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001[51] and 275 (around 200 were serviceable in 2005[5] and 2006[10]) in service in early 2003,[52] 2004[5] and 2006.[10] 300 T-54s and T-55s as well as an unknown amount of T-54/55-based ARVes are currently in service.[53]
Peru – 24 T-54s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1973. 250 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1974 and 1975.[7] At peak there were 375 T-54s and T-55s in service. 300 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001[51] and 275 (around 200 were serviceable in 2005[5] and 2006[10]) in service in early 2003,[52] 2004[5] and 2006.[10] 300 T-54s and T-55s as well as an unknown amount of T-54/55-based ARVes are currently in service.[53] -
 Romania – 850 T-55s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1977. 400 TR-580s ordered in 1975 and produced between 1977 and 1981. 150 TR-580s were produced for Iraq.[7] At least 632 TR-85s were produced. Romania also acquired a number of T-54s which are now in reserve.[54] 398 TR-580s and 632 TR-85s were in service with the Romanian Army in 1993, around 88 TR-580s in early 1999, 717 T-55s, 314 TR-85M1s and 227 TR-580s in early 2003[55] and 2004,[5] 268 T-55s, 43 TR-580s and 157 TR-85M1s in 2006.[10] According to the UN register of conventional arms, Romanian Armed Forces operated 710 T-55s, 227 TR-580s, 312 TR-85s in 2006, 750 T-55s, 226 TR-580s and 269 TR-85s in 2007 and 748 T-55s, 226 TR-580s and 265 TR-85s.[12] 120 TR-580s were in service with the Romanian Naval Infantry in early 2001[56] and early 2003.[55]
Romania – 850 T-55s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1977. 400 TR-580s ordered in 1975 and produced between 1977 and 1981. 150 TR-580s were produced for Iraq.[7] At least 632 TR-85s were produced. Romania also acquired a number of T-54s which are now in reserve.[54] 398 TR-580s and 632 TR-85s were in service with the Romanian Army in 1993, around 88 TR-580s in early 1999, 717 T-55s, 314 TR-85M1s and 227 TR-580s in early 2003[55] and 2004,[5] 268 T-55s, 43 TR-580s and 157 TR-85M1s in 2006.[10] According to the UN register of conventional arms, Romanian Armed Forces operated 710 T-55s, 227 TR-580s, 312 TR-85s in 2006, 750 T-55s, 226 TR-580s and 269 TR-85s in 2007 and 748 T-55s, 226 TR-580s and 265 TR-85s.[12] 120 TR-580s were in service with the Romanian Naval Infantry in early 2001[56] and early 2003.[55] -
 Rwanda – 12 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001,[56] 30 in early 2003,[55] 24 in 2005[5] and 2006.[10]
Rwanda – 12 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2001,[56] 30 in early 2003,[55] 24 in 2005[5] and 2006.[10] -
 Sahrawi Republic – 50.[57] Some of them captured to the Moroccan Army during the Western Sahara War.
Sahrawi Republic – 50.[57] Some of them captured to the Moroccan Army during the Western Sahara War. -
 Somaliland – 85
Somaliland – 85 -
 South Ossetia – At peak there were 12 T-55s and 75 T-72s in service.[4] 15 T-55s and T-72s were in service before the 2008 South Ossetia war.[6][58][59] All T-55 in reserve since 2011.
South Ossetia – At peak there were 12 T-55s and 75 T-72s in service.[4] 15 T-55s and T-72s were in service before the 2008 South Ossetia war.[6][58][59] All T-55 in reserve since 2011. -
 Sri Lanka – 27 T-55s were ordered in 1991 from Czechoslovakia and delivered in 1991 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovak service). 18 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1995 from Czech Republic with 15 being delivered in 1996[12] and 3 in 1997[12] (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 2 MT-55s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and delivered in 2001 (aid against the LTTE rebels, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 36 T-55AM2s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and with 11 being delivered in 2000[12] and 25 in 2001[12] (possibly aid against the LTTE rebels, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 16 VT-55s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and delivered between 2002 and 2003 (aid against the LTTE rebels, delivered via and possibly modernized in Slovakia, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service).[7] 25 T-55s were in service in early 2001[60] and 65 in early 2003.[30] 62 T-55As and T-55AM2s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Sri Lanka – 27 T-55s were ordered in 1991 from Czechoslovakia and delivered in 1991 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovak service). 18 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1995 from Czech Republic with 15 being delivered in 1996[12] and 3 in 1997[12] (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 2 MT-55s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and delivered in 2001 (aid against the LTTE rebels, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 36 T-55AM2s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and with 11 being delivered in 2000[12] and 25 in 2001[12] (possibly aid against the LTTE rebels, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service). 16 VT-55s were ordered in 2000 from Czech Republic and delivered between 2002 and 2003 (aid against the LTTE rebels, delivered via and possibly modernized in Slovakia, the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service).[7] 25 T-55s were in service in early 2001[60] and 65 in early 2003.[30] 62 T-55As and T-55AM2s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]  Serbia – 510 T-55 in 2006 and in 2015 between 240 and 260 in reserve.
Serbia – 510 T-55 in 2006 and in 2015 between 240 and 260 in reserve.-
 Sudan – 50 T-54s and 50 T-55s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1970. 9 T-55s were ordered in 1996 from Belarus and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 20 T-55AM2BPs were ordered in 1998 from Poland and delivered in 1999 (these were the first batch of 50 originally sold to Yemen where it was illegally diverted to Sudan after which the delivery of the remaining 30 was put on hold, the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 60 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 1999 from Belarus with 40 being delivered in 1999[11] and 20 in 2001[11] (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 20 T-72Zs ordered in 2005 from Iran and delivered in 2006 (these could possibly be Sudanese T-54s, T-55s or Type 59s modernized to the T-72Z standard).[7] 170 T-55s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001,[61] 200 in early 2003.[62] 200 T-54s and T-55s in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Sudan – 50 T-54s and 50 T-55s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1970. 9 T-55s were ordered in 1996 from Belarus and delivered in 1996 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 20 T-55AM2BPs were ordered in 1998 from Poland and delivered in 1999 (these were the first batch of 50 originally sold to Yemen where it was illegally diverted to Sudan after which the delivery of the remaining 30 was put on hold, the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 60 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 1999 from Belarus with 40 being delivered in 1999[11] and 20 in 2001[11] (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service). 20 T-72Zs ordered in 2005 from Iran and delivered in 2006 (these could possibly be Sudanese T-54s, T-55s or Type 59s modernized to the T-72Z standard).[7] 170 T-55s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001,[61] 200 in early 2003.[62] 200 T-54s and T-55s in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Sudan People's Liberation Army – Some captured T-54s and T-55s.[5]
Sudan People's Liberation Army – Some captured T-54s and T-55s.[5] -
 Syria – 150 T-54s were ordered in 1956 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1957 and 1958. 300 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1972 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 75 T-55s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1968. 300 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1972. 400 T-54s and 400 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1978 (T-54s and probably T-55s were previously in Soviet service). 600 T-55s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1981.[7] 2,050 T-54s and T-55s were in service and in storage in 1990, 2,100 in 1995, 2,150 in 2000, 2,000 in 2001, 2003 and around 2,000 in 2005.[63]
Syria – 150 T-54s were ordered in 1956 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1957 and 1958. 300 T-54s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1972 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 75 T-55s were ordered in 1967 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1968. 300 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1969 and 1972. 400 T-54s and 400 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1978 (T-54s and probably T-55s were previously in Soviet service). 600 T-55s were ordered in 1978 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1979 and 1981.[7] 2,050 T-54s and T-55s were in service and in storage in 1990, 2,100 in 1995, 2,150 in 2000, 2,000 in 2001, 2003 and around 2,000 in 2005.[63] -
 Tanzania – 32 T-54s were ordered in 1979 from East Germany and delivered between 1979 and 1980 (the vehicles were probably previously in East German service).[7] 65 T-54s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001[64] and 45 in early 2003.[62] 30 T-54s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Tanzania – 32 T-54s were ordered in 1979 from East Germany and delivered between 1979 and 1980 (the vehicles were probably previously in East German service).[7] 65 T-54s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001[64] and 45 in early 2003.[62] 30 T-54s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Togo – 2 T-54s and 2 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Egypt and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were second-hand).[7] 1 T-54 and 1 T-55 were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][64][62]
Togo – 2 T-54s and 2 T-55s were ordered in 1982 from Egypt and delivered in 1982 (the vehicles were second-hand).[7] 1 T-54 and 1 T-55 were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][64][62] -
 Uganda – 16 T-54s were ordered in 1974 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service). 60 T-55s were ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1995 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 62 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 28 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, part of a $35 m deal for 90 vehicles including some bought by Bulgaria from Ukraine and possibly Romania for export to Uganda). 10 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 2000 from Belarus and delivered in 2000 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service).[7] 140 T-54s and T-55s and PT-76s were in service in early 2001.[65] 180 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003,[66] 152 in 2005 and 2006.[5][10]
Uganda – 16 T-54s were ordered in 1974 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (the vehicles were probably previously in Soviet service). 60 T-55s were ordered in 1994 from Ukraine and delivered in 1995 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 62 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Ukraine and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Ukrainian service). 28 T-55s were ordered in 1998 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1998 (the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, part of a $35 m deal for 90 vehicles including some bought by Bulgaria from Ukraine and possibly Romania for export to Uganda). 10 T-55Ms[11] were ordered in 2000 from Belarus and delivered in 2000 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet and later Belorussian service).[7] 140 T-54s and T-55s and PT-76s were in service in early 2001.[65] 180 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003,[66] 152 in 2005 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Uruguay – 15 Tiran-4Shes and Tiran-5Shes were ordered from Israel in 1997 and delivered the same year (the vehicles were previously in Israeli service).[7] 15 Tiran-4Shes and Tiran-5Shs were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][65][66]
Uruguay – 15 Tiran-4Shes and Tiran-5Shes were ordered from Israel in 1997 and delivered the same year (the vehicles were previously in Israeli service).[7] 15 Tiran-4Shes and Tiran-5Shs were in service in early 2001, early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][65][66] -
 Vietnam – 1,939 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s, PT-76s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001.[67] 850 T-54s and T-55s and 350 Type-59 were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][68]
Vietnam – 1,939 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s, PT-76s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001.[67] 850 T-54s and T-55s and 350 Type-59 were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][68] -
 Uzbekistan – 80
Uzbekistan – 80 -
 Yemen – 6 T-55s were received from Bulgaria in 1994.[11] 97 T-55s and 35 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1999 from Czech Republic with T-55s delivered in 2000 and T-55AM2s in 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service and were possibly modernized prior to being delivered).[7][11][12] 990 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and M60s were in service in early 2001.[69] 450 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][70]
Yemen – 6 T-55s were received from Bulgaria in 1994.[11] 97 T-55s and 35 T-55AM2s were ordered in 1999 from Czech Republic with T-55s delivered in 2000 and T-55AM2s in 2002 (the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian and later Czech service and were possibly modernized prior to being delivered).[7][11][12] 990 T-34s, T-54s, T-55s, T-62s and M60s were in service in early 2001.[69] 450 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][70] -
 Zambia – 5 T-54s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1976. 20 T-55s were ordered in 1980 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (part of a $72–100M deal).[7] 60 T-55s, PT-76s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001 and early 2003.[71][72] 10 T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10]
Zambia – 5 T-54s were ordered in 1975 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1976. 20 T-55s were ordered in 1980 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1981 (part of a $72–100M deal).[7] 60 T-55s, PT-76s and Type 59s were in service in early 2001 and early 2003.[71][72] 10 T-55s were in service in 2004 and 2006.[5][10] -
 Zimbabwe – 20 T-54 tanks received from USSR in September 1984.[73]
Zimbabwe – 20 T-54 tanks received from USSR in September 1984.[73]
Former operators
-
 Albania – 75 T-54s and 300 T-55s operated by Albania at one time along with 750 Chinese Type 59's, today all have been phased out of service.
Albania – 75 T-54s and 300 T-55s operated by Albania at one time along with 750 Chinese Type 59's, today all have been phased out of service. -
 Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula – operated small numbers of T-55's captured from Yemeni stocks.[74]
Al Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula – operated small numbers of T-55's captured from Yemeni stocks.[74] -
 Amal Movement – 50 T-54s were ordered in 1985-86 from Syria and delivered in 1985-86 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7]
Amal Movement – 50 T-54s were ordered in 1985-86 from Syria and delivered in 1985-86 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Syrian service).[7] -
 Bulgaria – 900 T-54s were ordered in 1953 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1954 and 1959. 900 T-55s were ordered in 1961 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1962 and 1970.[7] 1,475 T-54s, T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[15] 1,042 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][16] Currently up to 430 are in reserve status. Some are used for basic tank driver training.
Bulgaria – 900 T-54s were ordered in 1953 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1954 and 1959. 900 T-55s were ordered in 1961 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1962 and 1970.[7] 1,475 T-54s, T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[15] 1,042 T-54s and T-55s were in service in early 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][16] Currently up to 430 are in reserve status. Some are used for basic tank driver training. -
 Croatia – The majority of the Croatian T-55s were captured from the Yugoslav army forces.[75] Around 209 T-55s were in service in 1998 and 222 in 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][76]
Croatia – The majority of the Croatian T-55s were captured from the Yugoslav army forces.[75] Around 209 T-55s were in service in 1998 and 222 in 2003, 2004 and 2006.[5][10][76] -
 Chile – At least 4 captured Egyptian T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1978 from Israel and delivered in 1979, in order to train Chilean crews to operate captured Peruvian T-55s.[77]
Chile – At least 4 captured Egyptian T-54s and T-55s were ordered in 1978 from Israel and delivered in 1979, in order to train Chilean crews to operate captured Peruvian T-55s.[77] -
 Czech Republic – At least 296 T-54s and T-55s, 2 MT-55s, 25 VT-55s were inherited from Czechoslovakia.[7][12] 792 T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[22] According to the UN register of conventional arms Czech Armed Forces operated 948 T-55s and T-72s in 1997, 938 in 1998, 792 in 1999 and 652 as of 1 January 2001.[12] Last vehicles were withdrawn from service in early years of the 2000s (decade).
Czech Republic – At least 296 T-54s and T-55s, 2 MT-55s, 25 VT-55s were inherited from Czechoslovakia.[7][12] 792 T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[22] According to the UN register of conventional arms Czech Armed Forces operated 948 T-55s and T-72s in 1997, 938 in 1998, 792 in 1999 and 652 as of 1 January 2001.[12] Last vehicles were withdrawn from service in early years of the 2000s (decade). -
 Czechoslovakia – 1,800 T-54s were ordered in 1957 and produced under license between 1958 and 1963. 1,700 T-55s were ordered in 1963 and produced under license between 1964 and 1973.[7] Overall 2,700 T-54s were produced under license between 1957 and 1966 and 8,300 T-55s and T-55As between 1964 and 1983 (T-55A was probably produced since 1968) (most for export). Passed on to successor states.
Czechoslovakia – 1,800 T-54s were ordered in 1957 and produced under license between 1958 and 1963. 1,700 T-55s were ordered in 1963 and produced under license between 1964 and 1973.[7] Overall 2,700 T-54s were produced under license between 1957 and 1966 and 8,300 T-55s and T-55As between 1964 and 1983 (T-55A was probably produced since 1968) (most for export). Passed on to successor states. -
 Finland – 50 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1960 and 1961. 70 T-55s were ordered in 1965 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1965 and 1967. An additional 10 T-55AMs were bought from Poland and converted into T-55AM-Marksman SPAAGs (the turrets were delivered in two batches, the first one was ordered in 1988 and delivered between 1990 and 1991 and the second one was ordered in 1992 and delivered in 1993).[7] 230 T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[78] 74 T-55s were in service in early 2003.[9] 33 T-54s and 74 T-55Ms were in storage in 2004[79] and 74 T-55Ms in 2005.[5] 56 T-55 turrets were purchased from the Soviet Union in the late 1960s and emplaced in coastal fortifications as 100 56 TK light coastal guns. The last of these were deactivated in 2012.
Finland – 50 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1960 and 1961. 70 T-55s were ordered in 1965 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1965 and 1967. An additional 10 T-55AMs were bought from Poland and converted into T-55AM-Marksman SPAAGs (the turrets were delivered in two batches, the first one was ordered in 1988 and delivered between 1990 and 1991 and the second one was ordered in 1992 and delivered in 1993).[7] 230 T-55s and T-72s were in service in early 2001.[78] 74 T-55s were in service in early 2003.[9] 33 T-54s and 74 T-55Ms were in storage in 2004[79] and 74 T-55Ms in 2005.[5] 56 T-55 turrets were purchased from the Soviet Union in the late 1960s and emplaced in coastal fortifications as 100 56 TK light coastal guns. The last of these were deactivated in 2012. -
 East Germany – 202 T-54s were ordered in 1956 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1956 and 1957. 488 T-54As and T-54AMs were ordered from Poland and delivered between 1959 and 1964 1766 T-55s and T-55As were ordered in 1964 from the Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1964 and 1980. 333 T-55s and T-55A(P)s were ordered from Poland and delivered between 1965 and 1973. 362 VT-55s were ordered in 1964 from the Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1965 and 1969.[7] Passed on to the unified German state.
East Germany – 202 T-54s were ordered in 1956 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1956 and 1957. 488 T-54As and T-54AMs were ordered from Poland and delivered between 1959 and 1964 1766 T-55s and T-55As were ordered in 1964 from the Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1964 and 1980. 333 T-55s and T-55A(P)s were ordered from Poland and delivered between 1965 and 1973. 362 VT-55s were ordered in 1964 from the Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1965 and 1969.[7] Passed on to the unified German state. -
 West Germany/
West Germany/ Germany – taken from GDR's army, all scrapped, sold to other countries or given to museums.
Germany – taken from GDR's army, all scrapped, sold to other countries or given to museums. -
 Ecuador – 3 T-55s were in service in early 2001,[31] 30 in early 2003,[30] more than 30 in 2004 (possibly non in operational service as of 2005)[5] and more than 30 in storage in 2006.[10]
Ecuador – 3 T-55s were in service in early 2001,[31] 30 in early 2003,[30] more than 30 in 2004 (possibly non in operational service as of 2005)[5] and more than 30 in storage in 2006.[10] - Hezbollah – Ti-67s Captured from the South Lebanon Army in 2000.
-
 Hungary
Hungary -
 India – 300 T-54s were ordered in 1964 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1965 and 1967. 225 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1968 and 1971. 650 T-55s were ordered in 1971 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1971 and 1974.[7] 274 T-54s, 44 T-55s and 7 T-55AKs were ordered in 1970 from Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1970 and 1971 (some of the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian service). 300 T-55s were ordered in 1971 from Poland and delivered in 1971 (some of the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 800 T-55s and modernized T-55s were in service in 1990, around 750 in 1995, around 700 in 2000, early 2001[69] and early 2003,[70] 450 in 2002, 2005 and 2008. The number of T-55s and modernized T-55s in service is to stay at 450 in 2010 and to be reduced to 220 by 2015.[80] There were around 550 T-55s in active service and around 200 in storage in 1999.[81] In 2004, Indian Army possessed a total of 700 T-55s, 450 of which were in operational service.[5] in 2006 Indian Army possessed 715 T-55s, modernized with night-fighting equipment and new fire control systems, out of which around 67 were in reserve.[10] In May 2011, the last of T-55s were retired from active service and moved to reserve storage.[82]
India – 300 T-54s were ordered in 1964 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1965 and 1967. 225 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1968 and 1971. 650 T-55s were ordered in 1971 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1971 and 1974.[7] 274 T-54s, 44 T-55s and 7 T-55AKs were ordered in 1970 from Czechoslovakia and delivered between 1970 and 1971 (some of the vehicles were previously in Czechoslovakian service). 300 T-55s were ordered in 1971 from Poland and delivered in 1971 (some of the vehicles were previously in Polish service). 800 T-55s and modernized T-55s were in service in 1990, around 750 in 1995, around 700 in 2000, early 2001[69] and early 2003,[70] 450 in 2002, 2005 and 2008. The number of T-55s and modernized T-55s in service is to stay at 450 in 2010 and to be reduced to 220 by 2015.[80] There were around 550 T-55s in active service and around 200 in storage in 1999.[81] In 2004, Indian Army possessed a total of 700 T-55s, 450 of which were in operational service.[5] in 2006 Indian Army possessed 715 T-55s, modernized with night-fighting equipment and new fire control systems, out of which around 67 were in reserve.[10] In May 2011, the last of T-55s were retired from active service and moved to reserve storage.[82] -
 Israel – Israeli army captured during the Six-Day War, repaired, modernized and put into service around 200 T-54s, T-55s and PT-76s. T-54s and T-55s were modernized to Ti-67 standard prior to the Yom Kippur War.[3] During that conflict Israel captured additional T-54s and T-55s. Ti-67s were withdrawn from active service at the end of the 1980s. Some were sold and some were converted into Achzarit APCs.[33][83] However some T-54s, T-55s and Ti-67s are still in possession of the Israeli Army, possibly in reserve or in storage. Israeli Army had 1,500 T-54s and T-55s in 1990, 300 in 1995, 200 in early 2001[69] and early 2003[70] and 114 in 2004,[5] 126 T-54s, T-55s and Tiran 6s in 2006[10] and 2008 and 488 Ti-67s in 1990, 300 in 1995, 200 in 2000, 2001 and 2002 and 261 in 2006 and 2008. The Achzarits are in service with the Israeli Army since at least 1995. There were 270 Achzarits in service in 2004, 276 in 2006 and 2008.[5][10][84]
Israel – Israeli army captured during the Six-Day War, repaired, modernized and put into service around 200 T-54s, T-55s and PT-76s. T-54s and T-55s were modernized to Ti-67 standard prior to the Yom Kippur War.[3] During that conflict Israel captured additional T-54s and T-55s. Ti-67s were withdrawn from active service at the end of the 1980s. Some were sold and some were converted into Achzarit APCs.[33][83] However some T-54s, T-55s and Ti-67s are still in possession of the Israeli Army, possibly in reserve or in storage. Israeli Army had 1,500 T-54s and T-55s in 1990, 300 in 1995, 200 in early 2001[69] and early 2003[70] and 114 in 2004,[5] 126 T-54s, T-55s and Tiran 6s in 2006[10] and 2008 and 488 Ti-67s in 1990, 300 in 1995, 200 in 2000, 2001 and 2002 and 261 in 2006 and 2008. The Achzarits are in service with the Israeli Army since at least 1995. There were 270 Achzarits in service in 2004, 276 in 2006 and 2008.[5][10][84] -
 LTTE – Operated small numbers of T-55 tanks captured from Sri Lankan stocks during the Sri Lankan Civil War.[85]
LTTE – Operated small numbers of T-55 tanks captured from Sri Lankan stocks during the Sri Lankan Civil War.[85] -
 Macedonia – Between 58 and 114 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, up to 56 of the vehicles were bought for spares). 36 T-55AM-2s were ordered in 1999 and delivered in 1999 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service).[7][11] 94 T-55s were in service in early 2001,[45] 125 T-55s and T-72s in early 2003,[46] 30 T-55As in 2004[5] and 2006.[10]
Macedonia – Between 58 and 114 T-55s were ordered in 1999 from Bulgaria and delivered in 1999 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service, up to 56 of the vehicles were bought for spares). 36 T-55AM-2s were ordered in 1999 and delivered in 1999 (aid, the vehicles were previously in Bulgarian service).[7][11] 94 T-55s were in service in early 2001,[45] 125 T-55s and T-72s in early 2003,[46] 30 T-55As in 2004[5] and 2006.[10] -
 Montenegro – 61 T-55s Scrapped.[86]
Montenegro – 61 T-55s Scrapped.[86] -
 Morocco – 40 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1962. 80 T-54s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1968 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line).[7]
Morocco – 40 T-54s were ordered in 1960 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1962. 80 T-54s were ordered in 1966 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1967 and 1968 (the vehicles were probably from Czechoslovakian production line).[7] -
 Pakistan – 100 T-54s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1969 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1968.[7] As of 2010, 54 T-54/55 tanks in Reserve.[87]
Pakistan – 100 T-54s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1969 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 100 T-55s were ordered in 1968 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1968.[7] As of 2010, 54 T-54/55 tanks in Reserve.[87] -
 Poland – 3,000 T-54, T-54A, T-54AD and T-54AM produced between 1956 and 1964. 7,000 T-55, T-55L, T-55AD-1 and T-55AD-2 produced between 1964 and 1979. Some T-54A upgraded to T-55 standard. 200 T-54 tanks have been upgraded to T-55LD in 1975, 10 of which were later sold to Libya. In 1980 Ludowe Wojsko Polskie (LWP) operated 1,207 T-55L, T-55LD, T-55AD-1 and T-55AD-2, 146 T-55, 986 T-55U and 340 T-54, T-54A, T-54AD and T-54AM. Eventually almost all T-54 and T-55 tanks have been upgraded to T-55AM "Merida" standard (There are some not upgraded ones in the museums). Last 839 were withdrawn from service in 2002. All Polish T-54 and T-55 that were withdrawn from service were either used as shooting targets at proving grounds, sold to other countries or given to the museums.
Poland – 3,000 T-54, T-54A, T-54AD and T-54AM produced between 1956 and 1964. 7,000 T-55, T-55L, T-55AD-1 and T-55AD-2 produced between 1964 and 1979. Some T-54A upgraded to T-55 standard. 200 T-54 tanks have been upgraded to T-55LD in 1975, 10 of which were later sold to Libya. In 1980 Ludowe Wojsko Polskie (LWP) operated 1,207 T-55L, T-55LD, T-55AD-1 and T-55AD-2, 146 T-55, 986 T-55U and 340 T-54, T-54A, T-54AD and T-54AM. Eventually almost all T-54 and T-55 tanks have been upgraded to T-55AM "Merida" standard (There are some not upgraded ones in the museums). Last 839 were withdrawn from service in 2002. All Polish T-54 and T-55 that were withdrawn from service were either used as shooting targets at proving grounds, sold to other countries or given to the museums. -
 Republika Srpska – 72 T-55s were in service and in storage in 2005.[5] Passed on to the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Republika Srpska – 72 T-55s were in service and in storage in 2005.[5] Passed on to the Armed Forces of Bosnia and Herzegovina. -
 Rhodesia – 8 T-55LD tanks given by the Republic of South Africa, together with SADF advisers for the purpose of training the Rhodesian crews. It is unknown whether these tanks were passed on to the successor state or destroyed during the Rhodesian Bush War.[35]
Rhodesia – 8 T-55LD tanks given by the Republic of South Africa, together with SADF advisers for the purpose of training the Rhodesian crews. It is unknown whether these tanks were passed on to the successor state or destroyed during the Rhodesian Bush War.[35] -
 Russia – At least 3,000 inherited from the Soviet Union. 412 T-54s and T-55s were in active service in 1995 and 20 in 2000. 1,200 T-54s and T-55s were in storage in 2000, 2005 and 2008.[5][10][88] As of 2013 there are 100 T-55s in reserve and less than 500 in storage, however those in storage may have been scrapped already.[89]
Russia – At least 3,000 inherited from the Soviet Union. 412 T-54s and T-55s were in active service in 1995 and 20 in 2000. 1,200 T-54s and T-55s were in storage in 2000, 2005 and 2008.[5][10][88] As of 2013 there are 100 T-55s in reserve and less than 500 in storage, however those in storage may have been scrapped already.[89] -
 Slovakia – At least 206 were inherited from Czechoslovakia.[90] 1 T-55AM2B received from Czech Republic in 2000. 1 T-55AM2 received from Czech Republic in 2001.[12] 2 T-55AM2s received from Czech Republic in 2005.[11][12] 275 T-55s and T-72s were in service in 1999.[12] 3 T-55s were in service in early 2001.[61]
Slovakia – At least 206 were inherited from Czechoslovakia.[90] 1 T-55AM2B received from Czech Republic in 2000. 1 T-55AM2 received from Czech Republic in 2001.[12] 2 T-55AM2s received from Czech Republic in 2005.[11][12] 275 T-55s and T-72s were in service in 1999.[12] 3 T-55s were in service in early 2001.[61] -
 Slovenia – 46 T-55s (14 were in storage) and 12 M-55Ss and M-55S-1s were in service in 1998.[91] Overall 30 T-55s were modernized to the M-55S/M-55S-1 standard.[35] 30 M-55S-1s were in service in early 2003,[62] 2004[5] and 2006.[10] Currently 30 M-55S-1s are in service and are in the process of being withdrawn.
Slovenia – 46 T-55s (14 were in storage) and 12 M-55Ss and M-55S-1s were in service in 1998.[91] Overall 30 T-55s were modernized to the M-55S/M-55S-1 standard.[35] 30 M-55S-1s were in service in early 2003,[62] 2004[5] and 2006.[10] Currently 30 M-55S-1s are in service and are in the process of being withdrawn. -
 Somalia – 100 T-54s were ordered in 1972 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1974. 50 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 35 T-54s were ordered in 1977 from Egypt and delivered in 1977 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service).
Somalia – 100 T-54s were ordered in 1972 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1974. 50 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered in 1975 (the vehicles were previously in Soviet service). 35 T-54s were ordered in 1977 from Egypt and delivered in 1977 (the vehicles were previously in Egyptian service). -
 Soviet Union – 35,000 T-54-1 (T-54 Model 1946), T-54-2 (T-54 Model 1949), T-54 (T-54-3 or T-54 Model 1951), T-54A, T-54B, T-54AK1, T-54AK2, T-54BK1 and T-54BK2. produced between 1946 and 1958. 27,500 T-55, T-55A, T-55K1, T-55K2, T-55K3, T-55AK1, T-55AK2 and T-55AK3 produced between 1955 and 1981. Passed on to successor states.
Soviet Union – 35,000 T-54-1 (T-54 Model 1946), T-54-2 (T-54 Model 1949), T-54 (T-54-3 or T-54 Model 1951), T-54A, T-54B, T-54AK1, T-54AK2, T-54BK1 and T-54BK2. produced between 1946 and 1958. 27,500 T-55, T-55A, T-55K1, T-55K2, T-55K3, T-55AK1, T-55AK2 and T-55AK3 produced between 1955 and 1981. Passed on to successor states. -
 North Vietnam – 400 T-54s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1972 (aid). 600 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1975 (aid).[7] Passed on to the successor state.
North Vietnam – 400 T-54s were ordered in 1969 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1970 and 1972 (aid). 600 T-55s were ordered in 1973 from the Soviet Union and delivered between 1973 and 1975 (aid).[7] Passed on to the successor state. -
 Ukraine – At least 700 T-54s and T-55s were originally inherited from the Soviet Union.[92] 680 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 1995 and 149 in 2000.[93] 112 T-55s were in service in 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2010.[5][10][93] There's also an unknown amount of IMRs and MTP-3s in service.[92]
Ukraine – At least 700 T-54s and T-55s were originally inherited from the Soviet Union.[92] 680 T-54s and T-55s were in service in 1995 and 149 in 2000.[93] 112 T-55s were in service in 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2010.[5][10][93] There's also an unknown amount of IMRs and MTP-3s in service.[92] -
 Yugoslavia – passed on to successor states.
Yugoslavia – passed on to successor states.
Evaluation-only operators
-
 South Africa – 10 Polish-built T-55LD tanks (part of a batch of 200 T-54s rebuilt in 1975) seized from a French ship, the Astor, which had been transporting a heavy weapons consignment from Libya for Idi Amin in Uganda. Amin's regime collapsed on the day that the ship docked in Mombasa, and it was redirected to Angola. The ship called in to Durban where the cargo was seized. Two T-55LD tanks have been kept by the South Africans for evaluation while eight were given to Rhodesia, together with SADF advisers for the purpose of training Rhodesian crews. The rumor was spread that the tanks had been captured in Mozambique in order to obscure South Africa's part in the deal.[35]
South Africa – 10 Polish-built T-55LD tanks (part of a batch of 200 T-54s rebuilt in 1975) seized from a French ship, the Astor, which had been transporting a heavy weapons consignment from Libya for Idi Amin in Uganda. Amin's regime collapsed on the day that the ship docked in Mombasa, and it was redirected to Angola. The ship called in to Durban where the cargo was seized. Two T-55LD tanks have been kept by the South Africans for evaluation while eight were given to Rhodesia, together with SADF advisers for the purpose of training Rhodesian crews. The rumor was spread that the tanks had been captured in Mozambique in order to obscure South Africa's part in the deal.[35]
Models and variants

Models
T-54


- T-54-1 (Ob'yekt 137) or T-54 Model 1946 – Produced 1946–1948. With streamlined turret and wide gun mantlet, similar to T-44, new V-54 engine, unstabilized D-10T 100 mm main gun, and two SG-43 machine guns in bins on the fenders.[94] Only a small number was built for trials that were a fiasco; as a result, the production of the T-54 series was halted until the implementation of modifications.[95]
- T-54-2 (Ob'yekt 137R) or T-54 Model 1949 – Produced 1949–1952. It incorporated a number of improvements to the turret as well a wider track (580 mm) and modernized transmission. The turret is dome-shaped with flat sides inspired by the IS-3 heavy tanks, similar to later T-54s but with a distinctive overhang at the rear. The hull machine gun replaced the fender bin mounted ones. It also had a shorter bustle.[94][95][96]
- T-54-3 (Ob'yekt 137Sh) or T-54 Model 1951 – Produced 1952–1954, in Poland 1956–1964. Adopted the familiar, fully egg-shaped turret and new TSh-2-22 telescopic gunner's sight instead of the TSh-20.[94][95] Also early T-54 lacked a snorkel. The tank is also able to use its engine exhaust smoke system to create smokescreen by injecting vaporized diesel fuel onto the exhaust system. This feature was continued throughout the entire T-54/T-55 series and was used in the T-62 series.[35][97]
- T-54A (Ob'yekt 137G)[94][98] - Produced 1955–1957, in Poland 1956–1964, in Czechoslovakia 1957–1966, and in China as the Type 59. Added STP-1 "Gorizont" vertical-plane gun stabilizer to D-10T tank gun and this new weapon was designated D-10TG. Originally had a small muzzle counter-weight, which was later replaced with a fume extractor.[96] Also introduced were the OPVT wading snorkel, the TSh-2A-22 telescopic sight, the TVN-1 infrared driver's periscope and IR headlight, the new R-113 radio, a multi-stage engine air filter and radiator controls for improved engine performance, an electrical oil pump, bilge pump, automatic fire extinguisher and extra fuel tanks.[35]
- T-54B (Ob'yekt 137G2)[95][98][99] - Produced from 1957 to 1958. It is armed with the D-10T2S tank gun with STP-2 "Tsyklon" 2-plane stabilization.[96] From 1959, infrared night-fighting equipment was added: L-2 "Luna" infrared searchlight, TPN-1-22-11 IR gunner's day-and-night sight, OU-3 IR commander's searchlight. NATO code: T-54(M).[35]
- T-54A (Ob'yekt 137G)[94][98] - Produced 1955–1957, in Poland 1956–1964, in Czechoslovakia 1957–1966, and in China as the Type 59. Added STP-1 "Gorizont" vertical-plane gun stabilizer to D-10T tank gun and this new weapon was designated D-10TG. Originally had a small muzzle counter-weight, which was later replaced with a fume extractor.[96] Also introduced were the OPVT wading snorkel, the TSh-2A-22 telescopic sight, the TVN-1 infrared driver's periscope and IR headlight, the new R-113 radio, a multi-stage engine air filter and radiator controls for improved engine performance, an electrical oil pump, bilge pump, automatic fire extinguisher and extra fuel tanks.[35]
- T-54-3 (Ob'yekt 137Sh) or T-54 Model 1951 – Produced 1952–1954, in Poland 1956–1964. Adopted the familiar, fully egg-shaped turret and new TSh-2-22 telescopic gunner's sight instead of the TSh-20.[94][95] Also early T-54 lacked a snorkel. The tank is also able to use its engine exhaust smoke system to create smokescreen by injecting vaporized diesel fuel onto the exhaust system. This feature was continued throughout the entire T-54/T-55 series and was used in the T-62 series.[35][97]
- T-54-2 (Ob'yekt 137R) or T-54 Model 1949 – Produced 1949–1952. It incorporated a number of improvements to the turret as well a wider track (580 mm) and modernized transmission. The turret is dome-shaped with flat sides inspired by the IS-3 heavy tanks, similar to later T-54s but with a distinctive overhang at the rear. The hull machine gun replaced the fender bin mounted ones. It also had a shorter bustle.[94][95][96]
- T-54K1, T-54K2, T-54AK1, T-54AK2, T-54BK1, T-54BK2, T-54MK1, T-54MK2 were command tanks corresponding to the main production models, with extra communications equipment at the expense of 5 tank rounds.[99] K1 version had a second R-113 (or R-123) radio for company commanders, K2 version had 10 m semi-telescoping antenna mast, for battalion and regimental commanders, and regimental chiefs-of-staff.[35] They were also equipped with the TNA-2 navigational system and AB-1-P/30 reloading device.[96]
T-55

- T-55 (Ob'yekt 155)[100] - Produced 1958–1963,[101] in Poland 1958–1964, in Czechoslovakia from 1958 to 1983. It has a new turret with floor, PAZ nuclear-blast protection and over-pressure NBC system, gamma ray detector, improved V-55 engine developing 580 horsepower (430 kW) (the engine output was boosted by increasing both pressure of injected fuel and degree of compression) and power-assisted clutch, MC-1 internal oil filter, AK-150S compressor which allows pneumatic start of the engine (the electric starter was removed), new internal fuel tanks with a capacity of 300 l situated in the front of the hull (this increased the overall capacity of the internal fuel tanks to 680 l), ammunition load for the main gun was increased from 34 rounds to 43 (18 of which are stored in "wet containers" situated inside the hull fuel tanks), "Rosa" fire-protection system and TDA exhaust smoke generator. The engine compartment was equipped with a heating system. To compensate for the increase in mass caused by the new equipment the rear hull armour was thinned. The loader's DShK 1938/46 antiaircraft heavy machine gun was removed. The T-55 also lacks a turret dome ventilator. Early units had flush loader's hatch. "Starfish" road wheels replaced earlier "spider" style. Also a snorkel can be placed on T-55 (unlike its predecessors) to allow it to cross 5.5 m depths at a speed of 2 kilometres per hour (1.2 mph) (without preparation T-55 can cross 1.4 m depths). This equipment takes about 30 minutes' preparation, but can be jettisoned immediately on leaving the water.[35][96][97][102]
- T-55A (Ob'yekt 155A)[100] - Produced 1963–1981, in Poland 1964–1979. The T-55A MBT was primarily developed to incorporate a new antiradiation lining and full PAZ/FVU chemical filtration system. One of the major internal additions was the use of a plasticized lead sheeting for antiradiation protection. This was evident externally due to use of an enlarged driver's hatch and enlarged combings over the commander's and loader's hatch to accommodate the new material. Improved POV anti-radiation protection (leading to visibly protruding turret hatches) and NBC filtration, dispensed with bow machine gun. SGMT coaxial machine gun was replaced with PKT coaxial machine gun. Hull machine gun has been removed which gave place for 6 more 100 mm gun rounds[103] Since 1970, T-55A tanks began to receive a new turret fitting for the 12.7mm DShK 1938/46 antiaircraft heavy machine gun.[104]
- T-55K1 (Ob'yekt 155K1), T-55K2 (Ob'yekt 155K2), T-55K3 (Ob'yekt 155K3), T-55AK1 (Ob'yekt 155AK1), T-55AK2 (Ob'yekt 155AK2), T-55AK3 (Ob'yekt 155AK3), T-55MK1 (Ob'yekt 155MK1), T-55MK2 (Ob'yekt 155MK2), T-55MK3 (Ob'yekt 155MK3) - Command tanks, fitted with additional radio sets. Sub-versions are the K1 and K2 models with two R-123 (or R-123M) and used at company and battalion level respectively. They carry 5 tank rounds less than the standard tanks. The regiment commander's K3 is equipped with an R-130M, an R-123M, a 10-metre antenna mast and a generator AB-1-P/30 at the expense of 12 100mm rounds.[100][105] Early models had the R-113 and R-112 sets instead of the R-123 and R-130, the upgraded M series is fitted with R-173 and R-143T2 sets respectively.
Modernization


The T-55AM2B has turret brow armour, laser rangefinder over the main gun, rubber side skirts, and thicker front hull armour than the T-55A. Panzermuseum Munster
T-54
- T-54-2 fitted with the ZET-1 vehicle protection system. It has net structure centered on vehicles main armament and flipper-type side plates.[35]
- T-54M (Ob'yekt 137M) (mid-1960s) – Upgrade program to bring T-54s up to T-55 standard.
- T-54M (Ob'yekt 137M) (1977) – Additional upgrades, including OPVT snorkel and KTD-1 laser rangefinder.
- T-54AM (Ob'yekt 137M) (mid-1960s) – Further upgrades, including increased ammunition, new radios, new V-55 engine. Some received new RMSh track and drive sprocket developed for the T-72 tank in the late 1970s and early 1980s.[99] Similar programs were carried out in other countries (T-54Z, T-54AZ, T-54AMZ for Zusatzausrüstung, 'additional equipment' in East Germany, T-54AR Řeka/Reka, 'river', with fording snorkel in Czechoslovakia).
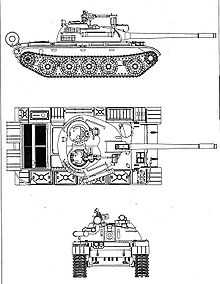
T-55

Early on during the production T-55s were fitted with the TSh-2B-32P sight. Starting in 1970 T-55s were being armed at Uralwagonzavod 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 or KPVT loader's anti-aircraft heavy machine guns. These tanks were known as Model 1970, or sometimes T-55AM. KTD-1 or KTD-2 laser rangefinders and R-123 or R-123M radio sets were fitted to older tanks starting in 1974 (Model 1974).[96][100] At the same time efforts were made to modernize and prolong the life of the drive train.[96]
- T-55 fitted with the ZET-1 vehicle protection system. It has net structure centred on vehicles main armament and flipper-type side plates.[35]
- T-55M (Ob'yekt 155M)/T-55AM (Ob'yekt 155AM)[100] - Modernization of respectively T-55 and T-55A with new "Volna" fire control system, 9K116-1 "Bastion" ATGM system with new 1K13 BOM guidance device/sight, improved "Tsiklon-M1" gun stabilization system and TShSM-32PV sights, V-55U engine,[103] improved suspension and RMSh tracks, increased armour, anti-mine, anti-napalm and improved anti-radiation protection and new R-173/173P radio set . Visual differences include a laser range-finder in an armoured box fitted over the main armament, side skirts, 81mm "Tucha" smoke grenade launchers, BDD turret brow armour and glacis appliqué, and rear RPG screens (only used rarely in Afghanistan).[35]
- T-55M-1 (Ob'yekt 155M-1)/T-55AM-1 (Ob'yekt 155AM-1) [100] – The "-1" suffix was applied to later modified tanks which are powered by the 691 hp (515 kW) V-46-5M engine which was derived from the T-72's 780 hp (582 kW) V-46-6.
- T-55AD "Drozd" (Ob'yekt 155AD)[100][106] - T-55A fitted with Drozd ('thrush') active protection system (KAZ - kompleks aktivnoj zashchity). Soviet Naval Infantry saved money by installing "Drozd" on a small number of tanks instead of opting for appliqué armour, or acquiring newer T-72s. About 250 were kept in stores for secrecy, but later switched to simpler reactive armour. T-55AD is also fitted with the radio set R-173, sight TShSM-32PV, "Tsiklon-M1" stabilizer etc. of the T-55AM.
- T-55AD-1 (Ob'yekt 155AD-1) - Version powered by the 691 hp (515 kW) V-46-5M engine which was derived from the T-72's 780 hp (582 kW) V-46-6.
- T-55MV (Ob'yekt 155MV)/T-55AMV (Ob'yekt 155AMV) [100][106] - "V" for vzryvnoj ('explosive') designated tanks which carried "Kontakt-1" explosive reactive armour (ERA) instead of the passive BDD armour. The ERA bricks (EDZ or elementi dinamicheskoj zashchity) are normally mounted on the turret front, hull front and the hull sides. This variant was adopted by Soviet Naval Infantry first, and by the Russian Army after the collapse of the Soviet Union. The T-55MV is a modernized T-55M and the T-55AMV is a modernized T-55AM.
- T-55MV-1 (Ob'yekt 155MV-1)/T-55AMV-1 (Ob'yekt 155AMV-1)[100] - Versions powered by the 691 hp (515 kW) engine V-46-5M.
- T-55M5 (Ob'yekt 155M5) - This modernization kit adds convex explosive reactive armour "Kontakt-5" panels around turret front, armour panel on glacis plate, a longer hull, a new style fire control equipment with stabilized TVK-3 and TKN-1SM sights for the gunner and commander, an improved V-55U engine (or V-46-5M) and a main gun stabilization system. The original 100 mm D-10T2S gun is maintained. Combat weight is less than 40 tonnes.[35]
- T-55M6 (Ob'yekt 155M6) - A more radical upgrade with longer chassis with 6 road wheels each side, a 690 hp V-46-5M diesel engine and with the complete turret with automatic loader and 2A46M 125mm main gun of the T-72B. Also the protection was increased to T-80U level. Optionally the tank can be equipped with the 1A40-1 fire control system with ATGM system 9K120 "Svir" (as T-72B) or with the 1A42 and 9K119 "Refleks" systems (as T-80U). Combat weight is 43 tonnes.[35]
Experimental vehicles
- T-54M (Ob'yekt 139) - Not to be confused with the T-54M modernization program. This was a testbed for the new rifled 100mm D-54, It had the "Raduga" stabilization systems, which were later used in the T-62. These were not completely successful, so further T-55 development continued to use the D-10 series guns. It is based on the T-54A.[107]
- Ob'yekt 141 - Developed by the Kharkiv design bureau from 1952 to the 1954 was a testbed for the D-54 and the U-5TS. In 1955 the "Raduga" stabilizer was installed however due to a malfunction worked on it was stopped. In spring of 1959 the Ob'yekt 141 was used as a testbed for the U-5TS however, due to excessive gas in the crew compartment and a low ammo count of 28 rounds worked on it was stopped.[108]
- Ob'yekt 137ML - Prototype of the T-54 with 9M14 "Malyutka" (NATO code: AT-3 Sagger) ATGM.
- Ob'yekt 155ML - Prototype of the T-55 with launcher for three 9M14 "Malyutka" (NATO code: AT-3 Sagger) ATGM mounted on the turret rear.[100]
- T-55K used as a testbed for the "Uran" television apparatus. The tank was fitted with a video camera and the footage was transmitted to a receiver in a BTR-50PU command vehicle.[96]
Table of tank models
| T-54-1 (Ob'yekt 137) | T-54-2 (Ob'yekt 137R) | T-54-3 (Ob'yekt 137Sh) | T-54A (Ob'yekt 137G) | T-54B (Ob'yekt 137G2) | T-55 (Ob'yekt 155) | T-55A (Ob'yekt 155A) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (tonnes) |
? | ? | 39.7[97] | ? | ? | 39.7[97] | ? |
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader, driver) | ||||||
| Main gun | 100 mm LB-1 rifled tank gun | 100 mm D-10T rifled tank gun | 100 mm D-10TG rifled tank gun | 100 mm D-10T2S rifled tank gun | 100 mm D-10T2G or D-10T2 rifled tank gun | ||
| Machine gun(s) | 7.62 mm SGMT medium coaxial 7.62 mm SGMT medium bow mounted 2 × 7.62 mm SG-43 fender mounted 12.7 mm DShK anti-aircraft heavy |
7.62 mm SGMT medium coaxial 7.62 mm SGMT medium bow mounted 12.7 mm DShK anti-aircraft heavy |
7.62 mm PKT tank coaxial 7.62 mm SGMT medium bow mounted 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 anti-aircraft heavy (added during routine maintenance since 1972) |
7.62 mm PKT tank coaxial 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 anti-aircraft heavy (added to the newly produced tanks since 1970, added to the old T-55A tanks during routine maintenance since 1972) | |||
| Engine | V-54 12-cylinder 38.88 liter water-cooled diesel developing 523 hp (390 kW) | V-55 12-cylinder 4-stroke one-chamber 38.88 liter water-cooled diesel developing 581 hp (433 kW) | |||||
| Speed | ? | ? | 48 km/h (30 mph) on road[97] | ? | ? | 6.85 km/h in 1st gear[101] 14.66 km/h in 2nd gear[101] 20.21 km/h in 3rd gear[101] 28.99 km/h in 4th gear[101] 55 km/h (34 mph) in 5th gear[97] 6.85 km/h in reverse gear[101] on road | ? |
| Operational range | ? | ? | 401 km (249 mi) 600 km (370 mi) with extra tanks | ? | ? | 501 km (311 mi) 600 km (370 mi) with extra tanks | ? |
| Fuel capacity | 215 US gal (810 L) | 254 US gal (960 L)[97] | |||||
Variants
Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun
- ZSU-57-2 (Ob'yekt 500) - Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG); significant changes from T-54 such as much thinner armour and one less road wheel, with a new turret armed with two 57mm guns.
Armoured Recovery Vehicle
- BTS-1 (Bronetankoviy Tyagach Sredniy - Medium Armoured Tractor) - T-54A converted into an ARV equipped with a stowage basket.[35][109]
- BTS-1M - Improved or remanufactured BTS-1.[35]
- BTS-2 (Ob'yekt 9) (Bronetankoviy Tyagach Sredniy - Medium Armoured Tractor) - BTS-1 fitted with a hoist and a small folding crane with a capacity of 3 tonnes. It was developed on the T-54 hull in 1951;series production started in 1955. The prototype Ob'yekt 9 had a commander's cupola fitted with a DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun, but the production model has a square commander's hatch, opening to the right. It has a combat weight of 32 tonnes. Only a very small number remains in service.[94]
- BTS-3 (Bronetankoviy TyagachSredniy - Medium Armoured Tractor) - JVBT-55A in service with the Soviet Army.[35]
- BTS-4B - T-54-1s and T-54-2s converted into an armoured recovery vehicle equipped with a dozer blade.[35]
- BTS-4BM- Experimental version of the BTS-4B with the capacity to winch over the front of the vehicle.[35]
Bridge-layer

- MT-55 or MTU-55 (Tankoviy Mostoukladchik) - Soviet designation for the Czechoslovakian MT-55A bridge-layer tank equipped with a scissors-type bridge.
- MTU-12 (Tankoviy Mostoukladchik)[112] - Bridge-layer tank equipped with a 12 m long single span bridge with a capacity of 50 tonnes. It entered service in 1955; today only a very small number remains in service. It has a combat weight of 34 tonnes.
- MTU-20 (Ob'yekt 602) (Tankoviy Mostoukladchik)[94] - T-54 converted into a bridge-layer tank. It has a twin-treadway superstructure mounted on a modified chassis. Each treadway is made up of a box-type aluminum girder with a folding ramp attached to both ends to save space while the bridge is in the travel position. The vehicle with the bridge in the traveling position is 11.6 m long. When set up the bridge is 20 m long. This is an increase of about 62% over that of the older MTU-1. The bridge is launched using the cantilever method. First the ramps are lowered and fully extended before the treadways are forward with the full load of the bridge resting on the forward support plate during launch. The span is moved out over the launching girder until the far end reaches the far bank. Next the near end is lowered onto the near bank. This method of launching gives the bridgelayer a low silhouette which makes it less vulnerable to detection and destruction.[35]
- MTU-20 based on the T-55 chassis.[35]
Combat engineering

- T-54/T-55 fitted with BTU dozer blade for clearing soil, obstacles and snow in combat situations. It was used by the tank units requiring specialized engineer support. The dozer blade itself can mounted in 1 hour and 30 minutes and dismounted in 1 hour. In the west it is known as T-54/T-55 Dozer.[97]
- ALT-55 - T-55 converted into an armoured tracked bulldozer. It has a large flat-plate superstructure, angular concave dozer blade mounted in the front and hydraulic rams for the dozer blade.[35]
- T-55 converted into a tracked armoured excavator. The turret has been replaced by a rotatable armoured cab with a boom and a bucket. A dozer blade is fitted to front of the hull.[35]
- T-55 MARRS - T-55 converted into an engineering vehicle fitted with the MARRS Vickers armoured recovery vehicle kit. The turret has been replaced by a new one, large flat-plate with slightly chamfered sides, vertical rear and very chmfered front and a large A-frame crane mounted in the front. The crane has cylindrical winch rope feer between legs of the crane. A dozer blade is fitted to the hull front.[35]
- IMR (Ob'yekt 616) (IMR stands for Inzhenernaya Mashina Razgrazhdeniya) - T-55 converted into a combat engineer vehicle. The turret was replaced with a hydraulically operated crane with capacity of 2 tonnes, capable of 360° turn. The crane is operated from an armoured copula with a visor can also be fitted with a small bucket and used as excavator arm or a pair of pincer type grabs for removing obstacles like trees. Its jib is telescopic and when in traveling position it is folded down and placed on a cradle in the rear of the hull which is folded down against the engine deck when the crane is in use. A hydraulically operated dozer blade is mounted to the front of the hull; it can be used in a straight or V-configuration only. The vehicle is fitted with a searchlight.[35][97] The IMR was developed in 1969 and entered service five years later.
- SPK-12G (SPK stands for Samokhodniy Pod’yomniy Kran) - Heavy crane mounted on T-55 chassis.[35] Only two were built.
- MTP-3 (MTP stands for Mashina Tekhnicheskoj Pomoshchi) - SU-122-54 converted into a technical support vehicle fitted with a light crane. This conversion was carried out beginning in 1973. It is sometimes known in the West as ARV M1977 and T-62T.
Mine clearing
- BMR-1 (Bronirovannaya Mashina Razminirovaniya) - MTP-3 converted into a mine-clearing vehicle. This conversion was carried out beginning in 1975.[35] It is equipped with KMT-5M mine-clearing systems and fitted with a machine gun turret, from BTR-60. The BMR-1s were used by the Soviet army during the war in Afghanistan and more recently by Ukraine's UNIFIL contingent in Lebanon.
- BMR-2 (Boyevaya Mashina Razminirovaniya) - Mine clearing tank based on T-55 chassis. This vehicle has no turret but a fixed superstructure, armed with an NSVT machine gun. It is fitted with a KMT-7 mine clearing set and entered service around 1987 during the war in Afghanistan.[35]
- BMR-2 fitted with a wide variety of mine roller designs.[35]
Flamethrowers
- OT-54 (Ob'yekt 481) - T-54 armed with ATO-54 flamethrower instead of 7.62 mm SGMT coaxial medium machine gun.[96][113]
- TO-55 (OT-55, Ob'yekt 482[114]) - This flame-thrower version of the T-55 tank incorporates the ATO-200 flame projector. The flame thrower is ignited by pyrotechnic charges, and 12 charges are the basic load. The stowage tank, which replaces the hull ammunition rack besides the driver, contains 460-litres of flammable liquid, and each burst averages 36 liters. The maximum effective range of the system is 200 meters, with the stream having an initial muzzle velocity of about 100 mps.[35][97][101]
- Ob'yekt 483 - Flame-thrower tank prototype, based on the T-54B. This version featured installation of the ATO-1 flame-thrower in short stubby barrel with internal tube instead of the main gun, resulting in a decrease of the tank's firepower. There's also a circular vertical vent on the rear of turret and a sight mount level with top of mantlet aperture. Following trials with the prototype vehicle, development work on this ceased.[101]

Armoured personnel carrier
- BTR-T - Heavy APC based on the T-55.
- DPM - Convoy escort vehicle.[35]
- Achzarit - Israeli military converted captured T-55/54s into a tracked APC.
Self-propelled gun
.jpg)
SU-122-54 (Ob'yekt 600) (Samokhodnaya Ustanovka) - Self-propelled 122mm gun, based on the T-54A and sometimes known as IT-122. Between 1955 and 1957, 77 vehicles were built with minor differences between production lots (different commander's cupola etc.). The SU-122-54 had a modified chassis, with small spaces between the first, second and fourth pair of wheels and a large gap between the third, similar to the T-62's and a superstructure, built into the hull, housing the 122 mm D-49 L/48.4 gun for which the vehicle carries 32 rounds. The secondary armament consisted of two KPVT heavy machine guns, one mounted as an anti-aircraft machine gun near the commander's hatch and the other mounted coaxially with the main gun. The vehicle carried 600 rounds for the machine guns. The main gun has a fume extractor positioned right behind the muzzle brake, some vehicles did not have the fume extractor. Other variations included a different commander's cupola.[35]
Firefighting
- GPM-54 (gusenichnaya pozharnaya mashina - tracked fire fighting vehicle) - T-54 converted into a tracked fire fighting vehicle. It is equipped with a dozer blade in the front of the vehicle, water tank and a spray unit mounted on the front of tank's top.[35]
- T-55 modified to fight major oil fires. Turret was replaced with twin-jet-engine mount and multiple water nozzles.[35]
International derivatives
Afghanistan
- T-55s have been in service with the Afghan Army for a number of years. Since there wasn't any kind of care taken as to what variant an individual tank may be, many T-55s have mixed parts from a number of different variants.[35]
Argentina
- T-55 modernization developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by the Argentinian company TENSA for Peru. The tank was fitted with appliqué armour on the turret, rubber side skirts, laser range finder over the main armament and a fire control system with a ballistic-computer and a mast with weather sensors mounted on the top of the turret.[35]
Croatia
- T-55A fitted with additional armour in form of sideskirts and appliqué armour on the turret.[35]
- T-55 Minocistac - T-55 MBT fitted with the UZR-3 explosive hose type mine sweeping system. It was used by the HVO.[35]
Cuba
- T-55 converted into the S-75 Dvina TEL.[35] The vehicle has a wheeled support frame for the nose of the missile.[115]
- T-55 converted into the S-125 TEL.[35] The vehicle is fitted with a large aft-mounted cable spool.[115]
Czechoslovakia


.jpg)
- T-54A produced under license in Czechoslovakia. Because it was of higher quality when compared to the Soviet produced T-54A, it became a hit on the export market. Unlike the Soviet produced T-54A, it had a redesigned engine access plates, three plates fitted to the hull to reduce track shedding and oval engine grills in the engine decks.[35]
- T-54AK produced in Czechoslovakia under license. It was fitted with a base plate on the turret roof for the radio mast.[35]
- T-54AR "Rieka" (Rieka - river) - T-54 modernization with a fording snorkel. It is similar to soviet T-54AM.
- T-54AM - T-54B produced under license in Poland and Czechoslovakia.[35]
- T-54AMK - T-54BK command tank produced in Czechoslovakia.[35]
- T-55AMB - Czechoslovak upgraded T-55A with Czechoslovakia-produced laser rangefinder, fire control system and wind sensor mast with thickened center section mounted on rear of turret roof.[35]
- T-55AM1 - Czechoslovakian version of the T-55AM with Czechoslovak-produced "Kladivo" fire control system with a ballistic computer, a laser range finder (different from the Russian KTD-1) on top of the gun and a cross-wind sensor mast mounted on rear of turret roof.
- T-55AM1K3 - Command tank version of the T-55AM1.[35]
- T-55AM2 - T-55AM1 fitted with the passive BDD appliqué armour for turret (horseshoe shape) and hull front (fitted to upper glacis plate), sideplates fitted with extensions protecting catwalk fuel tanks, the improved V-55U engine with an integral supercharger delivering 620 hp and the R-173P radio system. The BDD armour panels consist of armoured steel boxes filled with Penpolyurethane. In addition there are cavities which can be filled with water or sand for additional protection. There is also a cluster of 8 smoke-grenade launchers on the right-hand-side of turret. T-55AM2 is fitted with additional headlights on the front fenders.[35]
- T-55AM2 Dyna-1 - T-55AM2 fitted with new armour array.[35]
- T-55AM2B - T-55AM2 with the ability to fire the laser-guided 9M117 "Bastion" (AT-10 Stabber) ATGM via the main gun. The T-55AM2B is fitted with the 1K13 BOM gunner's sight in place of the original TPN-1M-22.
- T-55AM2K1 - command tank for company commanders with an additional radio set R-173.
- T-55AM2K2 - command tank for battalion commanders with an additional radio set R-173.
- T-55AM2K3 - regiment commander's version with radio sets R-173 and R-143T2, a generator NS1250B and a slim 10m antenna mast. Carries 12 rounds less than a standard tank.
- VT-55A (Vyprošt’ovací Tank - recovery tank) - Czechoslovak ARV built on T-55A hull and fitted with a crane with 15 tonnes capacity, a main winch with 44 tonnes capacity and a secondary winch with 800 kg capacity. It was first called MT-55 but this designation was given to the bridge laying tank and therefore the designation had to be changed.[35][111]
- VT-55KS (kapitalstické státy) - Export version for non-Warsaw Pact countries like Iraq and Syria. A total of 2,321 was produced between 1967 and 1983.
- ZS-55A (ženijní stroj) - VT-55A fitted with dozer blade BTU-55.[35]
- MT-55A (Mostni Tank - bridge layer tank) - Czechoslovakian redesigned version of MT-55. According to some Western sources there are two models, namely the basic model - also known as MT-55K - and the MT-55L with a longer bridge. Between 1969 and 1983, 1,278 MT-55A's were built by TS Martin.
- MT-55KS (kapitalstické státy) - Export version for non-Warsaw Pact countries like India, Iraq and Syria. 183 vehicles built from 1971.
- PM-55L (Přepravník Mostu) - Lightweight version that uses a Tatra T-813 truck as carrier and launch platform.
- JVBT-55A (Jeřábový-Vyprošťovací-Buldozerový Tank) - Czechoslovakian crane tank, fitted with a big 15t crane, a winch and a BTU-55 dozer blade. Combat weight is 42 tons. From 1967, 508 were produced.
- JVBT-55KS (kapitalstické státy) - Export version of JVBT-55A for non-Warsaw Pact states like Iraq. 172 produced.
Czech Republic
- T-55C-1 "Bublina" - Turret-less engineer vehicle with BTU-55 dozer blade.
- T-55C-2 "Favorit" - Czech driver training tank.[35]
- SPOT-55 (Speciální POžárnický Tank) - Czech fire-fighting conversion with large tank with chamfered edges placed on T-55 chassis, two spray units mounted on front of tank top and dozer blade fitted to hull front.[35] It was developed by VOP 025 and has two water tanks for a total of 11,000 liter. Weight is 45 tons.[116]
East Germany
- T-54Z (Z for Zusatzausrüstung - additional equipment) - East German modernization of T-54 similar to T-54AM.
- T-54AZ (Z for Zusatzausrüstung - additional equipment) - East German modernization of T-54 similar to T-54AM.
- T-54AMZ (Z for Zusatzausrüstung - additional equipment) - East German modernization of T-54 similar to T-54AM.
- T-54T (Panzerzugmaschine ohne Bergesatz) - East German development with recovery and welding equipment. 10 made on Polish-made T-54A chassis. NATO code: T-54(A).[117]
- T-54TB (Panzerzugmaschine mit Bergesatz) - similar to T-54T, but with 140-t winch. 10 made on Polish-made T-54A chassis. NATO code: T-54(B).[117]
- T-55AM2B with bin on left-hand-side of turret.[35]
- T-55 NAL NRD - East-German modernization of T-55. It wasn't finished because of the political changes in 1990.
- T-55T - Modified VT-55A with push bar and splashboard across glacis plate in service with the NVA.[35]
- Minenräumfahrzeug (Pz) - Prototype mine clearing vehicle developed by the East Germany. Two Versions:
- T-54 M1975/1 - Experimental East German roller/flail combination mine clearing vehicle.[35]
- T-54 M1975/2 - Flail only variant of the M1975/1.[35]
- T-55TK - East-Germany received 119 Czechoslovakian JVBT-55A's between 1968 and 1979 and called them Kranpanzer T-55TK.
- BLG-60 (Brückenlegegerät) - East German/Polish scissors-type bridge layer.[35] Development started in 1965 (one year after the BLG-34 project was cancelled [119]) and the first vehicle was delivered in 1967. Almost 200 BLG-60's were built by STAG Genthin and SKET Magdeburg.
Egypt
- T-55E Mark 0 ("E" stands for Egyptian variant) - T-55 modernization fitted with a new Russian engine developing 580 hp. It came in two variants:
- T-55E Mark 0 fitted with a German AEG infrared/white searchlight on the left hand side of the main armament and a Yugoslav "Iskra" laser rangefinder.[35][97]
- T-55E Mark 0 fitted with DShK 1938/46 antiaircraft heavy machine gun and German AEG searchlight.
- T-55E MK I ("E" stands for Egyptian variant) - T-55 modernization fitted with a more powerful engine developing 650 hp, fire control system (which includes a ballistic computer), searchlight, laser rangefinders and appliqué armour. All those additions resulted in weight increasing to 41 tonnes. It retains the original 100 mm tank gun but the performance and ammunition were improved.
- T-55E MK II ("E" stands for Egyptian variant) - Refurbished and modernized T-55 in the mid-1990s. It is fitted with a German engine developing 880 hp, M68 105 mm tank gun, Italian fire control system (which includes an Italian ballistic computer), infrared device, laser rangefinder, stabilization system, modernized suspension, six smoke grenade launchers on each side of the turret, NBC protection system, appliqué armor and armored side skirts. All those additions resulted in weight increasing to 44 tonnes. Conversions were scheduled to be completed by the end of 2008.
- Ramses II - T-54 modernization. In November 1984, US Teledyne Continental Motors corporation (taken over by General Dynamics Land Systems conglomerate) was awarded a contract to upgrade the firepower and mobility of a single T-54. The modernization initial designation was T-54E but it was subsequently renamed as Ramses II. The first prototype was sent to Egypt for extensive firepower and mobility trials in January 1987 and with them ending later that year. In late 1989 Egypt signed a technical assistance agreement with TCM to support continued Egyptian trials of the Ramses II. The new set of trials began in summer of 1990. Ramses II entered production and service between 2004-2005.
Finland
- T-55M - 70 Finnish T-55 tanks were upgraded to T-55M/MK level with new fire control system FCS-FV/K, new tracks, side skirts, NSVT machine gun, Wegmann 76mm smoke grenade launchers, Lyran 71mm mortar etc.
- KAM-1 - Finnish medium recovery tank built on T-54 hull, developed in 1984. Prototype only.[111][120]
- KAM-2 - Finnish light recovery tank built on T-54 hull, developed in 1985. Prototype only.[111][120]
- T-55 with 155 mm gun - Finnish 155 mm Tampella gun mounted on a T-55 chassis - experimental prototype only.
Germany
- T-54 upgrade developed in 1991 by Jung Jungenthal to meet the requirements of the Egyptian army (but was never purchased). The upgraded T-54 is equipped with additional passive armour, a new transmission LSG 3000, an improved cooling system, a new all-electric gun control system, under-armour fuel tanks "Superflexit" on either side of the hull and 76mm smoke grenade discharges. The original 100mm gun is retained.[35]

Great Britain
- T-54A, a proposal by Royal ordnance to upgrade the T-54A's of the Egyptian Army to the standard NATO 105mm gun.[35]
- T-55 upgrade package made by A F Budge, FFG and Perkins it included a Perkins Condor V8 800TCA engine, XTG-411-5 transmission, new cooling system oil-cooled brakes, Pilkington fire control system, IR25 thermal sight, and L7 105mm gun.[35]
- T-55AM tank with (bolt-on) Marksman (turret/system) - a T-55 SPAAG version equipped with the British Marksman anti-aircraft system. This variant is only found in Finnish service, as the ItPsv 90.
Hungary
- T-55AM was a 1980's modernization of the basic T-55 tank, which added a laser rangefinder, mounted over the barrel, inside a large rectangular armoured box. The T-55AM tank received better main weapon stabilization and sights, as well cast steel add-on armour blocks on the turret front-sides area (known as the "horse-shoes" or the "Brezhnev's eyebrow" armour). T-55AM tanks were withdrawn from service during the early years of the 2000s (decade), some scrapped, some mothballed, leaving only a handful of T-72B and T-72M vehicles in active Hungarian army service.

India
- T-54/T-55 fitted with sheet steel tubes placed on the barrels to distinguish them from Pakistani Type 59s.[97] They were supposed to imitate fume extractors.[3]
- T-54B modified by India.[35]
- T-55A upgraded with 105mm gun.[35]
Iraq

- T-55 Enigma - T-55, Type 59, and Type 69 tanks used by Iraqi Brigade commanders had appliqué armour on turrets and hulls composed of several layers of spaced armour (the technique of choice for the Iraqi Engineers) plates enclosed in steel boxes. It was successful at defeating shaped charge warheads during the battle of Khafji, where one unit is reported to have survived several hits from MILAN missiles before being dispatched by a helicopter.[121]
- T-55 Enigma with smoke grenade dischargers.[35]
- T-55QM - T-55 armed with NATO-standard 105 mm L7 or M68 gun instead of the old 100 mm gun. The tank was fitted with a French laser range-finder. The upgrades were done in the mid-to-late 1980s.
- T-55QM2 - T-55 upgraded by Soviet technicians with a Soviet 125 mm/L52 smoothbore gun and French laser range-finder, 1986-1991.
- Type-72Z - At the International Arms Exhibition, which took place in Baghdad between 28 April - 2 May 1989, a T-55 equipped with the 2A46 125mm gun with fume extractor one third of the way down the barrel from the T-72 tank was displayed. This modernized vehicle was designated as T-72Z, which at first mislead foreign experts since it was believed that the project was based on the T-72 tank. In fact, the number "72" originated from the year of modernization - 1372 according to the Muslim calendar. The loading mechanism of this vehicle was also taken from T-72. The fitting of the loading mechanism required increasing the aft section of the turret. A stub case ejection port on rear of turret. The tank's armour protection was also reinforced through the use of add-on armour on the tank's front glacis. The vehicle also mounted the EFCS-3 fire control system developed by the Slovenian firm 'Fotona' and a new transmission. A set of explosive reactive armour is an optional extra. It is believed that around 200 T-54/T-55 tanks and 150 Chinese Type-59 tanks were brought up to the T-72Z standard.[35]
- T-55 modified to fire 122 mm rockets by removing the main armament and fitting an multi-barrel-rocket launcher on the rear of the turret. Reloads appear to have been stowed in the turret and passed out through a crudely cut access on the rear of the turret. It has a square sided platform mount with drop down sides and rear.[35]
- T-54 fitted with 160mm mortar.[35]
- T-55 fitted with the S-60 anti-aircraft gun in a square sided platform mount with drop down sides and rear.[35]
- BTS-2 - Rebuilt late production BTS-2 fitted with antiaircraft heavy machine gun pintle mount and additional stowage boxes.[35]
- BTS-Saddam - Iraqi produced armoured recovery vehicle based on obsolete T-54 chassis. It's equipped with small fixed turret on left of driver fitted with antiaircraft heavy machine gun, large winch in fighting compartment covered with metal sheet framework, earth anchor on rear of hull. Like most Iraqi produced equipment it was named in honour of Saddam Hussein.[35]
Iran

- T-72Z/Type 72Z/Safir-74 - Iranian upgraded T-54/55 and Type-59 (Chinese copy of the T-54A), T-72Z being the name given to the upgraded T-55s, Safir 74 being the name given to the upgraded T-54s and Type 72Z being the name given to the upgraded Type-59s. The upgrades Include the new fire control system Fotona EFCS-3B (with laser rangefinder, cross-wind sensor, ballistic computer and gunner's passive night vision device), a 105mm tank gun, side skirts, smoke grenade launchers, ERA package, a new power-pack with 780 hp 12-cylinder V-46-6 diesel engine and new tracks. Iranian sources state there was also a plan to arm the tanks with a 2A46 125mm tank gun, but it seems as if this project was canceled.[35]
- Safir-86 - Standard T-55 fitted with an ERA kit developed by Iran.[35]
- Safir-86 with improved ERA layout.[35]

Israel



- Tiran-1 - Virtually unmodified T-54 in Israeli Army service.[35]
- Tiran-2 - Virtually unmodified T-55 in Israeli Army service.[35]
- Ti-67 - a collective designation for the Israeli-upgraded T-54s and T-55s built on tanks captured in 1967 and 1973. No longer in service in Israel but many were sold off.
- Tiran-4 - Modified T-54 with original 100 mm gun.[35] It has two water cans fitted to the rear of the turret, new fenders, new loader's hatch that opens to the rear and a new antenna mount. Later fitted were a rounded stowage bin on the rear of the turret, pintle-mounted .30 cal M1919A4 Browning medium machine gun in front of the loaders hatch and gas cans fitted to the front fenders.[83]
- Tiran-4Sh - upgraded Tiran-4, fitted with Sharir 105 mm gun. It also was fitted with a newer type of antenna mount in, new infrared spotlight for the commander, an aiming system from the Sherman medium tank, fire extinguisher mounted in front of the searchlight, new headlights, centrally mounted .30 cal M1919A4 Browning medium machine gun, signal flag holders and an oil can mounted on the rear of the left fender.[83] It also has ammunition racks modified to suit the 105mm ammunition, new communications equipment, modified commander's seat, new gunner's seat, azimuth indicator installed, driver's hatch modified so that it can opened from the outside, coaxial machine gun replaced by a 7.62mm Browning machine gun and the cupola mounted DShK 1938/46 antiaircraft heavy machine gun replaced by a 12.7 mm Browning heavy machine gun, new fire control, night vision equipment, electrical system, air-conditioning system, antennae mounts on the rear of the turret, infantry tank-telephone on the rear of the hull, exhaust outlet angled upwards, additional track stowage and fire-extinguishing system installed.[35]
- Tiran-5 - Modified T-55 with original 100 mm gun.[35] It has two water cans are fitted to the rear of the turret, new fenders, a rounded stowage bin on the rear of the turret and pintle-mounted .30 cal M1919A4 Browning medium machine gun in front of the loader's hatch. Later fitted were the .50 cal M2 heavy machine gun over the barrel of the tank gun, extra gas cans, first aid box, ring around the loader's hatch for the .30 cal, new lights similar to the ones used in the M60 Patton, a folded stretcher on the left hand side of the vehicle and an infantry tank-telephone on the rear of the hull.[83]
- Tiran-5Sh - upgraded T-55, fitted with Sharir 105 mm gun. It also has ammunition racks modified to suit the 105mm ammunition, new communications equipment, modified commander's seat, new gunner's seat, azimuth indicator installed, driver's hatch modified so that it can opened from the outside, coaxial machine gun replaced by a 7.62mm Browning machine gun and the cupola mounted DShK 1938/46 antiaircraft heavy machine gun replaced by a 12.7 mm Browning heavy machine gun, new fire control, night vision equipment, electrical system, air-conditioning system, antennae mounts on the rear of the turret, exhaust outlet angled upwards, additional track stowage and fire-extinguishing system installed. It is also known as T-55S.[35]
- Tiran-5Sh fitted with a dozer blade.
- Ti-67 fitted with Blazer ERA.[35]
- Ti-67s - This is the Ti-67 with many other improvements in addition to all of the previous modifications. They include fitting the American Detroit Diesel 8V-71T engine developing 609 hp, new semi-automatic hydromechanical transmission equipped with a torque converter, new air cleaners, Blazer explosive reactive armor added to the hull and turret, Cadillac-Gage-Textron gun stabilization system, installation of EL-OP Matador computerized fire control system, low-profile commander's cupola, IR detectors, Image-intensifier night vision equipment for the commander, gunner and driver, Spectronix fire detection and suppression system, new turret basket, extensive external stowage, modernized driver's station including replacement of tillers by a steering wheel, new final drives, new all-internal fuel system and improved suspension.[35]
- Achzarit - T-55 tank converted into heavy armored personnel carrier.
- VT-55A captured from Egyptians or Syrians and modified to meet the needs of Israeli Army. It has a post mount forward of commanders cupola for 50cal HMG.[35]
- VT-55KS captured from Egyptians or Syrians and modified to meet the needs of Israeli Army.[35]
- MT-55 captured from Egyptians or Syrians and modified to meet the needs of Israeli Army. It is fitted with an extended antenna.[83]
- T-54 converted into an improvised APC. Rebuilt/modified by the Israeli Army who quickly passed them on to the South Lebanon Christian militias. It has the armour screens around turret ring and armour shields on either side of drivers hatch. Known as the Tiran or T-54 APC, it consists of 5 crewmembers and an unknown number of transported troops.[35]
- T-55M3 - Designed by Israel and used by the Vietnamese People's Army. Around the turret, the tank fitted with composite armour plate protection. The T-55M3 main battle tanks equipped with an L7 105 mm tank gun, an NSVT 12.7 mm machine gun, a PKT 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun, Swiss MAWS6056B Idram SA meteorological sensors, a German 1000 horsepower engine, and a British gearbox and transmission system. The tank can also be equipped with a 60 mm mortar.[122]
Pakistan
- Al-Zarrar - Type 59 modernization which can also be applied to T-54s and T-55s.
People's Republic of China
- Type 59 - copy of T-54A
Peru
- T-55 modernization which replaces the V-55 diesel engine with a Caterpillar diesel one. It was not accepted by the Peruvian Army.
- T-55M1 Leon 1 - T-55 modernization designed by the Peruvian engineer Sergio Casanave. The project was named DIEDE 2005. The Peruvian Army assisted project since it began. This modernization fits the T-55 with a new fire control system, laser rangefinder and twin SACLOS 9M14-2T HEAT tandem system Malyutka 2M ATGM launchers on each side of the turret. Also the main gun is modified to fire 100 mm M-43A1 APFSDS. At least three physical demonstrator were made, but none become an operational prototype. Rejected by the Peruvian Army.
- T-55M2A1 Leon 2 - Also designed by the Peruvian engineer Sergio Casanave, this proposed upgrade include a new thermal fire control system and optics, ability to fire M-43A1/M-43A3 APFSDS ammo (up to 2,600 m) and the launcher for the 9M117 (3UBK23-1) Bastion laser beam-guided anti-tank missiles with a range up to 6,000 m and 750 mm RHAe penetration after ERA, new engine developing 630 hp and new night vision system. At least three physical demonstrators were made, but none become an operational prototype. Rejected by the Peruvian Army.
- Tifón-2 ((English) Typhoon-2) - T-55 modernization designed by engineer Sergio Casanave and developed jointly by the Desarrollos Industriales Casanave de Perú (DICSA), (Casanave Industrial Developments Peru) and Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau of Ukraine. It's based on the Ukrainian T-55AGM and is almost identical with the exception of the engine, the main armament, Fire Control System with 1G46M gunner sight, PKN-5 Commander sight, and both integrated with the Buran - Catherine Thermal sight, air conditioned system, Deflek Ceramic special alloy steel armor, and Nosh explosive reactive armor. The tank is powered by the new 5TDFMA two-stroke liquid-cooled multi-fuel supercharged diesel engine with boxing pistons developing 1,050 hp and has maximum speed of over 75 km/h on the road in forward gear and over 35 km/h in the reverse gear. The main armament is the 125 mm KBM-1M 48 caliber smoothbore gun capable of firing conventional ammunition with enhanced performance which can destroy modern tanks from a range of up to 3,500 m (APFSDS and HEAT-TANDEM) and barrel-launched Kombat ATGMs which have a penetration of 800 mm RHAe after ERA and are capable of destroying modern tanks from a distance up to 5,000 m. The gun weighs 2,5 tonnes, has a barrel length of 6 m (48 calibers) and can fire APFSDS, HEAT and HE-FRAG rounds.[123] The gun has a normal recoil length of 26–30 cm and maximum recoil length of 31 cm. Is not being considered as an option for upgrade by the Peruvian Army.[124]
- T-55 Fire Support - Uralvagonzavod is offering the Peruvian Army an upgrade for its T-55s as an alternative to replacement with new tanks. The proposal is to replace the turret of their current tanks with the turret of the BMPT. The BMPT turret is equipped with two 2A42 30 mm autocannons, two AGS-17 grenade launchers, four 9M120 Ataka-V ATGMs, and a PKTM machine gun. Every operator in the turret has a scope, and the main armament operator has a thermal camera, optical sight, and panoramic camera. It is also equipped with a laser detection system. Although the BMPT design fits onto a T-72 tank chassis, it can be adapted to fit on a T-55.[125]
Poland
- Polish-produced tanks often have different stowage arrangements. The arrangement includes a rectangular box mounted on the left side of the turret, a smaller square stowage box on the left side of the turret-rear, and a slightly different rear decking.[97]
- T-54AD - Polish T-54A command tank with additional radios and a radio range of 100 miles.[126]
- T-54AM - Polish and Czechoslovak production of the T-54B under license.[35]
- T-55U - Polish T-54 upgrade.[127]
- T-54 fitted with stand-off armour plates fitted to hull front and wire mesh screens around the turret to provide protection against ATGM.[35]
- T-55L - New-build polish versions of the T-55A.[35]
- T-55LD - Polish T-54 tanks rebuilt to T-55A standard. 200 T-54 tanks have been rebuilt in 1975.[35]
- T-55AD-1 - Polish T-55A command tank with additional R-130 radio and reduced ammo storage to 38 rounds.[111][128]
- T-55AD-2 - Polish T-55A command tank with additional R-123 radio and reduced ammo storage to 38 rounds.[111][128]
- T-55AM "Merida" - Polish version of T-55AM developed between the late 1970s and early 1980s, fitted with a new SKO "Merida" (SKO stands for System Kierowania Ogniem - fire control system) fire control system with cross-wind sensor and a new CCDN-1 (CCDN stands for celownik-dalmierz dzienno-nocny - day/night sight-rangefinder) day/night sight-rangefinder system. The tank is also equipped with additional passive armour (type BDD) on the hull and turret front, and with a protection system that consists of a laser-warning system WPL-1 "Bobrawa" (Wykrywacz Promieniowania Laserowego) and WWGD-1 "Erb" (Wyrzutnia Wybuchowych Granatów Dymnych) and WPD-1 "Tellur" (Wyrzutnia Pocisków Dymnych) 81 mm smoke grenade launchers, both in clusters of 8 on each side of the turret. Finally, the original engine has been replaced by an upgraded W-55 WAX developing 613 hp (457 kW).[129] Some were fitted with new radio sets like the R-123 or R-173. Considered to be a second generation MBT because of the high degree of modernization.[35][97][111]
- T-55AMS - Version without armour on the hull front, can be fitted with mine-clearing systems ZB/WLWD or KMT-5 or a dozer blade USCz-55. One per company.
- T-55AD-1M - T-55AM "Merida" command tank with additional R-130 radio and reduced ammo storage to 38 rounds.[129]
- T-55AD-2M - T-55AM "Merida" command tank with additional R-123 radio and reduced ammo storage to 38 rounds.[129]
- T-55AM2BP - Polish licence version of the Czech T-55AM2B. For export only.
- W-125SC - T-55A, or WZT-1 and BLG-67, converted into a transporter erector launcher of the S-125SC "Newa-SC" air-defence missile system. A fully rotating launcher for 4 missiles 5V27 is replacing the turret. Outer launcher arms fold against inner when moving and because of that two missiles are carried when moving and four when the vehicle is holding position.[35]
- WZT-1 (Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego - Armoured recovery vehicle) - Polish ARV based on soviet BTS-2. It was built on T-55 and later T-55A hull. It was produced between 1970 and 1978.[109]
- WZT-2 (Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego - Armoured recovery vehicle) - Polish ARV built on T-55 hull. It was built to perform repairs on T-55 and T-55A tanks. When it entered service in 1973 it was not only the best ARV in the whole Warsaw Pact but probably in the whole world. It is still able to carry out tasks that NATO gives ARVs of its class. Unlike the T-55 and the WZT-1, the WZT-2 is still the basic ARV of the Polish army used for field repairs. It's able to perform repairs not only on Soviet tanks like the T-54/T-55 and T-72 but also on Polish PT-91 and German Leopard 2A4. However because all tanks currently in Polish service weigh more than 40 tons it is unable to tow them. It is used to tow lighter vehicles like BWP-1 and 2S1. A total number of 600 was produced. 80 were in service as of 2004. Some are used by Ratownictwo Kolejowe (Railroad emergency respond services). Many have private owners who bought them from the Polish Army. 196 of these vehicles were also sold to India. The vehicles were also bought by Iraq and Yugoslavia.[111][130]
- T-55A engineer tank, with KMT-4 mine plow on the front and boxes containing PW-LWD rapid explosive breaching system (similar to Giant Viper).
- IWT (Inżynieryjny Wóz Torujący) - Polish combat engineer vehicle, based on the WZT-2 and fitted with a hydraulic dozer blade, a hydraulic arm and mine-clearing systems PW-LWD and KMT-5. It uses DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun for antiaircraft protection. Entered service in very small numbers in 1978.
- BLG-67 - Polish version of the East German bridge layer BLG-60.[131]
- BLG-67M - Similar to BLG-60M: improved model that makes it possible to attach 3 bridges together to bridge gaps of up to 52 m.
- BLG-67M2 - Similar to BLG-60M2: improved model, widened by 20 cm.
- BLG-67M - Similar to BLG-60M: improved model that makes it possible to attach 3 bridges together to bridge gaps of up to 52 m.
Republika Srpska
- SO 76 M-18 Mod - Late T-55 MBTs which were fitted by Bosnian Serbs with a turret of the M18 Hellcat tank destroyer. They were used for mechanic training before the war. Bosniak forces captured at least one.[35][132]
- T-55 converted by Bosnian Serbs into a SPAAG armed with a Bofors AA gun.
Rhodesia
- T-55LD with South African FM tactical radio sets adopted from the Eland armoured car. The Eland's communications utilised throat-activated microphones and was considered superior to Soviet models; this system was also unique in that radios were operated by a Rhodesian tank commander, rather than loaders as was standard to T-55 doctrine.[35]
Romania

- T-55AM - General designator for three different models in Romanian service: the Russian T-55AM with "Volna" fire control system, the Czech T-55AM2 with "Kladivo" FCS and a locally upgraded model with "Ciclop" FCS also used in the TR-85 (it is sometimes incorrectly called T-55AM2R [35]).
- TR-580 - (Tanc Românesc Model 580 - Romanian Tank Model 580) Romanian production variant of the T-55 with a new hull and stretched chassis with 6 road wheels and metal side skirts. It has a combat weight of 38,2 tonnes. The TR-580 still uses the 580 hp engine of the T-55 (hence the name). It was developed from 1974 and 400 were produced between 1977 and 1981.[7] The tank's official designator is TR-77-580 (Romanian tank Model 1977 with 580 hp engine) but initially it was simply called TR-77, M1977 or M-77 in the West.[35][133]
- TR-580M - TR-580 modernization equipping it with a laser rangefinder mounted over barrel.[35]
- TM-800 - Improved export model of the TR-580.[35]
- TER-800 - Armoured recovery vehicle version of the TM-800.[35]
- TCZ-580 - Recovery variant with the same specialized equipment as the Slovak VT-55A.[35]
- TR-85 - (Tanc Românesc Model 1985 - Romanian Tank Model 1985) TR-580 with a new turret equipped with a new fire control system. It also has new suspension, a more powerful German engine and a combat weight of 43.3 tonnes.[35]
Serbia
- T-55H - Mobility improvement is: engine of increased power by building-in new, domestically produced, high pressure pump, installing new water cooler and oil cooler and modification of transmission by installing new toothed wheels. Firepower improvement: installing antiaircraft machine gun 12,7mm M-87 and installing coupled machine-gun 7,62mm M-84. Protection improving in: installing explosive protective armor, installing anti cumulative shields, installing new fire extinguisher using halon, modernization of device for nuclear protection, installing of smoke screen laying active protection system (active masking) and installing assembly block for fixing crewis cupola lid partly closed. Other improvements include installing device for self-entrenching, installing device for digging and deactivating mines KMT-6, installing assembly block for fixing crew's cupola lid, partly closed and modernization of active IR (infrared) devices and converting them into passive.
- VIU-55 Munja - T-55 converted into engineering IFV, similar to Israeli IDF Achzarit
Slovakia
- UOS-155 "Belarty" (Univerzálny Odtarasovací Stroj) - Slovak combat engineer vehicle fitted with mine cleaner. The vehicle consist of a T-55 chassis with the armoured turret (with a hydraulic excavator fitted with shovel) of the UDS-214 engineer vehicle.[35][134]
- UOS-155B (Univerzálny Odtarasovací Stroj) - UOS-155 "Belarty" with hydraulic excavator fitted with mine clearing device.[35]
- SPOT-55" fire fighting tank with 2 water cannons and 11.000 litres of water, refurbished by the Voluntary Fire Brigade POLE to be used in special operations [135]
Slovenia
- T-55S - The prototype for the M-55S.[35]
- M-55S - T-55 modernization developed by the STO RAVNE company and engineers of the Israeli company Elbit. Slovenia modernized 30 T-55 tanks in the inventory of its armed forces. The last T-55 was modernized to the M-55S standard in May 1999. The original 100 mm tank gun was replaced by the 105 mm one with a thermal sleeve. The armour protection of the tank was improved considerably by attaching Rafael ERA blocks to the hull and the turret. A digital ballistic computer was installed in order to improve the fire control system (FCS). The gunner has the Fotona SGS-55 two-axis stabilized day-and-night sight with an integral laser rangefinder. In addition to the integral optic sight the commander has the Fotona COMTOS-55 sight with an independent line-of-sight stabilization, which allows him to acquire targets and lay the gun independently if required. The driver has the Fotona CODRIS combined day/night observation periscope. The LIRD-1A laser illumination warning receiver was mated with front-mounted IS-6 smoke grenade launchers (of which there are six in two clusters, one per side of the turret) and can be automatically activated in an emergency. Modernization of the V-12 diesel engine resulted in an increase in power from 520 hp to 600 hp. The running gear has rubber side skirts and the tank was outfitted with new rubber and metal tracks. Improvements were also made to the communications aids.[35]
- M-55S-USP - M-55S converted into a driver trainer vehicle. The turret has been replaced by a training enclosure with seats for an instructor and two trainee drivers. A third driver is in the normal driving position of the vehicle. It is also known as LM-55, M-55USP and USP9.[35]
- M-55S - T-55 modernization developed by the STO RAVNE company and engineers of the Israeli company Elbit. Slovenia modernized 30 T-55 tanks in the inventory of its armed forces. The last T-55 was modernized to the M-55S standard in May 1999. The original 100 mm tank gun was replaced by the 105 mm one with a thermal sleeve. The armour protection of the tank was improved considerably by attaching Rafael ERA blocks to the hull and the turret. A digital ballistic computer was installed in order to improve the fire control system (FCS). The gunner has the Fotona SGS-55 two-axis stabilized day-and-night sight with an integral laser rangefinder. In addition to the integral optic sight the commander has the Fotona COMTOS-55 sight with an independent line-of-sight stabilization, which allows him to acquire targets and lay the gun independently if required. The driver has the Fotona CODRIS combined day/night observation periscope. The LIRD-1A laser illumination warning receiver was mated with front-mounted IS-6 smoke grenade launchers (of which there are six in two clusters, one per side of the turret) and can be automatically activated in an emergency. Modernization of the V-12 diesel engine resulted in an increase in power from 520 hp to 600 hp. The running gear has rubber side skirts and the tank was outfitted with new rubber and metal tracks. Improvements were also made to the communications aids.[35]
Sudan
- Digna - Sudanese produced T-55 copy.[136]
Ukraine
- T-55 version modernized by Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau fitted with 4 smoke grenade discharges cluster fitted to each side of turret front and laser rangefinder fitted above main armament.[35]
- T-55 version modernized by Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau fitted with 125mm KBM1 smoothbore gun.[35]
- T-55AGM - Ukrainian T-54/T-55 modernization. It brings up the T-54/T-55 tanks to T-80 standard. It can also be applied to Chinese made Type 59 and Soviet T-62. It is fitted with 5TDFM, two-stroke liquid-cooled multi-fuel supercharged diesel engine with boxing pistons which develops 850 hp (634 kW), improved running gear, automated movement control system with a steering handlebar control, additional passive protection, built-in explosive reactive armour, countermeasures system, new fire suppression system with over-ride facilities at the commander's station, automatic loader which holds 18 rounds and anti-aircraft machine gun that can be aimed and fired from within the turret under a complete armour protection. The anti-aircraft machine gun is installed on the commander's cupola and is intended to be fired at air and ground targets. The buyer can choose between two main armament options: 125 mm KBM1 smoothbore gun or 120 mm KBM2 smoothbore gun. Both of them with use of enhanced performance conventional ammunition and barrel-launched ATGM can defeat modern tanks form distance of 2000–3000 m and up to 5,000 m using the ATGM. The tank can carry at least 30 rounds. The 125 mm KBM1 smoothbore gun weighs 2,5 tonnes, has a barrel length of 6 m (48 calibers) and can fire APFSDS, HEAT and HE-FRAG rounds while 120 mm KBM2 smoothbore gun weighs 2,63 tonnes, has a barrel length of 6 m (50 calibers) and can fire all types of ammunition that meet the requirements of NATO standards and Ukrainian-made ATGM. Both guns have normal recoil length of 26–30 cm and maximum recoil length of 31 cm. The tank can be armed with either the KT-7.62 or the PKT-7.62 coaxial machine gun and can carry 3,000 rounds for it. The tank can also be armed with either KT-12.7 or NSVT-12.7 heavy machine gun for AA protection and can carry 450 rounds for it. The approximate successful range is 2 km during day and 800 m during night. The AA HMG can be elevated between -5 to +70 degrees. The remote control for anti-aircraft machine gun is stabilized in the vertical axis during automatic mode (by using the TKN-5 sight) and is using the PZU-7 sight for semi-automatic mode.[35][137]
- T-55-64 - With T-64 suspension and powerplant.
- T-55MV - The former Soviet Army tank repair plants number 7 in Kiev and number 17 in Lvov in the Ukraine have been promoting the T-55MV on the world market for several years. The turret, hull front section and side skirts of this version are protected by the Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour capable of withstanding hits from the American M829 120mm armour-piercing depleted uranium ammunition. The main armament of the T-55MV was improved by employing the 9M117 "Bastion" (AT-10 Stabber) ATGM which can be launched through the barrel of the standard T-54/55 rifled gun. With an effective range of 4,000 m, the 9M117 "Bastion" (AT-10 Stabber) ATGM is capable of penetrating armour equivalent to 550mm of steel plate. If the missile is equipped with a tandem warhead, its armour penetration capability increases. The Volna fire control system with its digital ballistic computer was also fitted. Syria was the first country to order 200 of its T-55s upgraded into the T-55MV.[35]
Yugoslavia
- TZI-JVBT - Czechoslovak JVBT-55A in service with Yugoslav Army.[35]
- T-55TZI - Yugoslavian modification of the VT-55A armored recovery vehicle.[35]
- T-55AI "Igman" - Yugoslav upgrade of the T-55A, intended for modernization of YPA's aging fleet of T-55s. It was using sophisticated components from M-84, local produced advanced versions of T-72, with whom it was in parallel development. Major improvements included external mounting of 2 rails for AT-3 Sagger missiles, an engine from T-72, a simplified SUV with meteosensor and laser rangefinders from M-84, addition of spaced armor on turret and front body, and installation of smoke dispensers. About 20 were made before break-up of Yugoslavia. Prototypes were impressed into regular service, however there is no data of them being used in combat.
A variant of this modification, intended for export, was armed with L7A1 105 mm gun.
Notes and references
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to T-54/T-55. |
- ↑ Miller, David The great Book of Tanks Salamander Books London, England 2002 338-341 ISBN 1-84065-475-9
- ↑ Halberstadt, Hans Inside the Great Tanks The Crowood Press Ltd. Wiltshire, England 1997 94-96 ISBN 1-86126-270-1
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Czołgi Świata (Tanks of the World or World's Tanks) (in Polish) 25. Poland: Amercom. 2008. pp. 11–13. ISBN 978-83-252-0022-0.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "abkhaziya.ORG article". Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 5.23 5.24 5.25 5.26 5.27 5.28 5.29 5.30 5.31 5.32 5.33 5.34 5.35 5.36 5.37 5.38 5.39 5.40 5.41 5.42 5.43 5.44 5.45 5.46 5.47 5.48 5.49 5.50 5.51 5.52 5.53 Military balance 2004-2005
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "N 98 (4 2008)". gov.karelia.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 7.8 7.9 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 7.15 7.16 7.17 7.18 7.19 7.20 7.21 7.22 7.23 7.24 7.25 7.26 7.27 7.28 7.29 7.30 7.31 7.32 7.33 7.34 7.35 7.36 7.37 7.38 7.39 7.40 7.41 7.42 7.43 7.44 7.45 7.46 7.47 7.48 7.49 7.50 7.51 "Trade Registers". sipri.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 10.8 10.9 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 10.15 10.16 10.17 10.18 10.19 10.20 10.21 10.22 10.23 10.24 10.25 10.26 10.27 10.28 10.29 10.30 10.31 10.32 10.33 10.34 10.35 10.36 10.37 10.38 10.39 10.40 10.41 10.42 10.43 10.44 10.45 10.46 10.47 10.48 10.49 Military balance 2006-2007
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 11.9 11.10 11.11 11.12 11.13 Deagel T-55
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 12.8 12.9 12.10 12.11 12.12 12.13 UN register of conventional arms
- ↑ Angola - Security Information
- ↑ Orbat Almanac 2004 Angola
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Ivan Bajlo. "Armor of Army B&". vojska.net. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Orbat Almanac 2004 Bosnia
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Cambodian army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Chadian army
- ↑ "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Congolese army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Rubén Urribarres. "Cuban Tanks, II part". Cuban Aviation. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Georgia Army Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 John Pike. "Tiran 4/5 (T-54/T-55)". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Iranian Ground Forces Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 35.6 35.7 35.8 35.9 35.10 35.11 35.12 35.13 35.14 35.15 35.16 35.17 35.18 35.19 35.20 35.21 35.22 35.23 35.24 35.25 35.26 35.27 35.28 35.29 35.30 35.31 35.32 35.33 35.34 35.35 35.36 35.37 35.38 35.39 35.40 35.41 35.42 35.43 35.44 35.45 35.46 35.47 35.48 35.49 35.50 35.51 35.52 35.53 35.54 35.55 35.56 35.57 35.58 35.59 35.60 35.61 35.62 35.63 35.64 35.65 35.66 35.67 35.68 35.69 35.70 35.71 35.72 35.73 35.74 35.75 35.76 35.77 35.78 35.79 35.80 35.81 35.82 35.83 35.84 35.85 35.86 35.87 35.88 35.89 35.90 35.91 35.92 35.93 35.94 35.95 35.96 35.97 35.98 35.99 35.100 35.101 35.102 35.103 35.104 35.105 35.106 35.107 35.108 35.109 35.110 35.111 35.112 "JED The Military Equipment Directory"
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 John Pike. "Iraqi Ground Forces Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Shapir, Yiftah S., Middle East Military Balance, Tel Aviv University, 6, 7 Iraq.pdf
- ↑ "shex ja3far puk". YouTube. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Does the Islamic State have a Scud missile?". Telegraph.co.uk. 30 June 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Equipment Holdings - Korean People's Army". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 "soldering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Army Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Libyan army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 45.3 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Nigeria - Security Information
- ↑ "Ukraine rebels go to the museum -- for WWII tanks and cannons". Yahoo News. 25 July 2014. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Peru Peruvian army land ground forces military equipment armoured vehicle". armyrecognition.com. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "T-54 main battle tank romania romanian army technical data sheet description information". armyrecognition.com. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 55.2 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Flanco Sur - Frente Polisario
- ↑ "RG article". Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "CryptoGSM : СМИ о прослушивании GSM : Грузия : Война в Южной Осетии: сколько на самом деле потеряла Россия". Cryptogsm.ru. 2014-01-13. Retrieved 2014-12-09.
- ↑ "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 62.2 62.3 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Syria - Army Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 69.2 "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 70.2 "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "2001". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "soldiering article". soldiering.ru. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Moscow's Strategy in Southern Africa: A Country by Country Review
- ↑ "Arc of Convergence: AQAP, Ansar al-Shari`a and the Struggle for Yemen - Combating Terrorism Center at West Point". usma.edu. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Czołgi Świata (Tanks of the World or World's Tanks) (in Polish). no. 25. Poland: Amercom. 2008. pp. 11–13. ISBN 978-83-252-0022-0.
- ↑ Ivan Bajlo. "Croatian Armor". vojska.net. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Carvallo, Mauricio (2008-11-30). "La guerra no contada desde la primera línea de fuego" [The Untold War From the Front Line]. El Mercurio (in Spanish) (Chile). Retrieved 2014-09-21. (subscription required (help)).
Pero como nos faltaban tanques para el norte, mandamos a buscar al Medio Oriente cuatro tanques T-54 y T-55. La idea era preparar con ellos a sus eventuales tripulaciones para que, cuando atacaran los peruanos, dañar los tanques lo menos posible y así poder aprovecharlos
- ↑ {{cite web|url=http://www.soldiering.ru/country/c19.php|title=2001|work=soldiering.ru|accessdate=9 December 2014}}
- ↑ Orbat Almanac 2004 Finland
- ↑ John Pike. "Army Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Bharat Rakshak: Land Forces Site - T-55". bharat-rakshak.com. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Arjun Tank inducted into 75 armoured regiment". The Times Of India. 12 March 2011.
- ↑ 83.0 83.1 83.2 83.3 83.4 "IDF Tiran Series". idf-armour-group.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ John Pike. "Army Equipment - Israel". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Strategic Analysis. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑
- ↑ John Pike. "Pakistan Army Equipment". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- ↑ John Pike. "Russian Army Equipment". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Warfare.ru
- ↑ Slovakian army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ Ivan Bajlo. "Slovenian Armor". vojska.net. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 92.0 92.1 Ukrainian army armyrecognition.com
- ↑ 93.0 93.1 John Pike. "Ground Forces Equipment - Ukraine". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 94.0 94.1 94.2 94.3 94.4 94.5 Karpenko, A.V.Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.) Bastion Nevskij 269-71
- ↑ 95.0 95.1 95.2 95.3 Markov, David Andrew Hull, Steven Zaloga Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices: 1945 to Present. Darlington Productions. 1999 ISBN 1-892848-01-5, pp. 22-27
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 96.2 96.3 96.4 96.5 96.6 96.7 96.8 Czołgi Świata (Tanks of the World or World's Tanks) (in Polish). no. 25. Poland: Amercom. 2008. pp. 03–05. ISBN 978-83-252-0022-0.
- ↑ 97.0 97.1 97.2 97.3 97.4 97.5 97.6 97.7 97.8 97.9 97.10 97.11 97.12 97.13 "T-54/T-55 Main Battle Tank". inetres.com. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 98.0 98.1 "Czołgi Świata" (World's Tanks or Tanks Of The World) magazine issue 20
- ↑ 99.0 99.1 99.2 Karpenko, A.V.Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.) Bastion Nevskij 276-85
- ↑ 100.0 100.1 100.2 100.3 100.4 100.5 100.6 100.7 100.8 100.9 Karpenko, A.V.Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.) Bastion Nevskij 291-307
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 101.2 101.3 101.4 101.5 101.6 101.7 "KMDB - T-55AGM - version of modernisation of T-54, T-55, T-59 and T-62 main battle tanks". morozov.com.ua. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Czołgi Świata" (World's Tanks or Tanks Of The World) magazine issue 10
- ↑ 103.0 103.1 "T-54 [ZSRR] - Pancerni.net". abajt.pl. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Ace ACE-72156 1/72 T-55A Soviet Main Battle Tank". aviapress.com. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Gau, Lutz-Reiner Jürgen Plate, Jörg Siegert Deutsche Militärfahrzeuge - Bundeswehr und NVA. Motorbuch, Stuttgart 2001-10-01 ISBN 3613021528
- ↑ 106.0 106.1 Markov, David Andrew Hull, Steven Zaloga Soviet/Russian Armor and Artillery Design Practices: 1945 to Present. Darlington Productions. 1999 ISBN 1892848015
- ↑ Domestic armored vehicles 1945-1965
- ↑ Bronetankovaja serija, issue 1.
- ↑ 109.0 109.1
- ↑ Karpenko,A.V.Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.) BastionNevskij 461-62
- ↑ 111.0 111.1 111.2 111.3 111.4 111.5 111.6 111.7 "Pancerni.net". abajt.pl. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Karpenko, A.V.Obozreniye Bronetankovoj Tekhniki (1905-1995 gg.) Bastion Nevskij 455-56
- ↑ "KMDB - OT-54, TO-55 and Obiect 483 Flamethrower Tanks". morozov.com.ua. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia Index Page". jedsite.info. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 115.0 115.1 Dr C Kopp, SMAIAA, SMIEEE, PEng. "Legacy Air Defence System Upgrades". ausairpower.net. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "Fire Fighting Vehicle SPOT-55". army.cz. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 117.0 117.1 117.2 [Jörg Siegert Typenkompass Panzer der NVA 1956 -1990, Motorbuch Verlag, ISBN 978-3-613-02954-5]
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 [Jörg Siegert/Helmut Hanske Kapmpfpanzer der NVA, Motorbuch Verlag, ISBN 978-3-613-03294-1]
- ↑ 119.0 119.1 "BLP72". militaertechnik-der-nva.de. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ 120.0 120.1 Suomalaiset Panssarivaunut 1918-1997, page 24
- ↑ Zaloga, Steven: "T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tanks 1944-2004". Osprey Publishing, 2004. Page 36.
- ↑ "Sức mạnh T-54/55 Việt Nam tăng đáng kể". Tin Quân sự - Thủ tướng Nguyễn Tấn Dũng. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ Diseños Casanave SA - MODERNIZACIÓN DE VEHICULOS DE COMBATE
- ↑ Sin autorización del Mindef el CCFFAA evalúa modernización de tanques T-55. La República (2010-01-22). Retrieved on 2011-02-24.
- ↑ Peru; Russian Uralvagonzavod offers converted T-55 fire support version - Dmilt.com, 4 July 2013
- ↑ John Pike. "T-54 / T-55 Main Battle Tank". globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ free.polbox.pl
- ↑ 128.0 128.1 Technika Wojska Polskiego, Bellona, Warsaw 1998.
- ↑ 129.0 129.1 129.2 Technika Wojska Polskiego, Bellona, Warsaw 1998 page 87
- ↑ "Domena ratownictwo.org.pl jest utrzymywana na serwerach nazwa.pl". ratownictwo.org.pl. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ http://www.wzinz.com.pl/index.php?id=oferta&sprzet=czolg-pomostowy
- ↑ Tankograd Gazette
- ↑ "Revista A.F.T 3/2000 - Tancul romanesc - prezent si perspective". actrus.ro. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑ "SPAM protection / Ochrana proti SPAMu". ic.cz. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
- ↑
- ↑ Military Industry Corporation (MIC) - DIGNA
- ↑ "KMDB - T-55AGM - weapons". morozov.com.ua. Retrieved 9 December 2014.
