Supernode (circuit)
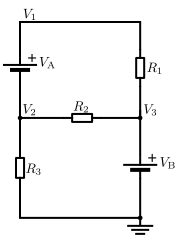
In this circuit, both VA and VB are super-nodes. VA has two unreferenced nodes, whereas VB has one referenced node (ground) and one unreferenced node.
In circuit theory, a super-node is a theoretical construct that can be used to solve a circuit. This is done by viewing a voltage source on a wire as a point source voltage in relation to other point voltages located at various nodes in the circuit, relative to a ground node assigned a zero or negative charge.
Each super-node contains two nodes, one a non-reference node and another node that may be a second non-reference node or the reference node. Super-nodes containing the reference node have one node voltage variable. For Nodal circuit analysis, the super-node construct is only required between two non-reference nodes.