Superficial transverse perineal muscle
| Superficial transverse perineal muscle | |
|---|---|
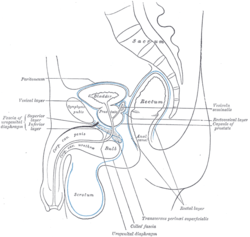 Median sagittal section of male pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciæ. (Transversus perinei superficialis visible at bottom right.) | |
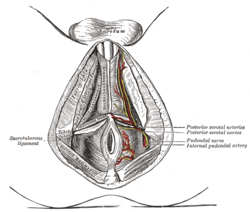 The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery in male pelvis. (Transversus perinei labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Latin | musculus transversus perinei superficialis |
| anterior part of ischial tuberosity | |
| Perineal body | |
| Internal pudendal artery | |
| Perineal nerve | |
| Actions | Fixation of central tendon of perineum, support of pelvic floor[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.427 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | m_22/12551265 |
| TA | A09.5.02.003 |
| FMA | 19731 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The superficial transverse perineal muscle ('transversus perinei;, transversus perinei superficialis ) is a narrow muscular slip, which passes more or less transversely across the perineal space anterior to the anus.
Origin and insertion
It arises by tendinous fibers from the inner and forepart of the tuberosity of the ischium, and, running medially, is inserted into the central tendinous point of the perineum (perineal body), joining in this situation with the muscle of the opposite side, with the Sphincter ani externus muscle behind, and with the Bulbospongiosus muscle in front.
In some cases, the fibers of the deeper layer of the Sphincter ani externus decussate in front of the anus and are continued into this muscle. Occasionally it gives off fibers, which join with the Bulbocavernosus of the same side.
Variations are numerous. It may be absent or double, or insert into Bulbocavernosus or External sphincter.
Additional images
-
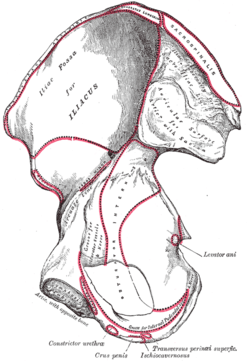
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
Notes
- ↑ Saladin (2003), Muscles of the Pelvic Floor, p 354
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Saladin, Kenneth S. (2003). Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function (3rd ed.). McGraw−Hill.
External links
- -697630643 at GPnotebook
- Anatomy photo:41:11-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Muscles of the Superficial Perineal Pouch"
- Anatomy image:9148 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:9163 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy image:9172 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||