Sukhoi Su-7
| Su-7 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Su-7BKL | |
| Role | Fighter-bomber/Ground-attack |
| Manufacturer | Sukhoi OKB |
| First flight | 7 September 1955 |
| Introduction | 1959 |
| Retired | 1990 |
| Primary user | Soviet Air Force Indian Air Force |
| Produced | 1957-1972 |
| Number built | 1,847 (mainly Su-7B series) |
| Developed into | Sukhoi Su-17 |
The Sukhoi Su-7 (NATO designation name: Fitter-A) was a swept wing, supersonic fighter aircraft developed by the Soviet Union in 1955. Originally, it was designed as tactical, low-level dogfighter, but was not successful in this role. On the other hand, soon-introduced Su-7B series became the main Soviet fighter-bomber and ground-attack aircraft of the 1960s. The Su-7 was rugged in its simplicity but its shortcomings included short range and low weapon load.[1]
Design and development
Original Su-7 fighters
On 14 May 1953, after Joseph Stalin's death, the Sukhoi OKB was reopened[2] and by the summer, it began work on a swept-wing front-line[N 1] fighter. The first prototype, designated S-1, was designed to use the new Lyulka AL-7 turbojet engine. It was the first Soviet aircraft to utilize the all-moving tailplane and a translating centerbody, a movable inlet cone in the air intake for managing airflow to the engine at supersonic speeds.[3] The aircraft also had a dramatic wing sweep of 60°, irreversible hydraulically boosted controls, and an ejection seat of OKB's own design.[2]
The S-1 first flew on 7 September 1955 with A. G. Kochetkov at the controls. Fitted with an afterburning version of the AL-7 engine after the first 11 flights, the prototype set a Soviet speed record of 2,170 km/h (1,170 kn, 1,350 mph, Mach 2.04) in April 1956.[3] The prototype was intended to be armed with three 37 mm Nudelman N-37 cannon and 32 spin-stabilized 57 mm (2.25 in) unguided rockets in a ventral tray.[3] The second prototype, S-2, introduced some aerodynamic refinements. Testing was complicated by the unreliable engine and S-1 was lost in a crash on 23 November 1956, killing its pilot I. N. Sokolov.[2] Only 132 had been produced between 1957–1960, and the aircraft entered service as Su-7 in 1959.
Su-7B fighter-bomber
On 31 July 1958, Soviet tactical aviation (Frontovaya Aviatsiya,[N 1] фронтовая авиация) tasked Sukhoi with developing a ground-attack variant of the Su-7, which could replace the scrapped Ilyushin Il-10. The resulting prototype, S-22, incorporated structural refinements for high-speed, low-altitude operations. It first flew in March 1959, and entered service in 1961 as the Su-7B.[3]
Operationally, Su-7s were hampered by a high landing speed of 340–360 km/h,[4] as dictated by the thin, highly-swept wing. Combined with poor visibility from the cockpit, and lack of an instrument landing system, it made operations very difficult, especially in poor weather or on poor airfields.[5] In 1961-1962, Sukhoi experimented with blown flaps on S-25 but the benefit was too small to warrant implementation. JATO rockets tested on S-22-4 proved more useful and were incorporated into Su-7BKL. Attempts to improve takeoff and landing performance eventually resulted in the Sukhoi Su-17.
Operational history
Su-7A fighter
The front-line[N 1] fighter version saw limited operational use in the Far East from 1958, but by 1959, a decision was made to proceed with production of the MiG-21, and less than 200 units were deployed. The Su-7A was retired in 1965.[2] They never saw combat.
Su-7B fighter-bomber

Su-7B and its variants became the main Soviet ground-attack aircraft of the 1960s. They were also widely exported (691 planes,[2] including also some trainers). However, the very short combat radius and need for long runways limited its operational usefulness. On the other hand, despite its notoriously heavy controls, the Su-7 was popular with pilots for its docile flight characteristics, simple controls and considerable speed even at low altitudes. It also had a reputation for easy maintenance. From 1977-1986 the Su-7s remaining in Soviet service have been replaced by Su-17 and MiG-27.
Egypt

The Su-7 saw combat with Egypt in the 1967 Six Day War, the subsequent War of Attrition, and saw use in the Yom Kippur War by the Egyptians to attack Israeli ground forces.
India
The Indian Air Force (IAF) used the Su-7 extensively in the 1971 war with Pakistan. Six squadrons, totaling in 140 aircraft, flew almost 1,500 offensive sorties during the war,[4] and undertook the bulk of the daytime attack efforts. The IAF managed to retain a very high operational tempo with its Su-7s, peaking at a sortie rate of six per pilot per day.[4] Fourteen Su-7s were lost during the war, mostly due to AA fire.[4] After the war was over, it was found that the aircraft had a high survivability, being able fly home safely despite receiving heavy damage. For example, Wing Commander H. S. Mangat's Su-7 was badly damaged by a Sidewinder missile fired from PAF MiG-19. The impact was so severe that half the rudder was missing, the elevators, ailerons and flaps were severely damaged, and half the missile was stuck in the chute pipe.[4] The pilot made it back to his base. The death of at least one Indian pilot can be attributed, at least indirectly, to poor cockpit design. A pilot set his seating at a dangerous position "because he found the bomb sight and the front gun sight easier to operate" while in that position, and was killed on ejection.[6]
Variants



A total of 1,847 Su-7 and its variants were built.[2]
- Su-7
- First production version. The only production version that was a tactical air superiority fighter. Factory designation S-2. Manufactured 1957-1960 with 132 built. Remained in operational service until 1965.
- Su-7B
- The first ground-attack version, factory designation S-22. Manufactured 1960-1962 with 431 built.[7]
- Su-7BM
- Upgraded AL-7F-1 engine, upgraded fuel system with external piping on either side of the fuselage spine, fuel tanks installed in the wings, "wet" underwing hardpoints for carrying external fuel tanks, capable of carrying tactical nuclear bombs. Manufactured 1963-1965 with 290 built.[7]
- Su-7BKL
- Rough-field capable variant with skids affixed to the sides of the main landing gear, provision for two SPRD-110 JATO rockets of 29.4 kN (13,300 lbf) thrust, and twin brake parachutes. Introduced in 1965, factory designation S-22KL. Manufactured 1965-1972 with 267 built.[7]
- Su-7BMK
- A simplified export version of Su-7BM. Manufactured 1967-1971 with 441 built.[7]
- Su-7U (NATO Moujik)
- Two-seat trainer version of the Su-7B with reduced fuel capacity. First flight 25 October 1965. Manufactured 1966-1972 in parallel with the export version, designated Su-7UMK.
- Su-7UM (NATO Moujik)
- Two-seat training version of the Su-7BM.
- Su-7UMK (NATO Moujik)
- Two-seat training version of the Su-7BMK. All Su-7 trainers amounted to 411 built.[7]
- Su-7IG
- Experimental variable geometry wing aircraft which was developed into Sukhoi Su-17.
- 100LDU Control Configured Vehicle
- A Su-7U modified with canards and a longitudinal stability augmentation system. It was designed as a testbed for a fly-by-wire system for the Sukhoi T-4. It was later used in 1973–1974 during the development of the Su-27's fly-by-wire system.
OKB-51 designations
- S-1
- (Strelovidnoye [krylo] – swept wings) OKB-51 designation for the first prototype of the Su-7 / Su-9 family.
- S-2
- OKB-51 designation for the first production version of the Su-7.
- S-22
- OKB-51 designation for the Su-7B production aircraft.
- S-22-2
- OKB-51 designation for the prototype of the Su-7BM.
- S-22M
- OKB-51 designation for the Su-7BM production aircraft.
- S-22KL
- OKB-51 designation for the Su-7BKL production aircraft, incorporating the Short field equipment tested on the S-22-4.
- S-23
- As a precursor to the S-22-4 tests, the S-23 was tested with a pure ski undercarriage and with skis on the main legs only
- S-22-4
- An S-22 tested with wheel / Ski undercarrriage, brake Parachute and SPRD-110 JATO boosters for rough/unpaved field operations.
- S-25
- This aircraft was used for Boundary Layer Control (BLC) tests, with compressor bleed air blown over the leading edges to reduce field length.
- S-25T
- A Su-7 fitted with the Boundary Layer Control system, rigged especially for use in a full-scale wind tunnel.
- S-26
- A continuation of the S-22-4 testing with wheel/ski undercarriage, double brake parachute and JATO boosters (The S-26 survives on display at the Russian Air Force Museum, Monino).
- S-22MK
- A simplified export version of the Su-7BKL, designated Su-7BMK
- U-22
- A belated trainer version with two seats in tandem in an extended nose based on the Su-7BM.
- U-22MK
- OKB-51 designation for the export version of the Su-7U, designated Su-7UMK by the Soviet Air Force
- S-3
- A projected interceptor version of the S-2, with "Izumrud" radar and avionic equipment in a re-configured nose section.
- S-41
- OKB-51 designation for the an experimental version of the S-1/S-2 with a lengthened nose and area-ruled rear fuselage.
- T-1
- A delta-wing tactical fighter project, based on the S-2, cancelled with the prototype nearly complete.
- T-3
- A delta-winged interceptor version of the S-2, developed in parallel to the S-3 and T-1. This would eventually lead to the T-43 prototype of the Su-9 interceptor.
Operators
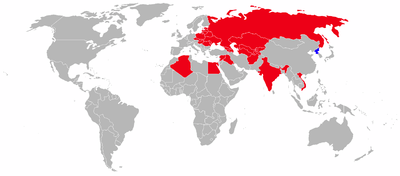 | |
| Blue = Current | Dark Red = Former |
|---|---|
Current Operators
- North Korean Air Force – received at least 28 Su-7BMK/-7UMK in 1971. The aircraft were ordered in 1969.
Former operators
- Afghan Air Force - 24 Su-7BMK and 16 Su-7U trainers, were delivered to Afghanistan from 1972. Constant fighting, a high accident rate in the high altitude and poor maintenance caused substantial attrition. An addition 79 used replacements from Soviet stocks were supplied during the 1980s. None remain in service.
- Algerian Air Force - 20 Su-7BMK and 8 Su-27UM.
- Czechoslovak Air Force – the Czechoslovak Air Force was the first foreign operator of the Su-7 in 1963. Totals included 64 Su-7BM, 31 Su-7BKL and Su-7U. During operations service, 30 aircraft were lost in accidents. The remaining aircraft were phased out in 1990.
- Egyptian Air Force – The first batch of 14 Su-7BMK was destroyed during the Six Day War. From 1967-1972, Egypt received an additional 185 Su-7BMK/SU-7UMK. Those which survived the October War with Israel were retired in the mid-1980s.
.jpg)
- Indian Air Force - 140 were delivered in 1968, equipping six squadrons. An additional 14 attrition replacements were provided. The last units were retired in 1986.[8]
- Iraqi Air Force – Iraq received 18 Su-7BKL in 1968, with 83 more subsequently delivered. No longer in service
- Polish Air Force - operated 6 Su-7BM, 33 Su-7BKŁ and 8 Su-7U from July 1964 until June 1990; no longer in service.
- Soviet Air Force
- Syrian Air Force - Shortly after the Six Day War, Syria received 25 Su-7s. In the October War Syria lost most of the aircraft supplied. After 1973, The Soviet Union resupplied Syria with 35 more aircraft. By the mid 1980s, the Su-7 had been transferred to the reserves, and by the 1990s were decommissioned.
Specifications (Su-7BKL)

General characteristics
- Crew: One
- Length: 16.80 m (55 ft 1 in)
- Wingspan: 9.31 m (30 ft 7 in)
- Height: 4.99 m (16 ft 4 in)
- Wing area: 34 m² (366 ft²)
- Empty weight: 8937 kg (lb)
- Loaded weight: 13,570 kg (29,915)
- Max. takeoff weight: 15,210 kg (33,530 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Lyulka AL-7F-1 afterburning turbojet
- Dry thrust: 66.6 kN (14,980 lbf)
- Thrust with afterburner: 94.1 kN (22,150 lbf)
- *Fuel capacity: 3,220 kg (7,100 lb)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,150 km/h (620 kn, 715 mph, Mach 0.94) at sea level; 2,150 km/h (1,160 kn, 1,335 mph) at high altitude
- Range: 1,650 km (890 nmi, 1,025 mi)
- Service ceiling: 17,600 m (57,740 ft)
- Rate of climb: 160 m/s (31,500 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 434.8 kg/m² (89.05 lb/ft²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.71
- Takeoff roll: 950 m (3,120 ft)
- Landing roll: 700 m (2,300 ft)
Armament
- 2 × 30 mm Nudelman-Rikhter NR-30 cannon, 80 rounds each
- Up to 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) on six hardpoints, typically including two 950 l or 600 l fuel tanks under the fuselage, and a combination of 250 kg (551 lb) or 500 kg (1,102 lb) bombs and 57-mm spin-stabilized unguided rockets in UB-16-57U pods. One 8U69 5-kiloton nuclear bomb could be carried on the left fuselage hardpoint. Some versions could also carry two 600 l underwing drop tanks.
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Dassault Mirage IIIE
- HAL HF-24 Marut
- Hawker Hunter
- Nanchang Q-5
- Republic F-105 Thunderchief
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 In Soviet terminology, the front-line fighter (frontovoi istrebitel, фронтовой истребитель; also called frontal or tactical fighter) is the one that is intended to be operationally deployed within fronts for use over the battlefield, as opposed to interceptor aircraft deployed by Soviet Air Defence Forces (PVO).
Citations
- ↑ Wheeler 1992, p. 143.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "Sukhoi Su-7." Sukhoi Company Museum. Retrieved: 28 January 2011
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. The Great Book of Fighters. St. Paul, Minnesota: MBI Publishing, 2001. ISBN 0-7603-1194-3.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Rakshak, Bharat. "A whale of a fighter: Su-7 in IAF service." bharat-rakshak.com. Retrieved: 28 January 2011.
- ↑ Nijboer and Patterson 2003, pp. 174–177.
- ↑ Dikshit, Mohan B. "To Err is Human Case Reports of Two Military Aircraft Accidents." SQU Med J, Volume 10, Issue 1, 2010, pp. 120–125.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Goebel, Greg. "Sukhoi Su-7." Aviation Vectors, 1 August 2009. Retrieved: 28 January 2011.
- ↑ Rakshak, Bharat. "Su-7." IAF History. Retrieved; 28 January 2011.
Bibliography
- Nijboer, Donald and Dan Patterson. Cockpits of the Cold War. Eden Prairie, Ontario: The Boston Mills Press, 2003. ISBN 1-55046-405-1.
- Wheeler, Barry C. The Hamlyn Guide to Military Aircraft Markings. London: Chancellor Press, 1992. ISBN 1-85152-582-3.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sukhoi Su-7. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||