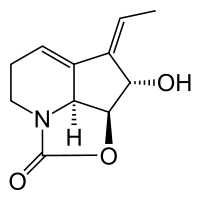
Streptazolin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2a1S,6Z,7S,7aS)-6-ethyliden-2a1,3,4,6,7,7a-hexahydro-7-hydroxy-1-oxa-2a-azacyclopenta[cd]inden-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:542525 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL450203 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 11769676 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C11H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 207.23 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Streptazolin is an antibiotic and antifungal substance isolated in 1981 from Streptomyces viridochromogenes.[1][2]
Because of its polymerisation tendency, it is not suitable for therapeutic use. 1,4-reduction of the conjugated diene gives dihydrostreptazolin which is stable, but has very limited microbial properties.<ref name=" name="Drautz" />
The first total synthesis of (racemic) streptazolin was achieved in 1985 with the aid of a modified Ferrier rearrangement.[3][4]
References
- ↑ Drautz, H, Zähner, H (1981). "Isolation and structure of streptazolin". Helv. Chim. Act. 64 (6): 1752–65. doi:10.1002/hlca.19810640605.
- ↑ Karrer, A, Dobler, M (1982). "Stoffwechselprodukte von Mikroorganismen 217. Mitteilung Röntgenstrukturanalyse von O-Acetyldihydrostreptazolin". Helv. Chim. Act. 65 (5): 1432–35. doi:10.1002/hlca.19820650516.
- ↑ Kozikowski, AP, Pyeong-uk Park (1984). "Synthesis of 2-substituted .DELTA.3-piperidines: the nitrogen analog of the Ferrier rearrangement. An approach to streptazolin". J. Org. Chem. 49 (9): 1674–1676. doi:10.1021/jo00183a044.
- ↑ Kozikowski, AP, Pyeong-uk Park (1985). "Total synthesis of streptazolin - an application of the aza-analogue of the ferrier rearrangement". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107 (6): 1763–65. doi:10.1021/ja00292a054.