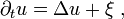Stochastic partial differential equation
| Differential equations | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Navier–Stokes differential equations used to simulate airflow around an obstruction. | |||||
| Classification | |||||
|
Types
|
|||||
|
Relation to processes
|
|||||
| Solution | |||||
|
General topics
|
|||||
Stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) are similar to ordinary stochastic differential equations. They are essentially partial differential equations that have random forcing terms and coefficients. They can be exceedingly difficult to solve. However, they have strong connections with quantum field theory and statistical mechanics.
One difficulty encountered when dealing with stochastic PDEs is their lack of regularity. For example, one of the most classical SPDEs is given by the stochastic heat equation which can formally be written as
where 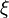 denotes space-time white noise and
denotes space-time white noise and 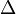 is the Laplacian.
In one space dimension, solutions to this equation are only almost 1/2-Hölder continuous in space and 1/4-Hölder continuous in time. For dimensions two and higher, solutions are not even function-valued, but can be made sense of as random distributions.
is the Laplacian.
In one space dimension, solutions to this equation are only almost 1/2-Hölder continuous in space and 1/4-Hölder continuous in time. For dimensions two and higher, solutions are not even function-valued, but can be made sense of as random distributions.