Sternum
| Sternum | |
|---|---|
 Position of breastbone in human (shown in red). | |
 Posterior surface of breastbone. | |
| Details | |
| Latin | Sternum |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.119 |
| MeSH | A02.835.232.904.766 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | s_23/12758288 |
| TA | A02.3.03.001 |
| FMA | 7485 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The sternum (a modern Latin word from Greek στέρνον, sternon, "chest"; plural "sternums" or "sterna") or breastbone is a long flat bony plate shaped like a necktie located anteriorly to the heart in the center of the thorax (chest). It connects to the rib bones via cartilage, forming the anterior section of the rib cage with them, and thus helps to protect the lungs, heart and major blood vessels from physical trauma. Although it is fused, the breastbone can be sub-divided into three regions: the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process.[1]
Structure
The sternum is an elongated, flattened bone, forming the middle portion of the anterior wall of the thorax. The superior end supports the clavicles (collarbones), and its margins articulate with the cartilages of the first seven pairs of ribs. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It consists of three main parts, listed superior to inferior:
- Manubrium
- Body
- Xiphoid process
In its natural position, the inclination of the bone is oblique from above, downward and forward. It is slightly convex in front and concave behind; broad above, shaped like a "T", becoming narrowed at the point where the manubrium joins the body, after which it again widens a little to below the middle of the body, and then narrows to its lower extremity. Its average length in the adult is about 17 cm, and is rather longer in the male than in the female.
In the early life of a person, the breastbone's body is divided into four segments, not three, called sternebrae (singular: sternebra).
|
Manubrium

The manubrium, (Latin: handle), or manubrium sterni is the broad upper part of the breastbone. It has a quadrangular shape, narrowing from the top, which gives it four borders. The suprasternal (jugular) notch is medially located at the upper broadest part of the manubrium. This notch can be felt between the two clavicles (collarbones). On other side of this notch are the right and left clavicular notches.[1] The manubrium articulates with the body of the breastbone, the clavicles and the cartilages of the first pair of ribs. The inferior border, oval and rough, is covered in a fresh state with a thin layer of cartilage for articulation with the body. The lateral borders are each marked above by a depression for the first costal cartilage, and below by a small facet, which, with a similar facet on the upper angle of the body, forms a notch for the reception of the costal cartilage of the second rib. Between the depression for the first costal cartilage and the demi-facet for the second is a narrow, curved edge, which slopes from above downward towards the middle.
Body
The body, or gladiolus, is the longest part. It is flat and considered to have only a front and back surface. The front surface is flat, directed upward and forward, and marked by three transverse ridges which cross the bone opposite the third, fourth, and fifth articular depressions. It affords attachment on either side to the sternal origin of the pectoralis major. At the junction of the third and fourth parts of the body, is occasionally see an orifice, the sternal foramen, of varying size and form. The posterior surface, slightly concave, is also marked by three transverse lines, less distinct, however, than those in front; from its lower part, on either side, the transversus thoracis takes origin.
The sternal angle is located at the point where the body joins the manubrium. The sternal angle can be felt at the point where the sternum projects farthest forward. However, in some people the sternal angle is concave or rounded. During physical examinations, the sternal angle is a useful landmark because the second rib attaches here.[1]
Each lateral border, at its superior angle, has a small facet, which with a similar facet on the manubrium, forms a cavity for the cartilage of the second rib; below this are four angular depressions which receive the cartilages of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth ribs. The inferior angle has a small facet, which, with a corresponding one on the xiphoid process, forms a notch for the cartilage of the seventh rib. These articular depressions are separated by a series of curved interarticular intervals, which diminish in length from above downward, and correspond to the intercostal spaces. Most of the cartilages belonging to the true ribs, articulate with the breastbone at the lines of junction of its primitive component segments. This is well seen in many of the lower animals, where the parts of the bone remain ununited longer than in man.
The upper border is oval and articulates with the manubrium, at the sternal angle (angulus Ludovici). The lower border is narrow, and articulates with the xiphoid process.
Xiphoid process
Located at the inferior end of the sternum is the pointed xiphoid process. Improperly performed chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation can cause the xiphoid process to snap off, driving it into the liver which can cause a fatal hemorrhage.[1]
The breastbone is composed of highly vascular tissue, covered by a thin layer of compact bone which is thickest in the manubrium between the articular facets for the clavicles.
Articulations
The superior seven costal cartilages articulate with the sternum forming the costal margin anteriorly. The right and left clavicular notches articulate with the right and left clavicles, respectively. The costal cartilage of the second rib articulates with the breastbone at the sternal angle making it easy to locate.[2]
The transversus thoracis muscle is innervated by the intercostal nerve and superiorly attaches at the posterior surface of the lower breastbone. Its inferior attachment is the internal surface of costal cartilages two through six and works to depress the ribs.[3]
Development
The breastbone originally consists of two cartilaginous bars, situated one on either side of the median plane and connected with the cartilages of the upper nine ribs of its own side.
These two bars fuse with each other along the middle line to form the cartilaginous breastbone which is ossified from six centers: one for the manubrium, four for the body, and one for the xiphoid process [Fig. 4].
The ossific centers appear in the intervals between the articular depressions for the costal cartilages, in the following order: in the manubrium and first piece of the body, during the sixth month of fetal life; in the second and third pieces of the body, during the seventh month of fetal life; in its fourth piece, during the first year after birth; and in the xiphoid process, between the fifth and eighteenth years.
The centers make their appearance at the upper parts of the segments, and proceed gradually downward. To these may be added the occasional existence of two small episternal centers, which make their appearance one on either side of the jugular notch; they are probably vestiges of the episternal bone of the monotremata and lizards.
Occasionally some of the segments are formed from more than one center, the number and position of which vary [Fig. 6]. Thus, the first piece may have two, three, or even six centers.
When two are present, they are generally situated one above the other, the upper being the larger; the second piece has seldom more than one; the third, fourth, and fifth pieces are often formed from two centers placed laterally, the irregular union of which explains the rare occurrence of the sternal foramen [Fig. 7], or of the vertical fissure which occasionally intersects this part of the bone constituting the malformation known as fissura sterni; these conditions are further explained by the manner in which the cartilaginous sternum is formed.
More rarely still the upper end of the sternum may be divided by a fissure. Union of the various centers of the body begins about puberty, and proceeds from below upward [Fig. 5]; by the age of twenty-five they are all united.
The xiphoid process may become joined to the body before the age of thirty, but this occurs more frequently after forty; on the other hand, it sometimes remains ununited in old age. In advanced life the manubrium is occasionally joined to the body by bone.
When this takes place, however, the bony tissue is generally only superficial, the central portion of the intervening cartilage remaining unossified.
-

Figure 4 : Ossification of the breastbone.
-

Figure 5
-

Figure 6 : Peculiarities.
-

Figure 7
Clinical significance
Bone marrow biopsy
Because the breastbone contains bone marrow, it is sometimes used as a site for bone marrow biopsy. In particular, patients with high BMI (obese or grossly overweight) may present with excess tissue that makes access to traditional marrow biopsy sites (i.e. the pelvis) difficult.
Fractures
Fractures of the breastbone are rather uncommon. They may result from trauma, such as when a driver's chest is forced into the steering column of a car in a car accident. A fracture of the sternum is usually a comminuted fracture. The most common site of sternal fractures is at the sternal angle. Some studies reveal that repeated punches or continual beatings, sometimes called "breastbone punches", to the sternum area have also caused fractured sternums. Those are known to have occurred in contact sports such as rugby and football. Breastbone fractures are frequently associated with underlying injuries such as pulmonary contusions, or bruised lung tissue.[4] A somewhat rare congenital condition of the sternum is a sternal foramen, a single round hole in the breastbone that is present from birth and usually is off-centered to the right or left, commonly forming in the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th segments of the breastbone body. Congenital sternal foramens can often be mistaken for bullet holes.[5]
Sternotomy
The breastbone is sometimes cut open (a median sternotomy) to gain access to the thoracic contents when performing cardiothoracic surgery or other thoracic surgery.
Other animals


The sternum or breastbone, in vertebrate anatomy, is a flat bone that lies in the middle front part of the rib cage. It is endochondral in origin.[6] It probably first evolved in early tetrapods as an extension of the pectoral girdle; it is not found in fish. In amphibians and reptiles it is typically a shield-shaped structure, often composed entirely of cartilage. It is absent in both turtles and snakes. In birds it is a relatively large bone and typically bears an enormous projecting keel to which the flight muscles are attached.[7] Only in mammals does the sternum take on the elongated, segmented form seen in humans.
Insects
In arachnids, the sternum is the ventral (lower) portion of the cephalothorax. It consists of a single sclerite situated between the coxa, opposite the carapace.
Etymology
English sternum is a translation of Ancient Greek στέρνον.[8] The Greek writer Homer used the term στέρνον to refer to the male chest.[9][10] The term στῆθος was used by Homer to refer to the chest of both sexes.[9][10] The Greek physician Hippocrates used στέρνον to refer to the chest,[9][10] and στῆθος to the breastbone.[9][10] The Greek physician Galen was the first to use στέρνον in the present meaning of breastbone.[9][10]
The στέρνον can be considered as the solid bony part of the chest.[11] From that perspective, στέρνον can be related to Ancient Greek στερεός/στερρός,[11] firm/solid.[10] English breastbone is actually more akin to Latin os pectoris,[12][13] derived from classical Latin os, bone[14] and pectus, chest/breast.[14] Confusingly, pectus is also used in classical Latin as breastbone.[14]
Additional Images
-

Position of breastbone (shown in red). Animation.
-

Shape of human breastbone. Animation.
-

Breastbone seen posteriorly.
-

Breastbone cut along the frontal plane showing interior of the bone.
-

Lateral border of breastbone.
-

Sternum, lateral aspect.
-

Position of breastbone on the thoracic cage.
-
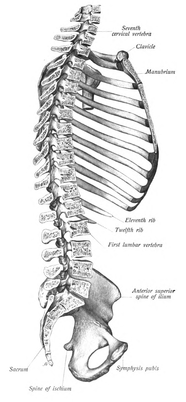
Breastbone in sagital section connected to axial skeleton.
-

Sternum in situ connected to ribcage and clavicle.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sternum. |
- This article uses anatomical terminology; for an overview, see anatomical terminology.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Saladin, Kenneth S. (2010). Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, Fifth Edition. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. p. 266. ISBN 978-0-07-352569-3.
- ↑ Agur, Anne M.R.; Dalley, Arthur F. II (2009). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy, Twelfth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2.
- ↑ Agur, Anne M.R.; Dalley, Arthur F. II (2009). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy, Twelfth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 21. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2.
- ↑ Sattler S, Maier RV (2002). "Pulmonary contusion". In Karmy-Jones R, Nathens A, Stern EJ. Thoracic Trauma and Critical Care. Berlin: Springer. pp. 235–243. ISBN 1-4020-7215-5. Retrieved 2008-04-21.
- ↑ Byers, S.N. (2008). Introduction to Forensic Anthropology. Toronto: Pearson.
- ↑ Kardong, Kenneth V. (1995). Vertebrates: comparative anatomy, function, evolution. McGraw-Hill. pp. 55, 57. ISBN 0-697-21991-7.
- ↑ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. p. 188. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ↑ Triepel, H. (1910). Die anatomischen Namen. Ihre Ableitung und Aussprache. Mit einem Anhang: Biographische Notizen.(Dritte Auflage). Wiesbaden: Verlag J.F. Bergmann.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Hyrtl, J. (1880). Onomatologia Anatomica. Geschichte und Kritik der anatomischen Sprache der Gegenwart. Wien: Wilhelm Braumüller. K.K. Hof- und Unversitätsbuchhändler.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with the assistance of. Roderick McKenzie. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kraus, L.A. (1844). Kritisch-etymologisches medicinisches Lexikon (Dritte Auflage). Göttingen: Verlag der Deuerlich- und Dieterichschen Buchhandlung.
- ↑ Schreger, C.H.Th.(1805). Synonymia anatomica. Synonymik der anatomischen Nomenclatur. Fürth: im Bureau für Literatur.
- ↑ Siebenhaar, F.J. (1850). Terminologisches Wörterbuch der medicinischen Wissenschaften. (Zweite Auflage). Leipzig: Arnoldische Buchhandlung.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Lewis, C.T. & Short, C. (1879). A Latin dictionary founded on Andrews' edition of Freund's Latin dictionary. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
