Springfield Union Station (Illinois)
|
Union Station | |
 | |
|
The former Springfield Union Station, renovated to serve as the Lincoln Presidential Library Visitor Center | |
 | |
| Location |
500 East Madison Street, Springfield, Illinois |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 39°48′13″N 89°38′55″W / 39.80361°N 89.64861°WCoordinates: 39°48′13″N 89°38′55″W / 39.80361°N 89.64861°W |
| Built | 1896 |
| Architect | Francis T. Bacon |
| Architectural style | Richardsonian Romanesque |
| NRHP Reference # | 78001189[1] |
| Added to NRHP | November 27, 1978 |
Springfield Union Station in Springfield, Illinois, is a former train station and now part of the complex of buildings that together form the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and is located at 500 East Madison Street (5th & Madison) in downtown Springfield, adjacent to the Lincoln Presidential Library.
History
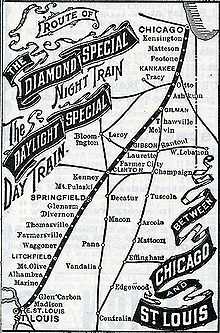
Springfield Union Station was designed in the Richardson Romanesque style in 1896 as a combined passenger terminal for several railroads serving Springfield, including the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad, Illinois Central Railroad, and the St. Louis, Peoria and Northern Railway. Although the structure was intended to be used jointly by these railroads, the Illinois Central was the predominant carrier, and the architect was Illinois Central chief architect Francis T. Bacon. The station was built in 1897-1898 at a cost of $75,000, and opened for business on January 2, 1898.[2] During its 73 years of active service, the station carried substantial passenger train traffic to and from Chicago, St. Louis, and other cities.
The vast majority of passenger trains serving Springfield Union Station were operated by the Illinois Central Railroad, although when the station was first opened, Illinois Central only served Springfield on a route extending northeast to Clinton, Gilman and Chicago. In 1899, Illinois Central acquired the Springfield to St. Louis segment of the former St. Louis, Peoria and Northern Railway, allowing expansion of Illinois Central service from Springfield south to St. Louis. On June 17, 1900, two premier trains (the Daylight Special and the Diamond Special) were inaugurated on this route to compete with existing St. Louis-Springfield-Chicago service offered by the Chicago and Alton Railroad. By 1936, the Illinois Central name trains serving Springfield were the Green Diamond and the Night Diamond.
Baltimore and Ohio passenger service through Springfield was secondary in nature, with service over one line from Indianapolis and Decatur to Springfield, and over a second route between Flora, Pana, Springfield and Beardstown. The B&O had been one of the original tenants in Springfield Union Station, but after purchasing the Alton Railroad in 1931, B&O trains were shifted from Union Station to the former Chicago and Alton station. The Indianapolis service was discontinued west of Decatur during World War II, leaving only a single motorcar train serving Springfield on the Flora to Beardstown line. Following the sale of the Alton Railroad to the Gulf, Mobile and Ohio Railroad in 1947, the B&O motorcar train briefly returned to Springfield Union Station before being discontinued on March 24, 1951.

The Chicago, Peoria and St. Louis Railroad, another tenant in Union Station, provided passenger service from Springfield to Peoria and from Springfield to St. Louis via Waverly and Alton. After evolving into the Chicago and Illinois Midland Railroad, the company constructed a new passenger depot near the north end of their Springfield yard, almost two miles north of Union Station. Completion of this smaller station allowed C&IM to withdraw their remaining passenger operations from Springfield Union Station in 1937.
Springfield Union Station is one of five significant rail terminals which served Illinois' capital city, and it was constructed in a far more ornate architectural style than the more utilitarian design of the other stations (Gulf, Mobile and Ohio, Great Western, Wabash, and Illinois Terminal.) The station was operated as a stub-end terminal by Illinois Central, and passenger trains backed into the station using now removed trackage which extended east along Madison Street to the Illinois Central mainline. This awkward operating arrangement reflected the original Illinois Central configuration with Springfield as an endpoint terminal rather than an intermediate station along a route.
One of the more prominent features of Springfield Union Station was a three-story (110 ft; 33m) clock tower. The tower made a striking addition to the Springfield skyline, helping the station become an immediately recognizable landmark. The hands on the clock faces were removed in 1936 as an economy move to avoid maintenance of the clock mechanism, and the tower was removed down to its base during the summer of 1946.
Passenger train service to and from Springfield Union Station ended on April 30, 1971, when the Governor's Special, the last Illinois Central passenger train between Springfield and Chicago, was discontinued as a result of the creation of Amtrak. Amtrak passenger trains continue to serve Springfield from the former Gulf, Mobile and Ohio station, located about three blocks west of Union Station.[2]
Redevelopment
After passenger train service ended, Union Station housed several private businesses before being used for Illinois state offices until September, 2004. The building was extensively restored as the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library visitor center, which reopened in March 2007. As part of the $12.5 million restoration project, the clock tower was rebuilt, substantially returning the station to its pre-1936 appearance.[3]
Gallery
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Union Station (Springfield, Illinois). |
-

New clock tower constructed in 2006 to replicate tower removed in 1946 from Springfield Union Station
-

Interior of former Springfield Union Station as renovated for use as Lincoln Presidential Library Visitor Center
Notes
- ↑ "NPS Focus". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. Retrieved May 21, 2010.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Julie Cellini, "Rebirth of a Landmark", (Springfield, Ill.) State Journal-Register, February 9, 2007, page 6A.
- ↑ John Reynolds, "All aboard: Union Station opens as visitors' center", (Springfield, Ill.) State Journal-Register, March 20, 2007, page 9.
References
- Downey, Clifford J (2002). Illinois Central Color Pictorial: Passenger Service. ISBN 1-885614-48-9.
- Stover, John F (1975). History of the Illinois Central Railroad. ISBN 0-02-614980-X.
- Wallin, Richard R (1979). Chicago & Illinois Midland. ISBN 0-87095-077-0.
- Engineering News and American Railway Journal, March 1, 1900, pages 151-152.
| Former services | ||||
| Preceding station | Baltimore and Ohio | Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Bradfordtown toward Beardstown | Beardstown – Shawneetown | Rochester toward Shawneetown |
||
| Terminus | Springfield – Hamilton | Buckhart toward Hamilton |
||
| Illinois Central | ||||
Toronto toward St. Louis | St. Louis – Chicago | Barclay toward Chicago Central Station |
||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||