Splanchnic
| Splanchnic | |
|---|---|
 Greater splanchnic nerve, seen in thoracic cavity seen from left side. | |
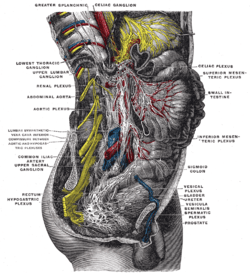 Lower half of right sympathetic cord. | |
| Details | |
| Latin | organa interna |
| splanchnic nerves | |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Splanchnic, from a Greek word splēn, meaning organ,[1] usually used to describe organs in the abdominal cavity (visceral organs).[2] The term "splanchnologia" is used for grouping in Nomina Anatomica,[3] but not in Terminologia Anatomica. It includes most of the structures usually considered "internal organs", but not all (for example, the heart is excluded.)[3]
More specifically, it can also refer to:
- Splanchnic tissue
- An adjective describing visceral organs including the intestines.
- Splanchnic nerves
- Splanchnic mesoderm
- Splanchnic circulation - The circulation of the gastrointestinal tract originating at the celiac trunk, the inferior mesenteric artery and the superior mesenteric artery.[4][5]
References
- ↑ Autonomics of the Head and Neck - Page 4 of 14 anatomy module at med.umich.edu
- ↑ "splanchnic - Definition from the Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary". Retrieved 2009-11-26.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Rosse C, Mejino JL, Modayur BR, Jakobovits R, Hinshaw KP, Brinkley JF (1998). "Motivation and organizational principles for anatomical knowledge representation: the digital anatomist symbolic knowledge base". J Am Med Inform Assoc 5 (1): 17–40. doi:10.1136/jamia.1998.0050017. PMC 61273. PMID 9452983.
- ↑ Parks, DA; Jacobson, ED (July 1985). "Physiology of the splanchnic circulation.". Archives of internal medicine 145 (7): 1278–81. doi:10.1001/archinte.1985.00360070158027. PMID 4015279.
- ↑ Takala, J (July 1996). "Determinants of splanchnic blood flow.". British journal of anaesthesia 77 (1): 50–8. doi:10.1093/bja/77.1.50. PMID 8703630.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||