Special administrative region
| Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China 中華人民共和國特別行政區 Regiões Administrativas Especiais da República Popular da China |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
  |
||||
 |
||||
| Largest SAR/city | Hong Kong | |||
| Languages | Chinese(Both Standard and Traditional Chinese), English, Cantonese, Portuguese | |||
| Demonym | Chinese | |||
| Special Administrative Regions | ||||
| Government | One country, two systems | |||
| - | Head of State | Xi Jinping | ||
| - | Chief Executive of Hong Kong | CY Leung | ||
| - | Chief Executive of Macau | Fernando Chui | ||
| Area | ||||
| - | Total | 1,135.7 km2 438 sq mi |
||
| Population | ||||
| - | 2014[lower-alpha 1] estimate | 7,858,800[1][2] | ||
| - | Density | 6920/km2 17,922.7/sq mi |
||
| Currency | Hong Kong Dollar Macanese pataca |
|||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy (AD) | |||
|
||||
| Special administrative region | |||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 中華人民共和國特別行政區 | ||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 中华人民共和国特别行政区 | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Portuguese name | |||||||||||||
| Portuguese | Regiões Administrativas Especiais da República Popular da China | ||||||||||||
The Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China (SAR; Portuguese: RAE) are autonomous territories that fall within the sovereignty of the People's Republic of China, yet do not form part of Mainland China. The legal basis for the establishment of SARs, unlike the administrative divisions of Mainland China, is provided for by Article 31, rather than Article 30, of the Constitution of the People's Republic of China of 1982. Article 31 reads: "The state may establish special administrative regions when necessary.[3][4][5] The systems to be instituted in special administrative regions shall be prescribed by law enacted by the National People's Congress in the light of the specific conditions".[6]
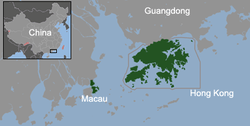
At present, there are two SARs, namely the Hong Kong SAR and the Macau SAR, former British and Portuguese dependencies respectively,[7] transferred to China in 1997 and 1999 pursuant to the Sino-British Joint Declaration of 1984 and the Sino-Portuguese Joint Declaration of 1987 respectively. Pursuant to their Joint Declarations, which are binding inter-state treaties registered with the United Nations, and their Basic laws, the Chinese SARs "shall enjoy a high degree of autonomy."[8]
The provision to establish special administrative regions appeared in the constitution in 1982, in anticipation of the talks with the United Kingdom over the question of the sovereignty over Hong Kong. It was envisioned as the model for the eventual reunification with Taiwan and other islands, where the Republic of China has resided since 1949. Special administrative regions should not be confused with special economic zones, which are areas in which special economic laws apply to promote trade and investments.
Under the One China, Two Systems principle, the two SARs continue to possess their own governments, multi-party legislatures, legal systems, police forces, monetary systems, separate customs territory, immigration policies, national sports teams, official languages, postal systems, academic and educational systems, and substantial competence in external relations that are different or independent from the People's Republic of China.
List of special administrative regions of China
| Name | Chinese (T) / (S) | Yale | Pinyin | Postal map | Abbreviation | Population | Area km2 | ISO | Admin. Division |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
香港 | Hēunggóng | Xiānggǎng | Hongkong | 港 (Gǎng), HK, HKSAR | 7,184,000 | 1,104.4 | CN-91 | List (18 districts) |
| |
澳門 / 澳门 | Oumùhn | Àomén | Macao | 澳 (Ào), MSAR, RAEM | 614,500 | 31.3 | CN-92 | List (7 freguesias) |
Characteristics
| This article is part of a series on |
| Administrative divisions of China |
|---|
|
|
|
Counties
Districts Management areas |
|
Townships
Subdistricts Prefectural bureaux Town-level city County-controlled districts |
|
|
| History: before 1912, 1912–49, 1949–present |
The two special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau (created in 1997 and 1999 respectively) each have a codified constitution called Basic Law.[7] The law provides the regions with a high degree of autonomy, a separate political system, and a capitalist economy under the principle of "one country, two systems" proposed by Deng Xiaoping.[7]
High degree of autonomy
Currently, the two SARs of Hong Kong and Macau are responsible for all affairs except those regarding diplomatic relations and national defense.[10] Consequently, the National People's Congress authorizes the SAR to exercise a high degree of autonomy and enjoy executive, legislative and independent judicial power,[11] and each with their own Courts of Final Appeal.[12]
External affairs
Special administrative regions are empowered to contract a wide range of agreements with other countries and territories such as mutual abolition of visa requirement, mutual legal aid, air services, extradition, handling of double taxation and others. In diplomatic talks involving a SAR, the SAR concerned may send officials to be part of the Chinese delegation. In sporting events the SARs participate under the respective names of "Hong Kong, China" and "Macau, China", and compete as different entities.[13]
Defense and military
The People's Liberation Army is garrisoned in both SARs. PRC authorities have said the PLA will not be allowed to interfere with the local affairs of Hong Kong and Macau, and must abide by its laws.[14] In 1988, scholar Chen Fang of the Academy of Military Science even tried to propose the "One military, two systems" concept to separate the defence function and public functions in the army.[14] The PLA does not participate in the governance of the SAR but the SAR may request them for civil-military participation, in times of emergency such as natural disasters. Defence is the responsibility of the PRC government.[10]
A 1996 draft PRC law banned People's Liberation Army-run businesses in HK, but loopholes allow them to operate while the profits are ploughed back into the military.[14] There are many PLA-run corporations in Hong Kong. The PLA also have sizable land-holdings in Hong Kong worth billions of dollars.[14]
Immigration and nationality
Each of the SARs issues passports on its own to its permanent residents who are concurrently nationals of the PRC. PRC nationals must also satisfy one of the following conditions:
- born in the SAR;
- born anywhere while either parent was a permanent resident of the SAR;
- resided continuously and legally for seven or more years in the SAR.
Apart from affording the holder consular protection by the People's Republic of China, these passports also specify that the holder has right of abode in the issuing SAR.
The National People's Congress has also put each SAR in charge of administering the PRC's Nationality Law in its respective realms, namely naturalization, renunciation and restoration of PRC nationality and issuance of proof of nationality.
Due to their colonial past, many inhabitants of the SARs hold some form of non-Chinese nationality (e.g. British National (Overseas) status, United Kingdom citizenship or Portuguese citizenship), however residents of Chinese descent have always been considered as Chinese citizens by the PRC. Special interpretation of the Nationality Law, while not recognizing dual nationality, has allowed Chinese citizens to keep their foreign "right of abode" and use travel documents issued by the foreign country. However, such travel documents cannot be used to travel to mainland China and the holder may not enjoy consular protection while in mainland China. Chinese citizens who also have foreign citizenship may declare a change of nationality at the Immigration Department of the respective SARs, and upon approval, would no longer be considered Chinese citizens.
Comparisons
Offer to Taiwan and other ROC-controlled areas
The status of a special administrative region for Taiwan and other areas controlled by the Republic of China was first proposed in 1981.[7] The 1981 proposal was put forth by Ye Jianying called "Ye's nine points" (葉九條).[15] A series of different offers have since appeared. On 25 June 1983 Deng Xiaoping appeared at Seton Hall University in the US to propose "Deng's six points" (鄧六條), which called for a "Taiwan Special Administrative Region" (台灣特別行政區).[15] It was envisioned that after Taiwan's unification with the PRC as an SAR, the PRC would become the sole representative of China.[15] Under this proposal, Taiwan would be guaranteed its own military,[15] its own administrative and legislative powers, an independent judiciary and the right of adjudication, although it would not be considered a separate government of China.[15] While there would be minimal interference by the PRC in Taiwan's political system, there may be representatives from the Taiwan SAR that would be appointed to the central government in Beijing by the Taiwan SAR.
In 2005 the Anti-Secession Law of the PRC was enacted. It promises the lands currently ruled by the authorities of Taiwan a high degree of autonomy, among other things.[16] The PRC can also employ non-peaceful means and other necessary measures to defend its claims to sovereignty over the ROC's territories from Taiwanese independence activists.[16]
References
- ↑ "Mid-year Population for 2014". Census and Statistics Department (Hong Kong). 12 August 2014.
- ↑ "Demographic Statistics for the 2nd Quarter 2014". Statistics and Census Service of the Government of Macau SAR. 11 August 2014.
- ↑ Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China (中华人民共和国行政区划; Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó Xíngzhèng Qūhuà), 15 June 2005, retrieved 5 June 2010
- ↑ Chapter II: Relationship between the Central Authorities and the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Article 12, retrieved 5 June 2010
- ↑ Chapter II Relationship between the Central Authorities and the Macau Special Administrative Region, Article 12, retrieved 5 June 2010
- ↑ Lauterpacht, Elihu. Greenwood, C. J. [1999] (1999). International Law Reports Volume 114 of International Law Reports Set Complete set. Cambridge University Press, 1999. ISBN 0521642442, 9780521642446. p 394.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Ghai, Yash P. (2000). Autonomy and Ethnicity: Negotiating Competing Claims in Multi-Ethnic States. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521786428, 9780521786423. p 92.
- ↑ Article 12, Basic Law of Hong Kong and Article 12, Basic Law of Macau
- ↑ References and details on data provided in the table can be found within the individual provincial articles.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Zhang Wei-Bei. [2006] (2006). Hong Kong: the pearl made of British mastery and Chinese docile-diligence. Nova Publishers. ISBN 1594546002, 9781594546006.
- ↑ Chan, Ming K. Clark, David J. [1991] (1991). The Hong Kong Basic Law: Blueprint for Stabiliree Legal Orders – Perspectives of Evolution: Essays on Macau's Autonomy After the Resumption of Sovereignty by China. ISBN 3540685715, 9783540685715. p 212.
- ↑ Oliveira, Jorge. Cardinal, Paulo. [2009] (2009). One Country, Two Systems, Three Legal Orders – Perspectives of Evolution: Essays on Macau's Autonomy After the Resumption of Sovereignty by China. ISBN 3540685715, 9783540685715. p 212.
- ↑ English.eastday.com. English.eastday.com. "China keeps low key at East Asian Games." Retrieved on 2009-12-13.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Gurtov, Melvin. Hwang, Byong-Moo Hwang. (1998). China's Security: The New Roles of the Military. Lynne Rienner Publishing. ISBN 1555874347, 9781555874346. p 203–204.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 Big5.china.com.cn. "Big5.china.com.cn." 鄧六條. Retrieved on 2009-12-14.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 United Nations refugee agency. "UNHCR." Anti-Secession Law (No. 34). Retrieved on 2009-12-14.
See also
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||