Spanish dialects and varieties
| Spanish language |
|---|
| Overview |
|
| Grammar |
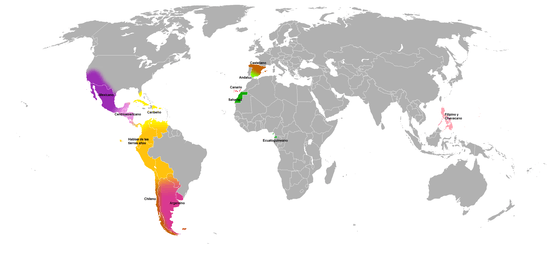
In other colors, the extent of the other languages of Spain in the bilingual areas.

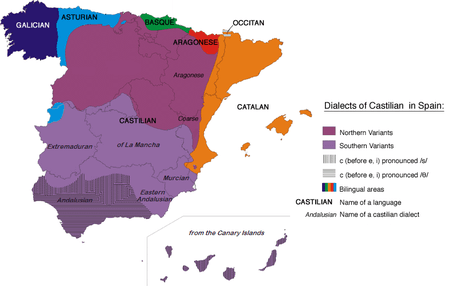
Some of the regional varieties of the Spanish language are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar.
While all Spanish dialects use the same written standard, all spoken varieties differ from the written variety, in different degrees. There are differences between European Spanish (also called Peninsular Spanish) and the Spanish of the Americas, as well as many different dialect areas both within Spain and within Hispanic America.
Prominent differences of pronunciation among dialects of Spanish include:
- the maintenance vs. loss of distinction between the phonemes /θ/ and /s/ (distinción vs. seseo);
- the maintenance or loss of distinction between phonemes represented orthographically by ll and y (yeísmo);
- the maintenance of syllable-final [s] vs. its weakening to [h] (called aspiration, or the more precise term debuccalization), or its loss; and
- the tendency, in areas of central Mexico and of the Andean highlands, to reduction (especially devoicing), or loss, of unstressed vowels, mainly when they are in contact with voiceless consonants.[1][2][3]
Among grammatical features, the most prominent variation among dialects is in the use of the second-person pronouns. In most of Spain, the informal second-person plural pronoun is vosotros, while in Hispanic America the only second-person plural pronoun, for both formal and informal registers, is ustedes. And for the second-person singular familiar pronoun, some dialects use tú (and its associated verb forms), while others use either vos (see voseo) or both tú and vos (which, together with usted, can make for a possible three-tiered distinction of formalities).
There are significant differences in vocabulary among regional varieties of Spanish, particularly in the domains of food products, everyday objects, and clothes; and many Latin American varieties show considerable lexical influence from Native American languages.
Sets of variants
In a broad sense, Latin American Spanish can be grouped into:
- Mexican
- Caribbean (Cuba, Venezuela, Puerto Rico, Dominican Republic, northern Colombia and Caribbean Mexico).
- Andean-Pacific (Peru, Ecuador, western Bolivia, Colombia and western Venezuela).
- Rioplatense (Argentina, Uruguay, and Paraguay)
- Chilean (Chiloé, Cuyo)
- Central American
Old World varieties are:
- Northern Peninsular (Asturias, Castilla y León, Cantabria, Basque country, Navarre, Aragón, Rioja, Provinces of Guadalajara and Cuenca)
- Central-Southern Peninsular (Madrid, Toledo, La Mancha)
- Southern Peninsular (Andalusia, Extremadura, and Murcia)
- Canarian (Canary Islands)
Pronunciation
Distinción vs. seseo and ceceo
The distinction between the historical phonemes /s/ and /θ/ is maintained in northern and central Spain, while the two phonemes are merged in Hispanic America and most of southern Spain. The maintenance of phonemic contrast is called distinción in Spanish. The merged phoneme is realized as [s] in the Spanish of the Americas and Canary Islands, and as either [s] or [s̄] (a sound similar to but not the same as /θ/) in different parts of Andalusia (southern Spain). Depending on this realization, the use of the merged phoneme is called either seseo or ceceo, respectively.
In dialects with seseo the words casa ("house") and caza ("hunt") are pronounced as homophones (generally [ˈkasa]), whereas in dialects with distinción they are pronounced differently (as [ˈkasa] and [ˈkaθa] respectively). The symbol [s] stands for a voiceless sibilant like the "s" of English sick, while [θ] represents a voiceless interdental fricative like the "th" of English thick.
In some cases where the phonemic merger would render words homophonic in Hispanic America, one member of the pair is frequently replaced by a synonym or derived form—e.g. caza replaced by cacería, or cocer ("to boil"), homophonic with coser ("to sew"), replaced by cocinar. For more on seseo, see González-Bueno.[4]
Yeísmo
Traditionally Spanish had a phonemic distinction between /ʎ/ (a palatal lateral approximant, written ll) and /ʝ/ (a voiced palatal fricative, written y). But for most speakers in Spain and the Americas, these two phonemes have been merged in the phoneme /ʝ/. This merger results in the words calló ("silenced") and cayó ("fell") being pronounced the same, whereas they remain distinct in dialects that have not undergone the merger. The use of the merged phoneme is called "yeísmo".
In Spain, the distinction is preserved in rural areas and smaller cities of the north, while in South America the contrast is characteristic of bilingual areas where Quechua languages, Guaraní and other indigenous languages that have the /ʎ/ sound in their inventories are spoken (this is the case of inland Peru, Bolivia and, especially, Paraguay).[5][6]
The phoneme /ʝ/ can be pronounced in a variety of ways, depending on the dialect. In most of the area where yeísmo is present, the merged phoneme /ʎ ~ ʝ/ is pronounced as the fricative or approximant [ʝ] or as the glide [j]. In the area around the Río de la Plata (Argentina, Uruguay), this phoneme is pronounced as a palatoalveolar sibilant fricative, either as voiced [ʒ] or, by some speakers, as voiceless [ʃ].
Variants of /s/
One of the most distinctive features of the Spanish variants is the pronunciation of /s/. In northern and central Spain, and in Antioquia, Colombia, as well as some other isolated dialects (e.g. some inland areas of Peru and of Bolivia), /s/ is pronounced as an apico-alveolar retracted fricative. However, in southern Spain and most of Hispanic America it is pronounced as a lamino-alveolar or dental.
Debuccalization of coda /s/
In much of Hispanic America—especially in the Caribbean and in coastal and lowland areas of Central and South America—and in the southern half of Spain, syllable-final /s/ is pronounced as a voiceless glottal fricative, [h]) (debuccalization, also frequently called "aspiration"), or even not pronounced at all in some variants in rapid speech. In some varieties of Latin American Spanish (notably Honduran Spanish) this may also occur intervocalically within an individual word, as with nosotros. which may be pronounced as [nohotroh]. In southeastern Spain (eastern Andalusia, Murcia and part of La Mancha), the distinction between syllables with a now-silent "s" and those originally without "s" is preserved by pronouncing the syllables ending in "s" with open vowels (that is, the open/closed syllable contrast has been turned into a tense/lax vowel contrast); this typically affects the vowels /a/, /e/ and /o/, but in some areas even /i/ and /u/ are affected. For instance, todos los cisnes son blancos ("all the swans are white"), can be pronounced [ˈto̞ðɔh lɔh ˈθihnɛh sõ̞m ˈblãŋkɔh], or even [ˈtɔðɔ lɔ ˈθĩ̞nːɛ sɔ̃m ˈblãŋkɔ] (standard Spanish [ˈto̞ðo̞z lo̞s ˈθizne̞s sõ̞m ˈblãŋko̞s]). This open-closed vowel contrast is sometimes reinforced by vowel harmony. For those areas of southeastern Spain where the deletion of final /s/ is complete, and where the distinction between singular and plural of nouns depends entirely on vowel quality, the case has been made to claim that a set of phonemic splits has occurred, resulting in a system with eight vowel phonemes in place of the standard five.[7][8]
Vowel reduction
Although the vowels of Spanish are relatively stable from one dialect to another, the phenomenon of vowel reduction—devoicing or even loss—of unstressed vowels in contact with voiceless consonants, especially /s/, can be observed in the speech of central Mexico (including Mexico City). For example, it can be the case that the words pesos ("pesos [money]"), pesas ("weights"), and peces ("fish [pl.]") sound nearly the same, as [ˈpe̞ss̩] (with the second [s] much like a syllabic consonant). One may hear pues ("well then") pronounced [p̩s]. Some efforts to explain this vowel reduction link it to the strong influence of Nahuatl and other Native American languages in Mexican Spanish.
Pronunciation of "j"
In the 16th century, as the Spanish colonization of the Americas was beginning, the phoneme represented by the letter "j" had begun to change its place of articulation from palato-alveolar [ʃ] to palatal [ç] and to velar [x], like German "ch" in Bach (see History of Spanish). In southern Spanish dialects and in those Latin American dialects strongly influenced by southern settlers (e.g. Caribbean Spanish), rather than the velar fricative [x], the result was a softer glottal sound [h], like English "h" in hope. Glottal [h] is nowadays the standard pronunciation for "j" in Caribbean dialects (Cuban, Dominican, and Puerto Rican) as well as in mainland Venezuela, much of Central America, and southern Mexico.[9] Both coastal and inland dialects of Colombian Spanish show [h] for "j". In the rest of the Americas, the velar fricative [x] is prevalent. In most of Argentina (Rioplatense) and Chile, [x] becomes the more frontal [ç] (like German "ch" in ich) when it precedes palatal vowels [i], [e]: gente [ˈçẽ̞nte̞], jinete [çiˈne̞te̞]. In Spain, glottal [h] is common in the Canary Islands and western Andalusia; in the rest of the country, [x] alternates with a "raspy" uvular fricative [χ], sometimes accompanied by uvular vibration.
Word-final "-n"
In standard European Spanish and many Latin American dialects (standard Argentine or Rioplatense, Colombian, and Mexican), word-final "-n" is alveolar, like English /n/ in pen, however it assimilates the place of articulation of the following consonant becoming dental, interdental, velar and palatal. Utterance-final nasals neutralize as /n/. In some dialects, final "-n" is pronounced as a velar nasal sound [ŋ] producing vowel nasalization, just as in English "-ng" in long. In these dialects, "-n" makes words like pan ('bread') and bien ('good') sound like pang and bieng to English-speakers. Velar "-n" is common in many parts of Spain (Galicia, León, Asturias, Murcia, Extremadura, and Andalusia). In the Americas, velar "-n" is prevalent in all Caribbean dialects, Central American dialects, the coastal areas of Colombia, Venezuela, much of Ecuador, Peru, and northern Chile.[9] Loss of final "-n" with strong nasalization of the preceding vowel is not infrequent in all those dialects where velar "-n" exists. In much of Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela (except for the Andean region) and Dominican Spanish, any pre-consonantal /n/ or /m/ can be realized [ŋ]; thus, a word like ambientación can be pronounced [ãŋbjẽ̞ŋtaˈsjõ̞ŋ].
"R" sounds
All varieties of Spanish distinguish between a "single-R" and a "double-R" phoneme. The single-R phoneme corresponds to the letter "r" written once (except when word-initial or following "l", "n", or "s") and is pronounced as [ɾ], an alveolar flap—like American English "tt" in better—in virtually all dialects. In some dialects, the single-R phoneme in syllable-final position loses its contrast with /l/, so a word such as artesanía may sound like altesanía. This neutralization or "leveling" of /ɾ/ and /l/ is frequent in dialects of southern Spain, the Caribbean, Venezuela, coastal Colombia, and central Chile.[9]
The double-R phoneme is spelled "rr" between vowels and "r" word-initially or following "l", "n", or "s". In most varieties it is pronounced as an alveolar trill, and that is considered the prestige pronunciation. Two notable variants occur, however, one sibilant and the other velar or uvular. The pronunciation of the phoneme as a voiced strident (or sibilant) apical fricative is common in New Mexico, Guatemala, Costa Rica; highland areas of Colombia, Ecuador, Bolivia, and Chile; western and northern Argentina, and Paraguay.[10] Some linguists have attempted to explain the assibilated "rr" as a result of influence from Native American languages, and it is true that in the Andean regions mentioned an important part of the population is bilingual in Spanish and one or another indigenous language. Nonetheless, other researchers have pointed out that sibilant "rr" in the Americas may not be an autonomous innovation, but rather a pronunciation that originated in some northern Spanish dialects and then was exported to the Americas. Spanish dialects spoken in the Basque Country, Navarre, la Rioja, and northern Aragon (regions that contributed substantially to Spanish-American colonization) show the fricative or postalveolar variant for "rr" (especially for the word-initial "rr" sound, as in Roma or rey).
The other major variant for the "rr" phoneme—common in Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic—is articulated at the back of the mouth, either as a glottal [h] followed by a voiceless apical trill or, especially in Puerto Rico, with a posterior articulation that ranges variously "from a velar [x] to a uvular trill [R]."[11] Canfield transcribes the sound as uppercase [R] with an under-ring, evidently for a voiceless trill.[12] These realizations for "rr" maintain their contrast with the phoneme /x/, as the latter tends to be realized as a soft glottal [h]: compare Ramón [χaˈmõ̞ŋ]~[xaˈmõ̞ŋ] ('Raymond') with jamón [haˈmõ̞ŋ] ('ham').
Pronunciation of "x"
The letter "x" usually represents the phoneme sequence /ks/.[13] In careful speech, this is pronounced [ks], but in casual speech the /k/, being syllable-final, can weaken to a voiced fricative [ɣ][14] or even disappear, especially when the "x" is followed by a consonant. The tendency to delete the /k/ element is generally stronger in Spain than in the Spanish of Latin America. When the "x" is followed by "ce" or "ci" (e.g. excelente, excitar), in dialects using seseo (see above), the /s/ of the /ks/ sequence may merge with the /s/ that corresponds to the letter "c", so excelente may be pronounced either [e̞kse̞ˈlẽ̞nte̞] or [e̞sːe̞ˈlẽ̞nte̞]. But in those areas of northern and central Spain that distinguish between the phonemes /s/ and /θ/, excelente is pronounced [e̞s̺θe̞ˈlẽ̞nte̞]. Dialects that practice debuccalization of syllable-final /s/ (see above) treat the /s/ of a syllable-final (letter) "x" in the same way (e.g. exclamar [ɛhklaˈmar]~[ɛkːlaˈmar]).
Adoption of the affricates "tz" and "tl"
Mexican Spanish and some other Latin American dialects have adopted from the native languages the voiceless alveolar affricate [t͡s] and a voiceless alveolar lateral affricate [t͡ɬ] represented by the respective digraphs <tz> and <tl>, as in the names Atzcapotzalco and Tlaxcala. In these dialects, even words of European origin with <tl>, such as Atlántico and atleta, are pronounced with the affricate: e.g. [aˈt͡ɬãntiko̞] (compare [aðˈlãntiko̞] in Spain[15]). Classical Spanish does not have these affricates.
Judaeo-Spanish
Judaeo-Spanish (often called Ladino) refers to the Romance dialects spoken by Jews whose ancestors were expelled from Spain near the end of the 15th century.
These dialects have important phonological differences compared to varieties of Spanish proper; for example, they have preserved the voiced/voiceless distinction among sibilants as they were in Old Spanish. For this reason, the letter "s", when written single between vowels, corresponds to a voiced [z]—e.g. rosa [ˈro̞za] ("rose"). Where "s" is not between vowels and is not followed by a voiced consonant, or when it is written double, it corresponds to voiceless [s]—thus assentarse [asẽ̞nˈtarse̞] ("to sit down"). And due to a phonemic neutralization similar to the seseo of other dialects, the Old Spanish voiced "z" [dz] and the voiceless "ç" [ts] have merged, respectively, with /z/ and /s/—while maintaining the voicing contrast between them. Thus fazer ("to make") has gone from the medieval [faˈdze̞r] to [faˈze̞r], and plaça ("town square") has gone from [ˈplatsa] to [ˈplasa].
A related dialect is Haketia, the Judaeo-Spanish of northern Morocco. This too tended to assimilate with modern Spanish, during the Spanish occupation of the region.
Grammar
Variation in second-person pronouns and verbs
Spanish is a language with a "T-V distinction" in the second person, meaning that there are different pronouns corresponding to "you" which express different degrees of formality. In most varieties, there are two degrees, namely "formal" and "familiar" (the latter is also called "informal").
For the second person formal, virtually all Spanish dialects of Spain and the Americas use usted and ustedes (singular and plural respectively). But for the second person familiar, there is regional variation—between tú and vos for the singular, and, separately, between vosotros and ustedes for the plural. The use of vos (and its corresponding verb forms) rather than tú is called voseo.[16]
Each of the second-person pronouns has its historically corresponding verb forms, used by most speakers. Most voseo speakers use both the pronoun vos and its historically corresponding verb forms (e.g. vos tenés, "you have"). But some dialects use the pronoun tú with "vos verb forms" (verbal voseo—tú tenés), while others use vos with "tú verb forms" (pronominal voseo—vos tienes).
Second person singular
In most dialects the familiar second person singular pronoun is tú (from Latin tū), and the formal pronoun is usted (usually considered to originate from vuestra merced, meaning "your grace" or, literally, "your mercy"). In a number of regions in the Americas, tú is replaced by another pronoun, vos, and the verb conjugation changes accordingly (see details below). Spanish vos comes from Latin vōs, which was the second person plural pronoun in that language.
In any case, there is wide variation as to when each pronoun (formal or familiar) is used. In Spain, tú is familiar (for example, used with friends), and usted is formal (for example, used with older people). In recent times there has been a noticeable tendency to extend the use of tú even in situations previously reserved for usted. Meanwhile, in several countries—in parts of Middle America, especially, Costa Rica and Colombia—the formal usted is also used to denote a closer personal relationship. Many Colombians and some Chileans, for instance, employ usted not only for a child to address a parent, but also for a parent to address a child. Some countries, such as Cuba and the Dominican Republic, prefer the use of tú even in very formal circumstances, and usted thus is seldom used. Meanwhile, in other countries, the use of formal rather than familiar second-person pronouns denotes authority. In Peru, for example, senior military officers use tú to speak to their subordinates, while junior officers use only usted to address their superior officers.
Using the familiar tú, especially in contexts where usted was to be expected, is called tuteo. The corresponding verb is tutear (a transitive verb, the direct object being the person addressed with the pronoun). The verb tutear is used even in those dialects where the familiar pronoun is vos, to mean "to treat with the familiar second-person pronoun".[17]
Pronominal voseo, the use of the pronoun vos instead of tú, is the prevalent form of the familiar second person singular pronoun in Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Argentina and Uruguay. In these countries it is used by many to address others in all kinds of contexts, often regardless of social status or age, including by cultured/educated speakers and writers, in television, advertisements, and even in translations from other languages. In Guatemala and Uruguay vos and tú are used concurrently, though vos is much more common. Both pronouns use the verb forms normally associated with vos (vos querés / tú querés, "you want").
The name Rioplatense is applied to the dialect of Spanish spoken around the mouth of the Río de la Plata and the lower course of the Paraná River, where vos, not tú, is inviariably used, with the vos verb forms (vos tenés). This area comprises the most populous part of Argentina (the provinces of Buenos Aires and Santa Fe) as well as an important part of Uruguay, including Montevideo, the capital.
In Ecuador, vos is the most prominent form throughout the Sierra region of the country, though it does coexist with usted and the lesser-used tú. In this region, vos is regarded as the conversational norm, but it is not used in public discourse or the mass media. The choice of pronoun to be used depends on the participants' likeness in age and/or social status. Based on these factors, speakers can assess themselves as being equal, superior, or inferior to the addressee, and the choice of pronoun is made on this basis, sometimes resulting in a three-tiered system. Ecuadorians of the highlands thus generally use vos among familiarized equals, or by superiors (in both social status and age) to inferiors; tú among unfamiliarized equals, or by a superior in age but inferior in social status; and usted by both familiarized and unfamiliarized inferiors, or by a superior in social status but inferior in age. In the more-populated coastal region, the form tú is used in most situations, usted being used only for unfamiliar and/or superior addressees.
Vos can be heard throughout most of Chile, Bolivia, and a small part of Peru as well, but in these places it is regarded as substandard. It is also used as the conversational norm in the Paisa Region and the southwest region of Colombia, in Zulia State (Venezuela), in Honduras, El Salvador, Costa Rica, Guatemala, and the state of Chiapas in Mexico.
In Chile, even though tú is the prestige pronoun among educated speakers, the use of "verbal voseo", i.e. «tú + verb conjugation of vos» (e.g. "tú podís") is widespread. On the other hand, "pronominal voseo", the use of the pronoun vos—pronounced with aspiration of the final "-s"—is used derisively in informal speech between close friends as playful banter (usually among men) or, depending on the tone of voice, as an offensive comment.
In Colombia, the choice of second person singular varies with location. In most of inland Colombia (especially the Andean region), usted is the pronoun of choice for all situations, even in speaking between friends or family; but in large cities (especially Bogotá), the use of tú is becoming more accepted in informal situations, especially between young interlocutors of opposite sexes and among young women. In Valle del Cauca (Cali), Antioquia (Medellín) and the Pacific coast, the pronouns used are vos and usted. On the Caribbean coast (mainly Barranquilla and Cartagena), tú is used for practically all informal situations and many formal situations as well, usted being reserved for the most formal environments. A peculiarity occurs in Boyacá and among older speakers in Bogotá: usted is replaced by sumercé for formal situations (it is relatively easy to identify a Boyacense by his/her use of this pronoun). Sumercé comes from su merced ("your mercy").
In parts of Spain, fifty years ago a child would not use tú, but rather usted to address a parent. Today, however, this usage is unusual. Among the factors for the ongoing replacement of usted by tú are the new social relevance of youth and the reduction of social differences. In particular, it has been attributed to the egalitarianism of the right-wing Falange party. By contrast, Spanish leftists of the early 20th century would address their comrades as usted as a show of respect and workers' dignity.
According to Joan Coromines, by the 16th century, the use of vos (as a second person singular pronoun) had been reduced to rural areas of Spain, regions which were a source of many emigrants to the New World, and thus vos became the unmarked form in many areas of Hispanic America.[18][19]
A slightly different explanation is that in Spain, although vos (as a singular) originally denoted the high social status of those who were addressed as such (monarchs, nobility, etc.), these people never used the pronoun themselves, since there were few or no people above them in society. Those who used vos were people of the lower classes and peasants. When the waves of Spanish immigrants arrived to populate the New World, they primarily came from these lower classes. In the New World, wanting to raise their social status from what it was in Spain, they demanded to be addressed as vos. Through the widespread use of vos in the Americas, the pronoun was transformed into an indicator of low status not only for the addresser, but also for the addressee. Conversely, in Spain today vos is considered a highly exalted archaism that is virtually confined to liturgy.
Speakers of Ladino still use vos as it was used in the Middle Ages, to address people higher on the social ladder. The pronoun usted had not been introduced to this dialect of Spanish when the Jews were expelled from Spain in 1492, hence vos is still used in Ladino much as usted is used in modern Spanish.
A variant of usted, namely vusted, can be heard in Andean regions of South America. Other, less frequent forms analogous to usted are vuecencia (short for "vuestra excelencia"), and usía (from "vuestra señoría").
Second person plural
In Standard European Spanish the plural of tú is vosotros and the plural of usted is ustedes. In Hispanic America vosotros is not used, and the plural of both tú and usted is ustedes. This means that speaking to a group of friends a Spaniard will use vosotros, while a Latin American Spanish-speaker will use ustedes. Although ustedes is semantically a second-person form, it is treated grammatically as a third-person plural form because it originates from the term vuestras mercedes ("your [pl.] graces," sing. vuestra merced).
The only vestiges of vosotros in the Americas are boso/bosonan in Papiamento and the use of vuestro/a in place of sus (de ustedes) as second person plural possessive in the Cusco region of Peru.
In very formal contexts, however, the vosotros conjugation can still be found. An example is the Mexican national anthem, which contains such forms as apretad and empapad.
The plural of the Colombian (Cundi-Boyacense Plateau) sumercé is sumercés/susmercedes, from sus mercedes ("your mercies").
In some parts of Andalusia (the lands around the Guadalquivir river and western Andalusia), the usage is what is called ustedes-vosotros: the pronoun ustedes is combined with the verb forms for vosotros. However, this sounds extremely colloquial and most Andalusians prefer to use each pronoun with its correct form.
In Ladino, vosotros is still the only second person plural pronoun, since usted does not exist.
Second-person verb forms
Each second-person pronoun has its historically corresponding verb forms. The formal usted and ustedes, although semantically second person, take verb forms identical with those of the third person, singular and plural respectively, since they are derived from the third-person expressions vuestra merced and vuestras mercedes ("your grace", "your graces"). The forms associated with the singular vos can generally be derived from those for the plural vosotros by deleting the palatal semivowel of the ending (vosotros habláis > vos hablás, "you speak"; vosotros coméis > vos comés, "you eat").
General statements about the use of voseo in different localities should be qualified by the note that individual speakers may be inconsistent in their usage, and that isoglosses rarely coincide with national borders. That said, a few assertions can be made:
- "Full" voseo (involving both pronoun and verb—vos comés, "you eat") is characteristic of two zones: that of Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay and that of Central America and the Mexican state of Chiapas.
- "Full" voseo coexists with the use of tú and its verb forms (e.g. tú comes) in Colombia and Ecuador, and in parts of Colombia also with usted (with its standard verb forms) as a familiar form.
- In Chile there is coexistence of three usages:
- tú and its verb forms (tú comes);
- "full" voseo with uniquely Chilean voseo verb endings (-ái, -ís, and -ís respectively for -ar, -er, and -ir verbs: vos hablái—"you speak", vos comís—"you eat", vos vivís—"you live"); and
- verbal voseo with the Chilean verb endings (tú hablái, tú comís, etc.).
- "Full" voseo coexists with verbal voseo (tú comés) in Uruguay.
- In Zulia state and parts of Falcón in Venezuela there is no deletion of the palatal semivowel, so you have "vos coméis", "vos habláis", "vos seáis". In Trujillo state "voseo" is like the Argentinean one with the exception of the imperative mode which is like the standard "tú".[20]
- Voseo is absent from the Spanish of Spain, and from most of Mexico, Peru, and the islands of the Caribbean.
As for the second person familiar plural, it can be said that northern and central Spain use vosotros and its verb forms (vosotros habláis, "you [pl.] speak"), while the rest of the Spanish-speaking world merges the familiar and formal in ustedes (ustedes hablan). Usage in western Andalusia includes the use of ustedes with the traditional vosotros verb form (ustedes habláis).
In Ladino, the second-person pronouns are quite different from those of Spain and Hispanic America. The forms usted and ustedes had not yet appeared in 1492 when the Jews were expelled from Spain. Speakers of Ladino still use vos as it was used in the Middle Ages (as a singular) to address people higher on the social ladder. And vosotros is the only second person plural pronoun. In Ladino the formal singular for "you speak" is vos avláis (pronounced [aˈvlaʃ], and the same verb form serves for the plural, both formal and familiar: vosotros avláis ([voˈzotros aˈvlaʃ]). The subjunctive "that you lose" (formal singular) is que vos pedráis ([ke vos peˈdraʃ]), while the plural (both formal and familiar) is que vosotros pedráis ([ke voˈzotros peˈdraʃ]). The formal singular imperative ("come") is venid or vení, and the same form serves as the plural imperative, both formal and familiar.
Verb tenses for past events
In a broad sense, when expressing an action viewed as finished in the past, speakers (and writers) in most of Spain use the perfect tense—e.g. he llegado "I have arrived"—more often than their Latin American counterparts, while Spanish-speakers in the Americas more often use the preterite (llegué "I arrived").[21]
The perfect is also called the "present perfect" and, in Spanish, pasado perfecto or pretérito perfecto compuesto. It is described as a "compound" tense (compuesto in Spanish) because it is formed with the auxiliary verb haber plus a main verb.
The preterite, also called the "simple past" and, in Spanish, pretérito indefinido or pretérito perfecto simple, is considered a "simple" tense because it is formed of a single word: the verb stem with an inflectional ending for person, number, etc.
The choice between preterite and perfect, according to prescriptive grammars from both Spain[22][23] and Hispanic America,[24] is based on the psychological time frame—whether expressed or merely implied—in which the past action is embedded. If that time frame includes the present moment (i.e. if the speaker views the past action as somehow related to the moment of speaking), then the recommended tense is the perfect (he llegado). But if the time frame does not include the present—if the speaker views the action as only in the past, with little or no relation to the moment of speaking—then the recommended tense is the preterite (llegué). This is also the real spontaneous usage in most of Spain.
Following this criterion, an explicit time frame such as hoy "today" or este año "this year" includes the present and thus dictates the compound tense: Este año he cantado "I have sung this year". Conversely, a time frame such as ayer "yesterday" or la semana pasada "last week" does not include the present and therefore calls for the preterite: La semana pasada canté "I sang last week".
However, in most of Hispanic America, and in the Canary Islands, the preterite is used for all actions viewed as completed in the past. It tends to be used in the same way in those parts of Spain where the local languages and vernaculars do not have compound tenses, that is, the Galician-speaking area and the neighbouring Astur-Leonese-speaking area.
In most of Spain, the compound tense is preferred in most cases when the action described is close to the present moment:
- He viajado a los Estados Unidos. "I have (just) traveled to the USA."
- Cuando he llegado, la he visto. "When I arrived, I saw her."
- ¿Qué ha pasado? "What (has) happened?"
Prescriptive norms would rule out the compound tense in a cuando-clause, as in the second example above.
Meanwhile, in Galicia, León, Asturias, Canary Islands, and Hispanic America, speakers follow the opposite tendency, using the simple past tense in most cases, even if the action takes place at some time close to the present:
- Ya viajé a los Estados Unidos. "I (have already) traveled to the USA."
- Cuando llegué, la vi. "When I arrived, I saw her."
- ¿Qué pasó? "What happened?"
For some speakers of Latin American Spanish, the compound tense can sound affected, bookish, or foreign.
In Hispanic America one could say He viajado a España varias veces, "I have traveled to Spain several times", to express a repeated action, as in English. But to say El año pasado he viajado a España would sound ungrammatical (as it would also be in English to say "Last year, I have traveled to Spain", as "last year" implies that the relevant time period does not include the present). In Spain, speakers use the compound tense when the period of time considered has not ended, as in He comprado un coche este año "I have bought a car this year". Meanwhile a Latin American Spanish-speaker is more likely to say Compré un carro este año meaning "I bought a car this year".
Vocabulary
Different regional varieties of Spanish vary in terms of vocabulary as well. This includes both words that exist only in certain varieties (especially words borrowed from indigenous languages of the Americas), and words that are used differently in different areas. Among words borrowed from indigenous languages are many names for food, plants and animals, clothes, and household object, such as the following items of Mexican Spanish vocabulary borrowed from Nahuatl.[1]
| Word | English translation |
|---|---|
| camote | sweet potato |
| pipián | stew |
| chapulín | grasshopper |
| huipil | blouse |
| metate | grinder, mortar and pestle |
In addition to loan words, there are a number of Spanish words that have developed distinct senses in different regional dialects. That is, for certain words a distinct meaning, either in addition to the standard meaning or in place of it, exists in some varieties of Spanish.
| Word | Standard meaning | Regional meaning |
|---|---|---|
| almacén | warehouse, department store | grocery store (Andean Spanish, Rioplatense Spanish)[25] |
| colectivo | collective | collective taxi, minibus (Argentine Spanish, Bolivian Spanish,[25] Chilean Spanish) |
| cuadra | stable, pigsty | city block (American Spanish)[25] |
| chaqueta | jacket | (vulgar) male masturbation (Central American Spanish)[26] |
| coger | to take, to catch, to start, to feel | (vulgar) to fuck (Rioplatense Spanish and Mexican Spanish)[27] |
| concha | shell, tortoiseshell | (vulgar) cunt (Andean Spanish, Rioplatense Spanish)[25] |
| peloteo | knock-up (in tennis), warm up | fawning, adulation (Peninsular Spanish)[25] |
Mutual comprehension
The different dialects and accents do not block cross-understanding among the educated. Meanwhile, the basilects have diverged more. The unity of the language is reflected in the fact that early imported sound films were dubbed into one version for the entire Spanish-speaking market. Currently, films not originally in Spanish (usually Hollywood productions) are dubbed separately into two accents: one for Spain and one for Latin America (using a Mexican or Puerto Rican accent without regionalisms). Some high-budget productions, however, such as the Harry Potter film series, have had dubs in three or more of the major accents. On the other hand, productions from another Spanish-language country are seldom dubbed. Exceptionally, the made-in-Spain animated features Dogtanian and the Three Muskehounds and The World of David the Gnome, as well as TV serials from the Southern Cone such as Karkú (Chile) and Lalola (Argentina), have had a Mexican dub. The popularity of telenovelas and music familiarizes the speakers with other accents of Spanish.
Prescription and a common cultural and literary tradition, among other factors, have contributed to the formation of a loosely-defined register which can be termed Standard Spanish (or "Neutral Spanish"), which is the preferred form in formal settings, and is considered indispensable in academic and literary writing, the media, etc. This standard tends to disregard local grammatical, phonetic and lexical peculiarities, and draws certain extra features from the commonly acknowledged canon, preserving (for example) certain verb tenses considered "bookish" or archaic in most other dialects.
See also
Other dialects
- Judaeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino, the language of the Sephardic Jews
Cants and argots
- Bron of migrant merchants and artisans of Asturias and León
- Caló (Spanish Romani) of Gitanos
- Caló of Chicanos
- Cheli of Madrid
- Gacería of Cantalejo, Spain
- Germanía of Spanish Golden Century criminals
- Lunfardo of Porteño Spanish
Mixes with other languages
- Spanish-based creole languages
- Annobonese language of Annobón Province and Bioko, Equatorial Guinea
- Belgranodeutsch of Buenos Aires
- Castrapo of Galicia
- Chabacano of the Philippines
- Cocoliche of Buenos Aires
- Frespañol of French-Spanish contact
- Llanito of Gibraltar
- Palenquero of Colombia
- Papiamento of Aruba, Curaçao and Bonaire
- Pichinglis of Bioko, Equatorial Guinea
- Portuñol of the Brazilian border
- Spanglish of the United States of America
Other
- History of the Spanish language
- Spanish phonology
- Central American Spanish
- South American Spanish
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cotton & Sharp (1988)
- ↑ Lope Blanch (1972:222)
- ↑ Delforge (2008)
- ↑ González Bueno (1993)
- ↑ Whitley (2002:26)
- ↑ Hualde (2008:298)
- ↑ Navarro Tomás (1939)
- ↑ Alonso, Canellada & Zamora Vicente (1950)
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Canfield (1981)
- ↑ Canfield (1981:7–8)
- ↑ Lipski (1994:333)
- ↑ Canfield (1981:78)
- ↑ An exception to the correspondence of "x" with /ks/ is the pronunciation of the "x" in some place names, especially in Mexico, such as Oaxaca and the name México itself, reflecting an older spelling (see "Name of Mexico"). Some personal names, such as Javier, Jiménez, etc., also are occasionally spelled with "X": Xavier, Ximénez, etc. A small number of words in Mexican Spanish retain the historical /ʃ/ pronunciation, e.g. Mexica.
- ↑ Navarro Tomás (2004)
- ↑ Navarro Tomás (2004)
- ↑ Kany (1951:55–91)
- ↑ Kany (1951:56–57)
- ↑ Corominas (1987)
- ↑ Kany (1951:58–63)
- ↑ https://docs.google.com/file/d/13vnz0v4TOEKZmie2F4l_AouayjM1ITvGWGEizCXgY12ks8x1cWvANFDhPHv5/edit?pli=1
- ↑ Kany (1951:161–164)
- ↑ Seco (1986:302)
- ↑ Real Academia Española (1973:465 and 468)
- ↑ Bello (1903:134)
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 Webster's New World Concise Spanish Dictionary (2006)
- ↑ Velázquez Spanish and English Dictionary: Pocket Edition (2006)
- ↑ Miyara (2001)
Bibliography
- Real Academia Española (1973), Esbozo de una nueva gramática de la lengua española, Madrid: Espasa-Calpe
- Alonso, Dámaso; Canellada, María Josefa; Zamora Vicente, Alonso (1950), "Vocales andaluzas", Nueva Revista de Filología Hispánica 4: 209–230
- Bello, Andrés (1903), Gramática de la lengua castellana destinada al uso de los americanos, Paris: Roger & Chervoviz
- Canfield, D[elos] Lincoln (1981), Spanish Pronunciation in the Americas, Chicago: University of Chicago Press
- Corominas, Joan (1987), Breve diccionario etimológico de la lengua castellana, Madrid: Gredos
- Cotton, Eleanor Greet; Sharp, John M. (1988), Spanish in the Americas, Washington: Georgetown University Press, ISBN 0-87840-360-4
- Delforge, Ann Marie (2008), "Unstressed Vowel Reduction in Andean Spanish", in Colantoni, Laura; Steele, Jeffrey, Selected Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Laboratory Approaches to Spanish Phonology (PDF), Somerville, Mass., USA: Cascadilla, pp. 107–124
- González Bueno, Manuela (1993), "Variaciones en el tratamiento de las sibilantes: Inconsistencia en el seseo sevillano: Un enfoque sociolingüístico", Hispania 76 (2): 392–398
- Hualde, José Ignacio (2008), The Sounds of Spanish, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
- Kany, Charles E. (1951), American-Spanish Syntax, Chicago: University of Chicago Press
- Lipski, John (1994), Latin American Spanish, London: Longman
- Lope Blanch, Juan M. (1972), "En torno a las vocales caedizas del español mexicano", Estudios sobre el español de México (PDF), Mexico City: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, pp. 53–73
- Miyara, Alberto J. (2001), Diccionario argentino-español para españoles, (Online)
- Moreno Fernández, Francisco (2009), La lengua española en su geografía, Madrid: Arco/Libros
- Seco, Manuel (1986), Diccionario de dudas y dificultades de la lengua española, Madrid: Espasa-Calpe
- Velázquez Spanish and English Dictionary: Pocket Edition, El Monte, Cal., USA: Velázquez Press, 2006, ISBN 1-594-95003-2
- Webster's New World Concise Spanish Dictionary, Indianapolis: Wiley, 2006, ISBN 0-471-74836-6
- Whitley, M[elvin] Stanley (2002), Spanish-English Contrasts, Washington, D.C.: Georgetown University Press
Further reading
- Alonso Zamora Vicente, Dialectología Española (Madrid: Editorial Gredos, 1960) is highly detailed.
External links
- Isogloss maps of phonetic variants in the Iberian Peninsula
- Map of Spanish dialects in the Iberian Peninsula
- Costa Rican Spanish Dictionary
- Spanish learning site with Argentinian speakers
- Latin American Dictionary with variants for every country
- Spanish dialects, pronunciation maps
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||