Sp4 transcription factor
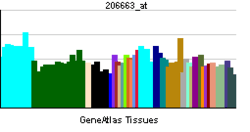
Transcription factor Sp4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP4 gene.[1][2]
Interactions
Sp4 transcription factor has been shown to interact with E2F1.[3]
References
Further reading
- Suske G (1999). "The Sp-family of transcription factors.". Gene 238 (2): 291–300. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00357-1. PMID 10570957.
- Hagen G, Dennig J, Preiss A et al. (1995). "Functional analyses of the transcription factor Sp4 reveal properties distinct from Sp1 and Sp3.". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (42): 24989–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.42.24989. PMID 7559627.
- Kalff-Suske M, Kunz J, Grzeschik KH, Suske G (1995). "Human Sp4 transcription factor gene (SP4) maps to chromosome 7p15.". Genomics 26 (3): 631–3. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80191-N. PMID 7607696.
- Majello B, De Luca P, Hagen G et al. (1995). "Different members of the Sp1 multigene family exert opposite transcriptional regulation of the long terminal repeat of HIV-1.". Nucleic Acids Res. 22 (23): 4914–21. doi:10.1093/nar/22.23.4914. PMC 523756. PMID 7800480.
- Rotheneder H, Geymayer S, Haidweger E (2000). "Transcription factors of the Sp1 family: interaction with E2F and regulation of the murine thymidine kinase promoter.". J. Mol. Biol. 293 (5): 1005–15. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3213. PMID 10547281.
- Nguyên-Trân VT, Kubalak SW, Minamisawa S et al. (2000). "A novel genetic pathway for sudden cardiac death via defects in the transition between ventricular and conduction system cell lineages.". Cell 102 (5): 671–82. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00089-1. PMID 11007485.
- Lerner LE, Gribanova YE, Ji M et al. (2001). "Nrl and Sp nuclear proteins mediate transcription of rod-specific cGMP-phosphodiesterase beta-subunit gene: involvement of multiple response elements.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (37): 34999–5007. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103301200. PMID 11438531.
- Lerner LE, Gribanova YE, Whitaker L et al. (2002). "The rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase beta-subunit promoter is a specific target for Sp4 and is not activated by other Sp proteins or CRX.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (29): 25877–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201407200. PMID 11943774.
- Lee DK, Suh D, Edenberg HJ, Hur MW (2002). "POZ domain transcription factor, FBI-1, represses transcription of ADH5/FDH by interacting with the zinc finger and interfering with DNA binding activity of Sp1.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (30): 26761–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202078200. PMID 12004059.
- Wistow G, Bernstein SL, Wyatt MK et al. (2002). "Expressed sequence tag analysis of human retina for the NEIBank Project: retbindin, an abundant, novel retinal cDNA and alternative splicing of other retina-preferred gene transcripts.". Mol. Vis. 8: 196–204. PMID 12107411.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Davis W, Chen ZJ, Ile KE, Tew KD (2003). "Reciprocal regulation of expression of the human adenosine 5'-triphosphate binding cassette, sub-family A, transporter 2 (ABCA2) promoter by the early growth response-1 (EGR-1) and Sp-family transcription factors.". Nucleic Acids Res. 31 (3): 1097–107. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg192. PMC 149212. PMID 12560508.
- Hillier LW, Fulton RS, Fulton LA et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 7.". Nature 424 (6945): 157–64. doi:10.1038/nature01782. PMID 12853948.
- Hong J, Samudio I, Liu S et al. (2004). "Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent activation of p21 in Panc-28 pancreatic cancer cells involves Sp1 and Sp4 proteins.". Endocrinology 145 (12): 5774–85. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0686. PMID 15345676.
- Phillips RJ, Tyson-Capper Née Pollard AJ, Bailey J et al. (2005). "Regulation of expression of the chorionic gonadotropin/luteinizing hormone receptor gene in the human myometrium: involvement of specificity protein-1 (Sp1), Sp3, Sp4, Sp-like proteins, and histone deacetylases.". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90 (6): 3479–90. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-1962. PMID 15788387.
- Higgins KJ, Liu S, Abdelrahim M et al. (2006). "Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression is induced by 17beta-estradiol in ZR-75 breast cancer cells by estrogen receptor alpha/Sp proteins.". Endocrinology 147 (7): 3285–95. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0081. PMID 16574784.
- Gao YQ, Danciger M, Ozgul RK et al. (2007). "Association of the Asn306Ser variant of the SP4 transcription factor and an intronic variant in the beta-subunit of transducin with digenic disease.". Mol. Vis. 13: 287–92. PMC 2633482. PMID 17356515.
PDB gallery |
|---|
| | 1va1: Solution Structure of Transcription Factor Sp1 DNA Binding Domain (Zinc Finger 1) |
|
|
|
External links
|
|---|
| | | | |
|---|
| | (2.1) Nuclear receptor (Cys4) | | subfamily 1 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 2 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 3 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 4 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 5 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 6 | |
|---|
| | subfamily 0 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| | (2.2) Other Cys4 | |
|---|
| | (2.3) Cys2His2 | |
|---|
| | (2.4) Cys6 | |
|---|
| | (2.5) Alternating composition | |
|---|
| | (2.6) WRKY | |
|---|
|
| | | | | (4) β-Scaffold factors with minor groove contacts |
|---|
| |
| | | (0) Other transcription factors |
|---|
| |
| | see also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
Index of genetics |
|---|
| | Description |
- Gene expression
- DNA
- replication
- cycle
- recombination
- repair
- binding proteins
- Transcription
- factors
- regulators
- nucleic acids
- RNA
- RNA binding proteins
- ribonucleoproteins
- repeated sequence
- modification
- Translation
- ribosome
- modification
- nexins
- Proteins
- domains
- Structure
- primary
- secondary
- tertiary
- quaternary
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Replication and repair
- Transcription factor
- Transcription
- Translation
|
|---|
|
|