Southern Europe
| Southern Europe | |
|---|---|
|
Geographic features of countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea |
The term Southern Europe, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, economic, civilizational and socio-cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical geographic, phytogeographic or climatic approach.
Geographic definition
.png)
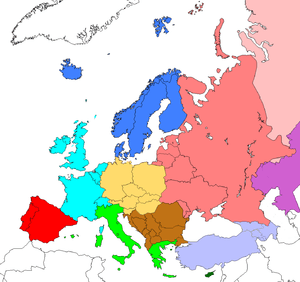
Geographically, southern Europe is the southern half of the landmass of Europe. This definition is relative, with no clear limits.
Countries geographically considered part of southern Europe include:
Southwestern Europe (Iberian peninsula)
- Countries whose borders lie within Southwestern Europe (Iberia)
Southcentral Europe (Italian Peninsula)[1]
Southeastern Europe (Balkan peninsula)
- Countries whose borders lie within Southeastern Europe (the Balkans)
-
 Albania
Albania -
 Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina -
 Bulgaria
Bulgaria -
 Croatia
Croatia -
 Greece
Greece - Kosovo
-
 Macedonia
Macedonia -
 Montenegro
Montenegro -
 Romania
Romania -
 Serbia
Serbia -
 Slovenia
Slovenia
Island countries
United Nations geoscheme
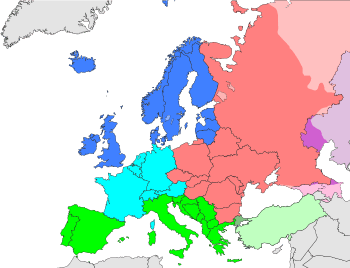
For its official works and publications, the United Nations Organization groups countries under a classification of regions. Southern Europe, as defined by the United Nations (the sub-regions according to the UN), comprises the following countries and territories:[2]
 Albania
Albania Andorra
Andorra Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia
Croatia Gibraltar (UK - British overseas territory)
Gibraltar (UK - British overseas territory) Greece (including: Aegean Islands, Crete, and Ionian Islands)
Greece (including: Aegean Islands, Crete, and Ionian Islands) Italy (including: Sardinia and Sicily)
Italy (including: Sardinia and Sicily) Macedonia
Macedonia Malta (including: Gozo)
Malta (including: Gozo) Montenegro
Montenegro Portugal (including: Madeira and Azores)
Portugal (including: Madeira and Azores) San Marino
San Marino Serbia
Serbia Slovenia
Slovenia-
 Spain (including: Balearic Islands, Canary Islands, Ceuta, Melilla, and plazas de soberanía)
Spain (including: Balearic Islands, Canary Islands, Ceuta, Melilla, and plazas de soberanía)  Vatican City
Vatican City
As of 2009, there were 153,506,431 people living in southern Europe with an average population density of 117 inhabitants per square kilometer:[2]
| Southern Europe:[2] | ||||
| Country | Area (km²) |
Population (2010 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
28,748 | 2,821,977 | 111.1 | Tirana |
| |
467.63 | 84,082 | 179.8 | Andorra la Vella |
| |
51,129 | 4,613,414 | 90.2 | Sarajevo |
| |
110,994 | 7,364,570 | 77 | Sofia |
| |
56,594 | 4,489,409 | 81 | Zagreb |
| |
6.8 | 29,431 | 4,328 | Gibraltar |
| |
131,990 | 11,295,002 | 85.3 | Athens |
| |
301,338 | 60,418,711 | 200.5 | Rome |
| |
25,713 | 2,114,550 | 82.2 | Skopje |
| |
316 | 412,966 | 1,306.8 | Valletta |
| |
13,812 | 672,181 | 50 | Podgorica |
| |
92,090 | 11,317,192 | 114 | Lisbon |
| |
61.2 | 31,716 | 501 | City of San Marino |
| |
88,361 | 7,120,666 | 102.46 | Belgrade |
| |
20,273 | 2,054,199 | 99.6 | Ljubljana |
| |
504,030 | 46,030,109 | 93 | Madrid |
| |
0.44 | 826 | 1877 | Vatican City |
| Total | 1,314,930 | 153,506,431 | 116.74 | |
Climatic definitions
Mediterranean climate
Southern Europe's most emblematic climate is that of the Mediterranean climate, which has become a typically known characteristic of the area. Those areas of Mediterranean climate present similar vegetations and landscapes throughout, including dry hills, small plains, pine forests and olive trees.
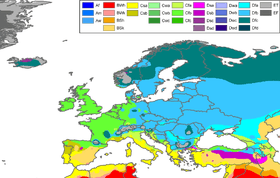
The area which belongs to the Mediterranean climate is:
 Albania
Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina (coasts) and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina (coasts) and Herzegovina Bulgaria (southern coast and extreme southwest)
Bulgaria (southern coast and extreme southwest) Croatia (coasts)
Croatia (coasts) Cyprus
Cyprus France (southeast coast (Nice), and the island of Corsica)
France (southeast coast (Nice), and the island of Corsica) Gibraltar
Gibraltar Greece
Greece Italy (except the Po River plain, Alps and Apennine mountains)
Italy (except the Po River plain, Alps and Apennine mountains) Macedonia (extreme south)
Macedonia (extreme south) Malta
Malta Monaco
Monaco Montenegro (coasts)
Montenegro (coasts) Portugal
Portugal Slovenia (coasts)
Slovenia (coasts) Spain (the whole of the country except the northern coast and the Pyreenes)
Spain (the whole of the country except the northern coast and the Pyreenes)
Humid- and temperate subtropical climate
Humid subtropical climate, as well as the temperate subtropical type, are found in the following Southern European countries:
 Italy (the Po River plain, Alps and Apennine mountains)
Italy (the Po River plain, Alps and Apennine mountains) Croatia (in Lika and Banovina)
Croatia (in Lika and Banovina) Bosnia and Herzegovina (in Bosanska Krajina)
Bosnia and Herzegovina (in Bosanska Krajina) Serbia (Central Serbia)
Serbia (Central Serbia) Montenegro (in the mountains)
Montenegro (in the mountains) Macedonia (in Polog)
Macedonia (in Polog) Greece (Greek Macedonia)
Greece (Greek Macedonia) Bulgaria (in provinces of Vidin, Vratsa, Montana, Varna and Dobrich)
Bulgaria (in provinces of Vidin, Vratsa, Montana, Varna and Dobrich)
Phytogeographic definition
.png)

Southern Europe's flora is that of the Mediterranean Region, one of the phytochoria recognized by Armen Takhtajan. The Mediterranean and Submediterranean climate regions in Europe comprise the following countries and territories:[3]
 Albania
Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria
Bulgaria Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus France (the southeastern part, and the island of Corsica)
France (the southeastern part, and the island of Corsica) Greece (including: Aegean Islands, Crete, and Ionian Islands)
Greece (including: Aegean Islands, Crete, and Ionian Islands) Hungary (the southwestern part till the Lake Balaton)
Hungary (the southwestern part till the Lake Balaton) Italy
Italy Macedonia
Macedonia Malta
Malta Montenegro
Montenegro Portugal (except for the northwestern part)
Portugal (except for the northwestern part) Romania (only the southern part along the Danube river)
Romania (only the southern part along the Danube river) Serbia (most of Central Serbia)
Serbia (most of Central Serbia) Slovenia
Slovenia Spain (except for the northwestern part)
Spain (except for the northwestern part) Switzerland (only Ticino)
Switzerland (only Ticino) Ukraine (only the southern part of Crimea)
Ukraine (only the southern part of Crimea)
Linguistic Southern Europe
Romance languages and modern Greek are the heirs of Latin and ancient Greek, which served as the main historical languages of the Mediterranean region.
Romance languages
Romance languages have spread from the Italian peninsula, and are emblematic of Southwestern Europe. (See the Latin Arch.)
 Andorra: Catalan (official); French; Portuguese; Spanish
Andorra: Catalan (official); French; Portuguese; Spanish Italy: Italian (official); Sardinian (recognised); Piedmontese; Friulian (recognised); Ladin (recognised); Ligurian; Lombard; Venetian; Emiliano-Romagnolo; Neapolitan; Sicilian
Italy: Italian (official); Sardinian (recognised); Piedmontese; Friulian (recognised); Ladin (recognised); Ligurian; Lombard; Venetian; Emiliano-Romagnolo; Neapolitan; Sicilian Moldova: Moldovan language (official)
Moldova: Moldovan language (official) Monaco: French (official); Monégasque; Occitan; Italian
Monaco: French (official); Monégasque; Occitan; Italian Portugal: Portuguese (official); Mirandese (recognised)
Portugal: Portuguese (official); Mirandese (recognised) Romania: Romanian (official)
Romania: Romanian (official) San Marino: Italian (official)
San Marino: Italian (official) Spain: Spanish (official); Catalan (recognised); Galician (recognised); Aragonese; Fala; Asturian; Leonese; Extremaduran; Occitan (recognised)
Spain: Spanish (official); Catalan (recognised); Galician (recognised); Aragonese; Fala; Asturian; Leonese; Extremaduran; Occitan (recognised) Switzerland: French (official); Italian (official); Romansh (official)
Switzerland: French (official); Italian (official); Romansh (official) Vatican City: Italian (official); Latin
Vatican City: Italian (official); Latin
- Small communities in
 Albania: Aromanian
Albania: Aromanian Bulgaria: Aromanian
Bulgaria: Aromanian Gibraltar: Llanito; Spanish
Gibraltar: Llanito; Spanish Greece: Aromanian; Ladino; Italian
Greece: Aromanian; Ladino; Italian Macedonia: Aromanian
Macedonia: Aromanian Malta: Sicilian; Italian
Malta: Sicilian; Italian Serbia: Vlach and Banat Romanian
Serbia: Vlach and Banat Romanian
Hellenic languages
 Greece: Greek (official); Cappadocian; Cretan; Maniot; Pontic; Tsakonian; Romano-Greek; Sarakatsan; Yevanic
Greece: Greek (official); Cappadocian; Cretan; Maniot; Pontic; Tsakonian; Romano-Greek; Sarakatsan; Yevanic Cyprus: Cypriot Greek (official)
Cyprus: Cypriot Greek (official)
- Small communities in
 Albania: Greek (recognised)
Albania: Greek (recognised) Bulgaria: Sarakatsan Greek
Bulgaria: Sarakatsan Greek Italy: Griko (recognised)
Italy: Griko (recognised) Macedonia: Sarakatsan Greek
Macedonia: Sarakatsan Greek Romania: Greek (recognised)
Romania: Greek (recognised) Ukraine: Crimean Greek (recognised)
Ukraine: Crimean Greek (recognised)
Albanian languages
 Albania: Albanian (official); Transitional dialects; Tosk Albanian, Gheg Albanian
Albania: Albanian (official); Transitional dialects; Tosk Albanian, Gheg Albanian Kosovo: Albanian (official); Gheg Albanian
Kosovo: Albanian (official); Gheg Albanian Macedonia: Albanian (semi-official); Gheg Albanian; Tosk Albanian
Macedonia: Albanian (semi-official); Gheg Albanian; Tosk Albanian
- Small communities in
 Montenegro: Gheg Albanian (recognised)
Montenegro: Gheg Albanian (recognised) Serbia: Gheg Albanian (recognised)
Serbia: Gheg Albanian (recognised) Greece: Tosk Albanian
Greece: Tosk Albanian Italy: Tosk Albanian (recognised)
Italy: Tosk Albanian (recognised) Croatia: Gheg Albanian
Croatia: Gheg Albanian Romania: Albanian (recognised)
Romania: Albanian (recognised)
South Slavic languages
 Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosnian (official); Croatian (official); Serbian (official)
Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosnian (official); Croatian (official); Serbian (official) Bulgaria: Bulgarian (official)
Bulgaria: Bulgarian (official) Croatia: Croatian (official); Serbian
Croatia: Croatian (official); Serbian Macedonia: Macedonian (official); Bulgarian; Serbian
Macedonia: Macedonian (official); Bulgarian; Serbian Montenegro: Montenegrin (official); Serbian (recognised)
Montenegro: Montenegrin (official); Serbian (recognised) Serbia: Serbian (official); Montenegrin (recognised)
Serbia: Serbian (official); Montenegrin (recognised) Slovenia: Slovene (official)
Slovenia: Slovene (official)
- Small communities in
 Albania: Macedonian (recognised); Montenegrin; Serbian
Albania: Macedonian (recognised); Montenegrin; Serbian Greece: Bulgarian (recognised in Mount Athos); Macedonian; Serbian (recognised in Mount Athos)
Greece: Bulgarian (recognised in Mount Athos); Macedonian; Serbian (recognised in Mount Athos) Italy: Slovene, Croatian
Italy: Slovene, Croatian Romania: Croatian (recognised); Serbian (recognised); Bulgarian
Romania: Croatian (recognised); Serbian (recognised); Bulgarian
Germanic languages
Due to the English colonisation of Malta and Gibraltar, Germanic languages have a small presence in Southern Europe, far from the core of Germanic languages in Northwestern Europe. Malta uses English as a second language in some cases (after Maltese, which still is the original and main native language). In Gibraltar, English is the official language but Spanish and Llanito (mix of Andalusian Spanish with some English) are also spoken.
- Small communities in
Semitic languages
Basque languages
The Basque language is a linguistic isolate spoken by the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France.
European Travel Commission classification
European Travel Commission divides the European region on the basis of Tourism Decision Metrics (TDM) model. Countries which belong to the Southern/Mediterranean Europe are:[4]
 Albania
Albania Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia
Croatia Cyprus
Cyprus Italy
Italy Greece
Greece Macedonia
Macedonia Malta
Malta Montenegro
Montenegro Serbia
Serbia Slovenia
Slovenia Spain
Spain
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Southern Europe. |
Notes
| a. | ^ Kosovo is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Republic of Serbia and the Republic of Kosovo. The latter declared independence on 17 February 2008, but Serbia continues to claim it as part of its own sovereign territory. Kosovo's independence has been recognised by 108 out of 193 United Nations member states. |
References
- ↑ According to Encyclopædia Britannica Italy is located in South-Central Europe http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/297474/Italy
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 United Nations Statistics Division- Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications (M49)
- ↑ Wolfgang Frey and Rainer Lösch; Lehrbuch der Geobotanik. Pflanze und Vegetation in Raum und Zeit. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, München 2004
- ↑ European Tourism in 2014: Trends & Prospects (Q3/2014), page 15
| ||||||||||
