Solar eclipse of February 16, 1999
| Solar eclipse of February 16, 1999 | |
|---|---|
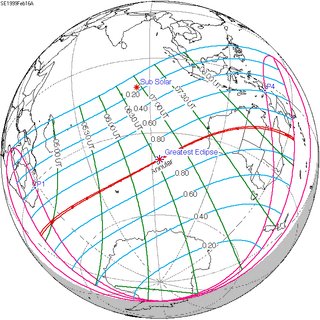 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | -0.4726 |
| Magnitude | 0.9928 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 40 sec (0 m 40 s) |
| Coordinates | 39°48′S 93°54′E / 39.8°S 93.9°E |
| Max. width of band | 29 km (18 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 6:34:38 |
| References | |
| Saros | 140 (28 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9505 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred on February 16, 1999. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
Images

Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1997-2000
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |||
120 Chita, Russia | March 9, 1997 Total |
125 | September 2, 1997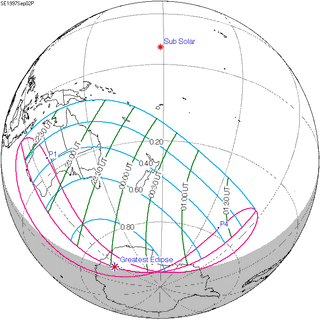 Partial | |||
| 130 | February 26, 1998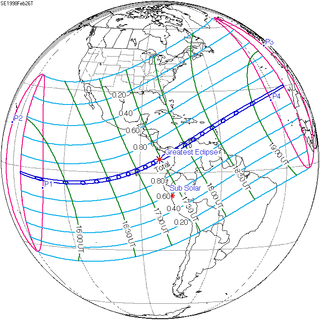 Total |
135 | August 22, 1998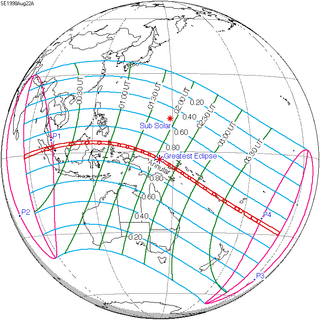 Annular | |||
| 140 | February 16, 1999 Annular |
145 Totality Cornwall, United Kingdom | August 11, 1999 Total | |||
| 150 | February 5, 2000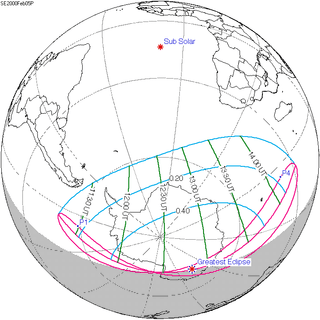 Partial |
155 | July 31, 2000 Partial | |||
| Partial solar eclipses on July 1, 2000 and December 25, 2000 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set. | ||||||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
This series has 21 eclipse events between July 11, 1953 and July 11, 2029.
| July 10-11 | April 29-30 | February 15-16 | December 4 | September 21-23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 11, 1953 |
 April 30, 1957 |
 February 15, 1961 |
 December 4, 1964 |
 September 22, 1968 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 10, 1972 |
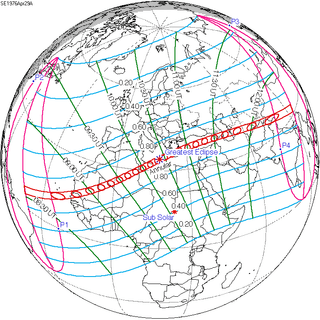 April 29, 1976 |
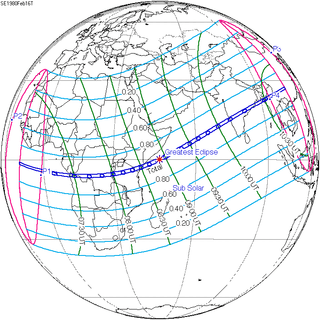 February 16, 1980 |
 December 4, 1983 |
 September 23, 1987 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 11, 1991 |
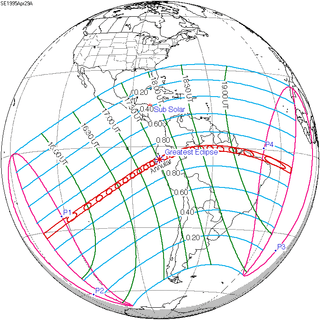 April 29, 1995 |
 February 16, 1999 |
 December 4, 2002 |
 September 22, 2006 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 11, 2010 |
 April 29, 2014 |
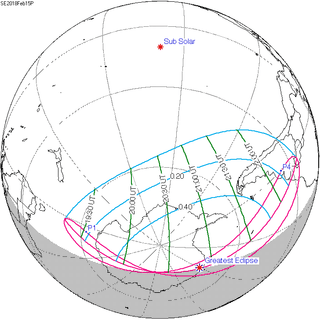 February 15, 2018 |
 December 4, 2021 |
 September 21, 2025 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 11, 2029 |
Notes
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 1999 February 16. |

