Small intestine
| Small intestine | |
|---|---|
 Diagram showing the small intestine and surrounding structures | |
| Details | |
| Latin | Intestinum tenue |
| Superior mesenteric artery | |
| Hepatic portal vein | |
| Celiac ganglia, vagus[1] | |
| Intestinal lymph trunk | |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.1168 |
| MeSH | A03.556.124.684 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | Small intestine |
| TA | A05.6.01.001 |
| FMA | 7200 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The small intestine (or small bowel) is the part of the GI tract following the stomach and followed by the large intestine, and is where much of the digestion and absorption of food takes place. The small intestine is composed of a duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. It receives bile juice and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct, controlled by the sphincter of Oddi.
This article is primarily about the human gastrointestinal tract. The information about its processes is directly applicable to most placental mammals. The primary function of the small intestine is the absorption of nutrients and minerals found in food.[2] A major exception to this is cows; for information about digestion in cows and other similar mammals, see ruminants. In invertebrates such as worms, the terms "gastrointestinal tract" and "large intestine" are often used to describe the entire intestine.
Structure
The average length of the small intestine in an adult human male is 6.9 m (22 ft 8 in), and 7.1 m (23 ft 4 in) in an adult female. It can vary greatly, from as short as 4.6 m (15 ft) to as long as 9.8 m (32 ft).[3][4] Recent studies indicate that small intestine may be shorter, around 3.5 m (11 ft 6 in), and that the length is less affected by age after childhood than expected[5]
It is approximately 2.5–3 cm in diameter. The surface area of the human small intestinal mucosa averages 30 square meter [6]
The small intestine is divided into three structural parts. The duodenum is a short structure (about 20–25 cm long) continuous with the stomach and shaped like a "C".[7] It surrounds the head of the pancreas. It receives gastric chyme from the stomach, together with digestive juices from the pancreas (digestive enzymes) and the gall bladder (bile). The digestive enzymes break down proteins and bile and emulsify fats into micelles. The duodenum contains Brunner's glands, which produce a mucus-rich alkaline secretion containing bicarbonate. These secretions, in combination with bicarbonate from the pancreas, neutralizes the stomach acids contained in gastric chyme.
The jejunum is the midsection of the small intestine, connecting the duodenum to the ileum. It is about 2.5 m long, and contains the plicae circulares, and villi that increase its surface area. Products of digestion (sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids) are absorbed into the bloodstream here. The suspensory muscle of duodenum marks the division between the duodenum and the jejunum.
The ileum: The final section of the small intestine. It is about 3 m long, and contains villi similar to the jejunum. It absorbs mainly vitamin B12 and bile acids, as well as any other remaining nutrients. The ileum joins to the cecum of the large intestine at the ileocecal junction.
The jejunum and ileum are suspended in the abdominal cavity by mesentery. The mesentery is part of the peritoneum. Arteries, veins, lymph vessels and nerves travel within the mesentery.[8]
The small intestine receives a blood supply from the coeliac trunk and the superior mesenteric artery. These are both branches of the aorta. The duodenum receives blood from the coeliac trunk via the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery and from the superior mesenteric artery visa the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery. These two arteries both have anterior and posterior branches that meet in the midline and anastaomose. The jejunum and ileum receive blood from the superior mesenteric artery.[9] Branches of the superior mesenteric artery form a series of arches within the mesentery known as vascular arcades, which may be several layers deep. Straight blood vessels known as vasa recti travel from the arcades closest to the ileum and jejunum to the organs themselves.[9]
Histology

The three sections of the small intestine look similar to each other at a microscopic level, but there are some important differences. The parts of the intestine are as follows:
| Layer | Duodenum | Jejunum | Ileum |
|---|---|---|---|
| serosa | 1st part serosa, 2nd - 4th adventitia | normal | normal |
| muscularis externa | longitudinal and circular layers, with Auerbach's (myenteric) plexus in between | same as duodenum | same as duodenum |
| submucosa | Brunner's glands and Meissner's (submucosal) plexus | no BG | no BG |
| mucosa: muscularis mucosae | normal | normal | normal |
| mucosa: lamina propria | no PP | no PP | Peyer's patches |
| mucosa: intestinal epithelium | simple columnar. Contains goblet cells, Paneth cells | Similar to duodenum | ? |
Development
The small intestine develops from the midgut of the primitive gut tube.[10] By the fifth week of embryological life, the ileum begins to grow longer at a very fast rate, forming a U-shaped fold called the primary intestinal loop. The loop grows so fast in length that it outgrows the abdomen and protrudes through the umbilicus. By week 10, the loop retracts back into the abdomen. Between weeks six and ten the small intestine rotates anticlockwise, as viewed from the front of the embryo. It rotates a further 180 degrees after it has moved back into the abdomen. This process creates the twisted shape of the large intestine.[10]
Function
Food from the stomach is allowed into the duodenum through the pylorus by a muscle called the pyloric sphincter.
Digestion
The small intestine is where most chemical digestion takes place. Many of the digestive enzymes that act in the small intestine are secreted by the pancreas and enter the small intestine via the pancreatic duct. Pancreatic enzymes and bile from the gallbladder enter the small intestine in response to the hormone cholecystokinin, which is produced in the small intestine in response to the presence of nutrients. Secretin, another hormone produced in the small intestine, causes additional effects on the pancreas, where it promotes the release of bicarbonate into the duodenum in order to neutralize the potentially harmful acid coming from the stomach.
The three major classes of nutrients that undergo digestion are proteins, lipids (fats) and carbohydrates:
- Proteins are degraded into small peptides and amino acids before absorption.[11] Chemical breakdown begins in the stomach and continues in the small intestine. Proteolytic enzymes, including trypsin and chymotrypsin, are secreted by the pancreas and cleave proteins into smaller peptides. Carboxypeptidase, which is a pancreatic brush border enzyme, splits one amino acid at a time. Aminopeptidase and dipeptidase free the end amino acid products.
- Lipids (fats) are degraded into fatty acids and glycerol. Pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids and monoglycerides. Pancreatic lipase works with the help of the salts from the bile secreted by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. Bile salts attach to triglycerides to help emulsify them, which aids access by pancreatic lipase. This occurs because the lipase is water-soluble but the fatty triglycerides are hydrophobic and tend to orient towards each other and away from the watery intestinal surroundings. The bile salts emulsify the triglycerides in the watery surroundings until the lipase can break them into the smaller components that are able to enter the villi for absorption.
- Some carbohydrates are degraded into simple sugars, or monosaccharides (e.g., glucose). Pancreatic amylase breaks down some carbohydrates (notably starch) into oligosaccharides. Other carbohydrates pass undigested into the large intestine and further handling by intestinal bacteria. Brush border enzymes take over from there. The most important brush border enzymes are dextrinase and glucoamylase which further break down oligosaccharides. Other brush border enzymes are maltase, sucrase and lactase. Lactase is absent in most adult humans and for them lactose, like most poly-saccharides, are not digested in the small intestine. Some carbohydrates, such as cellulose, are not digested at all, despite being made of multiple glucose units. This is because the cellulose is made out of beta-glucose, making the inter-monosaccharidal bindings different from the ones present in starch, which consists of alpha-glucose. Humans lack the enzyme for splitting the beta-glucose-bonds, something reserved for herbivores and bacteria from the large intestine.
Absorption
Digested food is now able to pass into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine through either diffusion or active transport. The small intestine is the site where most of the nutrients from ingested food are absorbed. The inner wall, or mucosa, of the small intestine is lined with simple columnar epithelial tissue. Structurally, the mucosa is covered in wrinkles or folds called plicae circulares, which are considered permanent features in the wall of the organ. They are distinct from rugae which are considered non-permanent or temporary allowing for distention and contraction. From the plicae circulares project microscopic finger-like pieces of tissue called villi (Latin for "shaggy hair"). The individual epithelial cells also have finger-like projections known as microvilli. The functions of the plicae circulares, the villi, and the microvilli are to increase the amount of surface area available for the absorption of nutrients, and to limit the loss of said nutrients to intestinal fauna.
Each villus has a network of capillaries and fine lymphatic vessels called lacteals close to its surface. The epithelial cells of the villi transport nutrients from the lumen of the intestine into these capillaries (amino acids and carbohydrates) and lacteals (lipids). The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body where they are used to build complex substances such as the proteins required by our body. The material that remains undigested and unabsorbed passes into the large intestine.
Absorption of the majority of nutrients takes place in the jejunum, with the following notable exceptions:
- Iron is absorbed in the duodenum.
- Vitamin B12 (Extrinsic factor) and bile salts are absorbed in the terminal ileum.
- Water and lipids are absorbed by passive diffusion throughout the small intestine.
- Sodium bicarbonate is absorbed by active transport and glucose and amino acid co-transport.
- Fructose is absorbed by facilitated diffusion.
Immunological
The small intestine supports the body's immune system.[12] The presence of probiotic gut flora appear to contribute positively to the host's immune system.[13]
Clinical significance
The small intestine is a complex organ, and as such, there are a very large number of possible conditions that may affect the function of the small bowel. A few of them are listed below, some of which are common, with up to 10% of people being affected at some time in their lives, while others are vanishingly rare.
- Small intestine obstruction or obstructive disorders
- Paralytic ileus
- Volvulus
- Hernia
- Adhesions
- Obstruction from external pressure
- Obstruction by masses in the lumen (foreign bodies, bezoar, gallstones)
- Infectious diseases
- Giardiasis
- Ascariasis
- Tropical sprue
- Tape worm (Diphyllobothrium latum, Taenia solium, Hymenolepsis nana)
- Hookworm (e.g. Necator americanus, Ancylostoma duodenale)
- Nematodes (e.g. Ascaris lumbricoides)
- Other Protozoa (e.g. Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora, Microsporidia, Entamoeba histolytica)
- Bacterial Infections
- Enterotoxigenic E. coli
- Salmonella enterica
- Campylobacter
- Shigella
- Yersinia
- Clostridium difficile (antibiotic-associated colitis, Pseudomembranous Colitis
- Mycobacterium (disseminated Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
- Whipple's Disease
- Vibrio (Cholera)
- Enteric (Typhoid) Fever (Salmonella enterica var. typhii) and Paratyphoid fever
- Bacillus cereus
- Clostridium perfringens (Gas Gangrene)
- Viral Infections
- Rotavirus
- Norovirus
- Astrovirus
- Adenovirus
- Calicivirus
- Neoplasms (Cancers)
- Adenocarcinoma
- Carcinoid
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST)
- Lymphoma
- Sarcoma
- Leiomyoma
- metastatic tumors, especially SCLC or Melanoma
- Developmental, Congenital or Genetic Conditions
- Duodenal (Intestinal) Atresia
- Hirschsprung's Disease
- Meckel's Diverticulum
- Pyloric Stenosis
- Pancreas Divisum
- Ectopic Pancreas
- Enteric duplication cyst
- Situs Inversus
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Malrotation
- Persistent Urachus
- Omphalocele
- Gastroschisis
- Disachharidase (lactase) deficiencies
- Primary Bile Acid Malsorption
- Gardner Syndrome
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Syndrome (FAP)
- Other Conditions
- Crohn's disease, and the more general Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Typhlitis (neutropenic colitis in the immunosuppressed
- Coeliac disease (Sprue or Non-Tropical Sprue)
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Embolus or Thrombus of the Superior Mesenteric Artery or the Superior Mesenteric Vein
- Arteriovenous malformation
- Gastric dumping syndrome
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Duodenal (Peptic) Ulcers
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- Lymphatic Obstruction due to various causes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Diverticulitis
- Radiation Enterocolitis
- Drug Induced Injury
- Diversion Colitis
- Mesenteric cysts
- Peritoneal Infection
- Sclerosing Retroperitonitis
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Other animals
The small intestine is found in all tetrapods and also in teleosts, although its form and length vary enormously between species. In teleosts, it is relatively short, typically around one and a half times the length of the fish's body. It commonly has a number of pyloric caeca, small pouch-like structures along its length that help to increase the overall surface area of the organ for digesting food. There is no ileocaecal valve in teleosts, with the boundary between the small intestine and the rectum being marked only by the end of the digestive epitheliu [14]
In tetrapods, the ileocaecal valve is always present, opening into the colon. The length of the small intestine is typically longer in tetrapods than in teleosts, but is especially so in herbivores, as well as in mammals and birds, which have a higher metabolic rate than amphibians or reptiles. The lining of the small intestine includes microscopic folds to increase its surface area in all vertebrates, but only in mammals do these develop into true villi.[14]
The boundaries between the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum are somewhat vague even in humans, and such distinctions are either ignored when discussing the anatomy of other animals, or are essentially arbitrary.[14]
There is no small intestine as such in non-teleost fish, such as sharks, sturgeons, and lungfish. Instead, the digestive part of the gut forms a spiral intestine, connecting the stomach to the rectum. In this type of gut, the intestine itself is relatively straight, but has a long fold running along the inner surface in a spiral fashion, sometimes for dozens of turns. This valve greatly increases both the surface area and the effective length of the intestine. The lining of the spiral intestine is similar to that of the small intestine in teleosts and non-mammalian tetrapods.[14]
In lampreys, the spiral valve is extremely small, possibly because their diet requires little digestion. Hagfish have no spiral valve at all, with digestion occurring for almost the entire length of the intestine, which is not subdivided into different regions.[14]
Society and culture
In traditional Chinese medicine, the small intestine is a yang organ.[15]
Additional images
-

The small intestine lies behind the greater omentum.
-

Small intestine in situ, greater omentum folded upwards.
-

Small intestine pulled out to the left, showing the underlying peritoneum, and the mesentierial connection.
-

Small intestine removed, showing underlying structures, and mesentery.
-

Cross section showing the small intestine as it passes back and forth in the peritoneal cavity.
-

Third state of the development of the intestinal canal and peritoneum, seen from in front (diagrammatic). The mode of preparation is the same as in Fig 400
-

Second stage of development of the intestinal canal and peritoneum, seen from in front (diagrammatic). The liver has been removed and the two layers of the ventral mesogastrium (lesser omentum) have been cut. The vessels are represented in black and the peritoneum in the reddish tint.
-

First stage of the development of the intestinal canal and the peritoneum, seen from the side (diagrammatic). From colon 1 the ascending and transverse colon will be formed and from colon 2 the descending and sigmoid colons and the rectum.
-
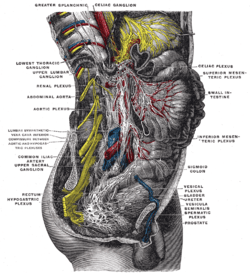
Lower half of right sympathetic cord
-
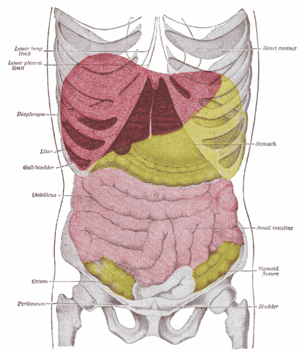
Topography of thoracic and abdominal viscera
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Small intestine. |
Notes and references
- ↑ Physiology at MCG 6/6ch2/s6ch2_30
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/275485/human-body
- ↑ "Elsevier: Gray's Anatomy, 40th Edition". 1928.
- ↑ "Lea Brothers and Co. 1907: Surgical Applied Anatomy".
- ↑ Gondolesi, G.; Ramisch, D.; Padin, J.; Almau, H.; Sandi, M.; Schelotto, P.B.; Fernandez, A.; Rumbo, C.; Solar, H. (15 Jun 2012). "What Is the Normal Small Bowel Length in Humans? First Donor-Based Cohort Analysis". American Journal of Transplantation (Arlington, VA: American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons) 12: S49-S54. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04148.x. English: {{{1}}}
- ↑ (Helander HF, Fändriks L. Surface area of the digestive tract – revisited. Scand J Gastroenterol 49: 681-9, 2014.)
- ↑ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 273. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 271. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. pp. 295–299. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Schoenwolf, Gary C.; Bleyl, Steven B.; Brauer, Philip R.; Francis-West, Philippa H. (2009). "Development of the Urogenital system". Larsen's human embryology (4th ed.). Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. p. 237. ISBN 9780443068119.
- ↑ Silk DB (1974). "Progress report. Peptide absorption in man". Gut 15 (6): 494–501. doi:10.1136/gut.15.6.494. PMC 1413009. PMID 4604970.
- ↑ http://www.massgeneral.org/about/pressrelease.aspx?id=1533
- ↑ http://iai.asm.org/content/76/8/3360.short
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 349–353. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ↑ Porter [ed.], Roy (1997). Medicine : a history of healing. [S.l.]: Diane Pub Co. p. 104. ISBN 9780756751432.
Bibliography
- Sherwood, Lauralee (2006). Fundamentals of physiology: a human perspective (Third ed.). Florence, KY: Cengage Learning. p. 768. ISBN 0-534-46697-4.
- Solomon et al. (2002) Biology Sixth Edition, Brooks-Cole/Thomson Learning ISBN 0-03-033503-5
- Townsend et al. (2004) Sabiston Textbook of Surgery, Elsevier ISBN 0-7216-0409-9
- Thomson A, Drozdowski L, Iordache C, Thomson B, Vermeire S, Clandinin M, Wild G (2003). "Small bowel review: Normal physiology, part 1.". Dig Dis Sci 48 (8): 1546–64. doi:10.1023/A:1024719925058. PMID 12924651.
- Thomson A, Drozdowski L, Iordache C, Thomson B, Vermeire S, Clandinin M, Wild G (2003). "Small bowel review: Normal physiology, part 2.". Dig Dis Sci 48 (8): 1565–81. doi:10.1023/A:1024724109128. PMID 12924652.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||