Sloth lemur
| Sloth lemur | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life restoration of a large sloth lemur (Palaeopropithecus ingens) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Superfamily: | Lemuroidea |
| Family: | †Palaeopropithecidae Tattersall, 1973[1] |
| Genera | |
The sloth lemurs (Palaeopropithecidae) is an extinct clade of lemurs that includes four genera.[2][3] Despite their common names, members of Palaeopropithecidae were not closely related to sloths but were closely related to the other lemur species.
-

Archaeoindris fontoynonti
-

Babakotia radofilai
-
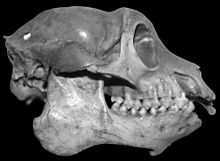
Mesopropithecus globiceps
| Taxonomy of family Palaeopropithecidae[4](Table 21.1) | Phylogeny of sloth lemurs and their closest relatives[5][6] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
References
- ↑ McKenna, MC; Bell, SK (1997). Classification of Mammals: Above the Species Level. Columbia University Press. p. 335. ISBN 0-231-11013-8.
- ↑ Mittermeier, Russell A. et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (2nd ed.). Conservation International. pp. 44–45. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
- ↑ Nowak, Ronald M. (1999). Walker's Primates of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 89–91. ISBN 0-8018-6251-5.
- ↑ Godfrey, L. R.; Jungers, W. L.; Burney, D. A. (2010). "Chapter 21: Subfossil Lemurs of Madagascar". In Werdelin, L.; Sanders, W. J. Cenozoic Mammals of Africa. University of California Press. pp. 351–367. ISBN 978-0-520-25721-4.
- ↑ Orlando, L.; Calvignac, S.; Schnebelen, C.; Douady, C. J.; Godfrey, L. R.; Hänni, C. (2008). "DNA from extinct giant lemurs links archaeolemurids to extant indriids" (PDF). BMC Evolutionary Biology 8 (121). doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-121. PMC 2386821. PMID 18442367.
- ↑ Godfrey, L. R.; Jungers, W. L. (2003). "Subfossil Lemurs". In Goodman, S. M.; Benstead, J. P. The Natural History of Madagascar. University of Chicago Press. pp. 1247–1252. ISBN 0-226-30306-3.