Siwa culture
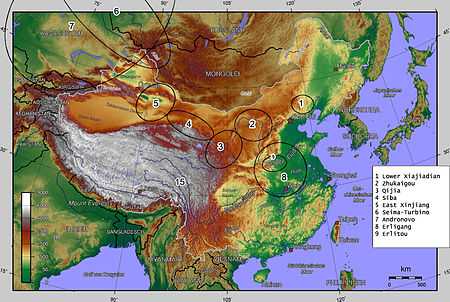
Siwa culture (also 'Siba'; Chinese: 寺洼文化; pinyin: Sìwā wénhuà) was a Bronze Age culture in the Gansu province of China. It was first discovered at Mount Siwa (寺洼山) in Lintao County, hence its name.[1] Siwa culture dating is approximately from 14th to 11th Century BC,[2] it is tentatively attributed to the cultures of the Di (氐) and Qiang (羌) peoples.[3]
Geography
The Siwa culture is divided into two types – Siwa and Anguo. The former is distributed along the Tao River (Taohe) and the latter along the Weihe river. Siwa-type is somewhat earlier than the Western Zhou dynasty, while the Anguo-type is more or less contemporaneous with it.[4]
One of Siwa culture's main characteristics is pottery with saddle-shaped openings (马鞍口陶罐),[5] It is also distinguished by its bronze objects.
Since 2006, the Siwa site (寺洼遗址) is on the list of the People's Republic of China's archeological monuments.
See also
Literature
Nicola Di Cosmo, The Northern Frontier in Pre-Imperial China//The Cambridge History of Ancient China: From the Origins of Civilization to 221 BC, Edited by M.Loewe and E.L.Shaughnessy. ISBN 0-521-47030-7
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Siba culture. |
- Late Neolithic Siwa Culture Amphora TN009
- A Study on Donghuishan Cemetery— Including a Discussion on the Siba Culture and its Position in Sino-Western Cultural Exchange (A Summary) Zhang Zhongpei
References
- ↑ Diese Stätte wird auch Miaopingyagou yizhi 庙坪鸦沟遗址 genannt.
- ↑ http://www.gscn.com.cn/Get/dingxi/101927379.htm
- ↑ 甘肃日报 [Gānsù Rìbào, Gansu Daily]. 《走进临洮县寺洼文化遗址》 [Zǒujìn Líntáoxiàn Sìwā Wénhuà Yízhǐ; "Entering Lintao County's Siwa Ruins"]. 2007. Accessed 17 Dec 2013. (Chinese)
- ↑ An Zhimin, THE BRONZE AGE IN EASTERN PARTS OF CENTRAL ASIA. (PDF) Unesco.org
- ↑ http://www.fareastasianart.com/stores/brianpage/items/517132/item517132fareastasianart.html
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Translated from http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Siwa-Kultur''