Sinoite
| Sinoite | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Category | Silicate mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Si2N2O |
| Strunz classification | 01.DB.10 |
| Dana classification | 1.3.9.1 |
| Crystal symmetry | Orthorhombic – pyramidal, H-M symbol (mm2), space group Cmc21 |
| Unit cell | a = 8.84 Å, b = 5.47 Å, c = 4.83 Å, Z = 4 |
| Identification | |
| Color | From colorless to light gray |
| Cleavage | None |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Streak | White |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent to translucent |
| Specific gravity | 2.83 |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (-) |
| Refractive index |
nα = 1.740 nβ = 1.855 nγ = 1.855 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.115 |
| References | [1][2][3] |
Sinoite is rare mineral with the chemical formula Si2N2O. It was first found in 1905 in chondrite meteorites and identified as a distinct mineral in 1965. Sinoite crystallizes upon meteorite impact as grains smaller than 0.2 mm surrounded by Fe-Ni alloys and the mineral enstatite. It is named after its SiNO composition and can be prepared in the laboratory as a silicon oxynitride ceramic.[4]
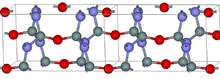
Crystal structure of sinoite. Atoms: red – O, blue – N, gray – Si.[5]
The crystalline structure of silicon oxynitride is built by SiN3O tetrahedra connected through oxygen atoms along the c axis and through nitrogen atoms perpendicular to it. The strong covalent bonding of this structure results in high flexural strength and resistance to heating and oxidation up to temperatures of about 1600 °C.[6]
References
- ↑ Sinoite. Handbook of Mineralogy
- ↑ Sinoite. Mindat.org
- ↑ Sinoite. Webmineral
- ↑ A. E. Rubin (1997). "Sinoite (Si2N2O): Crystallization from EL chondrite impact melts". American Mineralogist 82: 1001.
- ↑ Ohashi, Masayoshi et al. (1993). "Solid Solubility of Aluminum in O'-SiAlON". J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76 (8): 2112–2114. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1993.tb08343.x.
- ↑ Ralf Riedel (18 April 2008). Ceramics science and technology: Structures. Wiley-VCH. pp. 97–. ISBN 978-3-527-31155-2. Retrieved 8 October 2011.