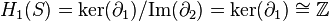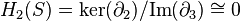Simplicial homology
In the area of algebraic topology, simplicial homology is a process that provides information about the simplicial complex by the number of cycles (a type of hole) it contains, including as the 0-dimensional cycles the number of pieces it is composed of. It also refers to the information produced by that process.
Simplicial homology concerns topological spaces whose building blocks are n-simplices, the n-dimensional analogs of triangles. This includes a point (0-dimensional simplex), a line segment (1-dimensional simplex), a triangle (2-dimensional simplex) and a tetrahedron (3-dimensional simplex). By definition, such a space is homeomorphic to a simplicial complex (more precisely, the geometric realization of an abstract simplicial complex). Such a homeomorphism is referred to as a triangulation of the given space. Replacing n-simplices by their continuous images in a given topological space gives singular homology. The simplicial homology of a simplicial complex is naturally isomorphic to the singular homology of its geometric realization. This implies, in particular, that the simplicial homology of a space does not depend on the triangulation chosen for the space.
It can be shown that all smooth manifolds allow a triangulation (via e.g. Morse theory). This, together with the fact that it is possible to resolve the simplicial homology of a simplicial complex automatically and efficiently, make this theory feasible for application to real life situations, such as image analysis, medical imaging, and data analysis in general.
Definition

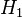 , the 1-cycle at right-middle is homologous to its sum with the boundary of the 2-simplex at left.
, the 1-cycle at right-middle is homologous to its sum with the boundary of the 2-simplex at left.Let S be a simplicial complex. A simplicial k-chain is a formal sum of k-simplices
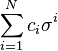 , where
, where 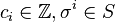 is the i-th k-simplex.
is the i-th k-simplex.
The group of k-chains on S, the free abelian group with basis the set of k-simplices in S, is denoted Ck.
Consider that a basis element of Ck, a k-simplex, is given by a tuple of 0-simplices, or vertices
The boundary operator
is a homomorphism defined by:
where the simplex
is the ith face of σ obtained by deleting its ith vertex.
In Ck, elements of the subgroup
are referred to as cycles, and the subgroup
is said to consist of boundaries.
Direct computation shows that Bk lies in Zk, that is, Bk ⊆ Zk. The boundary of a boundary must be zero. In other words,
form a simplicial chain complex.

The kth homology group Hk of S is defined to be the quotient
A homology group Hk is not trivial if the complex at hand contains k-cycles which are not boundaries. This indicates that there are k-dimensional holes in the complex. For example consider the complex obtained by gluing two triangles (with no interior) along one edge, shown in the image. This is a triangulation of the figure eight. The edges of each triangle form a cycle. These two cycles are by construction not boundaries (there are no 2-chains). Therefore the figure has two "1-holes".
Holes can be of different dimensions. The rank of the homology groups, the numbers
are referred to as the Betti numbers of the space S, and gives a measure of the number of k-dimensional holes in S.
Example
In order to compute the homology groups of the triangle, one should compute the different groups 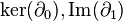 etc. Here, by the definition of the boundary operator, we have
etc. Here, by the definition of the boundary operator, we have ![\partial_0([v_i]) = 0](../I/m/b192669148792069603969d99c3c6f9a.png) , therefore the kernel is:
, therefore the kernel is:
that is every 0-chain is in the kernel. Next, given a 1-chain ![c_1 = b_1[v_1,v_2] + b_2[v_2,v_3] + b_3[v_3,v_1]](../I/m/bd727c582337a7c134cab84744317eca.png) there exists:
there exists:
That is,
![\mathrm{Im}(\partial_1) = \{(b_3-b_1)[v_1] + (b_1-b_2)[v_2] + (b_2-b_3)[v_3] | b_1,b_2,b_3\in \mathbb{Z}\}](../I/m/5699e3255b15651a38b27a558330f6a8.png) ,
,
which means that a 0-chain ![c_0 = a_1[v_1] + a_2[v_2] + a_3[v_3]](../I/m/dc5a854b67e99ed063f5c1820c785f5e.png) is in the image of
is in the image of  if and only if
if and only if


 .
.
This implies that we have only two degrees of freedom for choosing 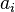 , or in other words:
, or in other words:
Now we can use the definition:
As for the other homology groups, computations are easier.  if and only if
if and only if  , therefore
, therefore
Now, since there are no 2-chains, the kernel and image of  are trivial, that is
are trivial, that is  . This yields:
. This yields:
Applications
A standard scenario in many computer applications is a collection of points (measurements, dark pixels in a bit map, etc.) in which one wishes to find a topological feature. Homology can serve as a qualitative tool to search for such a feature, since it is readily computable from combinatorial data such as a simplicial complex. However, the data points have to first be triangulated, meaning one replaces the data with a simplicial complex approximation. Computation of persistent homology (Edelsbrunner et al.2002 Robins, 1999) involves analysis of homology at different resolutions, registering homology classes (holes) that persist as the resolution is changed. Such features can be used to detect structures of molecules, tumors in X-rays, and cluster structures in complex data. A MATLAB toolbox for computing persistent homology, Plex (Vin de Silva, Gunnar Carlsson), is available at this site Stand-alone implementations in C++ are available as part of the Perseus and Dionysus software projects. More generally, simplicial homology plays a central role in topological data analysis, a technique in the field of data mining.
See also
- Homology theory
- Singular homology
- Cellular homology
References
- Lee, J.M., Introduction to Topological Manifolds, Springer-Verlag, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Vol. 202 (2000) ISBN 0-387-98759-2
- Hatcher, A., Algebraic Topology, Cambridge University Press (2002) ISBN 0-521-79540-0. Detailed discussion of homology theories for simplicial complexes and manifolds, singular homology, etc.
- Moise, E.E., Affine structures in 3-manifolds. V. The triangulation theorem and Hauptvermutung. Ann. Math. 96-114 (1952).


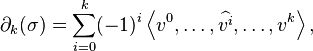

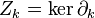




![\mathrm{ker}(\partial_0) = C_0 = \{a_1[v_1] + a_2[v_2] + a_3[v_3] | a_1,a_2,a_3 \in \mathbb{Z}\} \cong \mathbb{Z} \oplus \mathbb{Z} \oplus \mathbb{Z}](../I/m/92013c246227da92ee3a56643653fa1d.png)
![\partial_1(c_1) = (b_3-b_1)[v_1] + (b_1-b_2)[v_2] + (b_2-b_3)[v_3]](../I/m/95948f9703faf8a9f99dffdc41650842.png)

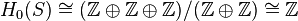
![\mathrm{ker}(\partial_1) = \{b[v_1,v_2] + b[v_2,v_3] + b[v_3,v_1] | b\in \mathbb{Z}\} \cong \mathbb{Z}.](../I/m/d25dc5289015c8863fb085f63e89734b.png)