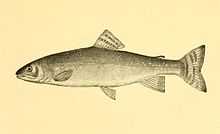
Silver trout
- The name "silver trout" is also sometimes used for rainbow trout.
| Silver trout | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Salmoniformes |
| Family: | Salmonidae |
| Genus: | Salvelinus |
| Species: | S. agassizi |
| Binomial name | |
| Salvelinus agassizi (Garman, 1885) | |
The silver trout, Salvelinus agassizi, is an extinct char species that inhabited a few waters in New Hampshire prior to 1939, when a biological survey conducted on the Connecticut watershed by the New Hampshire Fish and Game Department found none.
Description
The silver trout was often a foot long and was said to actually be olive green in color. In the lakes silver trout inhabited, large quantities of the species appeared in October to spawn. To formally describe the species and prevent local fishermen from overharvesting in the absence of bag limits, specimens were sent to Harvard and the U.S. National Museum for identification, where it was first described as a form of lake trout, and later as a variety of brook trout. The silver trout was described as Salvelinus agassizi in 1885. W.C.Kendall, who published a famous monograph on New England chars in 1914, concluded that the silver trout was related to the Arctic char.
Around 1967, ichthyologist Robert J. Behnke re-examined the 13 specimens in the U.S. National Museum and concluded the silver trout was actually derived from the brook trout by matching the markings on the dorsal fin and tail, the numbers of vertebrae, and the array of pelvic fin rays and gillrakers between the two species. While the silver trout was much more closely related to brook trout, the divergence of the silver trout was enough to place it outside of S. fontinalis. Behnke concluded the silver trout evolved from brook trout ancestors in New England lakes with deep, cold, clear, well-oxygenated depths as a planctivorous fish.[2]
Distribution
It was an exceedingly rare fish, having become trapped by changed drainage systems in two New Hampshire lakes (Monadnock Lake in Dublin and Christine Lake in Stark) that were left as successors of Lake Hitchcock, a very large glacial lake that persisted for 4000 years where the silver trout probably evolved from brook trout.[2] In the deep waters of these lakes, cut off from other species, the silver trout had no natural predators.
Extinction
By the late 19th century, as each lake developed its own steady summer tourism, recreational fishermen who sought to increase their catches began to introduce new fish species, and these eventually overwhelmed the native silver trout. Yellow perch, which eat trout eggs, and lake trout, which hold the same ecological niche, as well as eat and hybridize with other char species, were particularly devastating. Other species were also introduced that have proved to be devastating to native trout species in other waters, the rainbow trout, brown trout, Atlantic salmon, and rainbow smelt.[2]
While the silver trout is most likely lost, success stories like the Pyramid Lake (Alberta) Lahontan cutthroat trout and the Sunapee golden trout exist, and there may still be hope for the silver trout.
References
- ↑ World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1996). "Salvelinus agassizi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.1. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 10 May 2006.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Robert J. Behnke. About Trout: The Best of Robert J. Behnke from Trout Magazine. Retrieved 2014-01-29.
External links
- Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2005). "Salvelinus agassizi" in FishBase. October 2005 version.