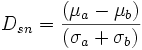Signal-to-noise statistic
In mathematics the signal-to-noise statistic distance between two vectors a and b with mean values 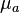 and
and  and standard deviation
and standard deviation 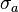 and
and 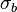 respectively is:
respectively is:
In the case of Gaussian-distributed data and unbiased class distributions, this statistic can be related to classification accuracy given an ideal linear discrimination, and a decision boundary can be derived.[1]
This distance is frequently used to identify vectors that have significant difference. One usage is in bioinformatics to locate genes that are differential expressed on microarray experiments.[2]
See also
- Distance
- Uniform norm
- Manhattan distance
- Signal-to-noise ratio
- Signal to noise ratio (imaging)
Notes
- ↑ Auffarth, B., Lopez, M., Cerquides, J. (2010). Comparison of redundancy and relevance measures for feature selection in tissue classification of CT images. Advances in Data Mining. Applications and Theoretical Aspects. p. 248--262. Springer. http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.170.1528
- ↑ Pomeroy, S.L. et al. Gene Expression-Based Classification and Outcome Prediction of Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors. Nature 415, 436–442.