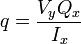Shear flow
The term shear flow is used in solid mechanics as well as in fluid dynamics. The expression shear flow is used to indicate:
- a shear stress caused by torsion on a closed, thin-walled tube (in solid mechanics);[1]
- the flow induced by a force (in a fluid).
This article is about shear flow in solid mechanics. See Viscosity for a fuller treatment about the concept in fluid dynamics.
Definition
In solid mechanics, shear flow q in a closed, thin-wall tube is defined as the internal shearing force V per unit of length of the perimeter around a thin section. Shear flow has the dimensions of force per unit of length.[1] This corresponds to units of newtons per meter in the SI system and pound-force per foot in the English Engineering and British Gravitational Systems.
Shear flow in semi-monocoque structures
The equation for shear flow in a particular web section of the cross-section of a semi-monocoque structure is:
where
- q - the shear flow
- Vy - the shear force perpendicular to the neutral axis x through the entire cross-section
- Qx - the first moment of area about the neutral axis x for a particular web section of the cross-section
- Ix - the second moment of area about the neutral axis x for the entire cross-section
Notes
References
- Riley, W. F. F., Sturges, L. D. and Morris, D. H. Mechanics of Materials. J. Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998 (5th Ed.), 720 pp. ISBN 0-471-58644-7