Serbo-Croatian grammar
Serbo-Croatian is a South Slavic language that has, like most other Slavic languages, an extensive system of inflection. This article deals exclusively with the Neo-Shtokavian dialect, which is a part of the South Slavic dialect continuum[1] and the basis for the Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, and Serbian standard variants of Serbo-Croatian.[2]
Pronouns, nouns, adjectives, and some numerals decline (change the word ending to reflect case, i.e. grammatical category and function), whereas verbs conjugate for person and tense. As in all other Slavic languages, the basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO); however, due to the use of declension to show sentence structure, word order is not as important as in languages that tend toward analyticity such as English or Chinese. Deviations from the standard SVO order are stylistically marked and may be employed to convey a particular emphasis, mood or overall tone, according to the intentions of the speaker or writer. Often, such deviations will sound literary, poetical, or archaic.
Nouns have three grammatical genders, masculine, feminine and neuter, that correspond to a certain extent with the word ending, so that most nouns ending in -a are feminine, -o and -e neuter, and the rest mostly masculine with a small but important class of feminines. The grammatical gender of a noun affects the morphology of other parts of speech (adjectives, pronouns, and verbs) attached to it. Nouns are declined into seven cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative, and instrumental.
Verbs are divided into two broad classes according to their aspect, which can be either perfective (signifying a completed action) or imperfective (action is incomplete or repetitive). There are seven tenses, four of which (present, perfect, future I and II) are used in contemporary Serbo-Croatian, and the other three (aorist, imperfect and plusquamperfect) used much less frequently—the plusquamperfect is generally limited to written language and some more educated speakers, whereas the aorist and imperfect are considered stylistically marked and rather archaic. However, some non-standard dialects make considerable (and thus unmarked) use of those tenses.
All Serbo-Croatian lexemes in this article are spelled in accented form in both scripts (Gaj's Latin and Vuk's Cyrillic), as well as in both accents (Ijekavian and Ekavian, with Ijekavian bracketed) where these differ. (See Serbo-Croatian phonology.) Translations are given as tooltips, and can be seen by hovering the cursor over a marked entry.
Morphology
Serbo-Croatian makes a distinction among three genders (masculine, feminine and neuter) seven cases (nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, vocative, locative, instrumental) and two numbers (singular and plural).
The category of animacy is important for the choosing of accusative singular of o-stems, and of pronouns. Animate nouns have the accusative case like the genitive, and inanimate nouns have the accusative case like the nominative. This is also important for adjectives and numerals which agree with masculine nouns in case.
Nouns
Serbo-Croatian has three main declensional types, traditionally called a-type, e-type and i-type respectively, according to their genitive singular ending.
a-type nouns
This type reflects Proto-Slavic o-stems, and is characterized by the endings (-o • -о), (-e • -е), or zero (-Ø) in the nominative singular, and (-a • -а) in genitive singular. It includes most of the masculine and all of the neuter nouns.
This type has two sets of case endings: one for masculine, and the other for neuter gender:
|
The zero ending -Ø is for masculine nouns that end in consonant in nominative singular, and also for neuter nouns that end in a -e • -е that is a part of the word stem. The alternative endings in the nominative, vocative, and instrumental singular are governed by the stem-final consonant: if it is a palatal consonant, the former endings are used, and if it is a non-palatal consonant, the latter endings are used. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Masculine nouns
Masculine nouns belonging to this declensional class are those that are not hypocorisms, and do not end in -a • -а, which undergo e-type declension.
According to the nominative singular forms they are divided in two classes:
- nouns having the zero ending -Ø in nominative singular (twelve declensional patterns)
- nouns having the ending -o • -о or -e • -е in nominative singular (two declensional patterns)
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pattern 4 | Nouns ending in -k • -к | Nouns ending in -g • -г | Nouns ending in -h • -х | |||
| Case | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | vòjnīk • во̀јнӣк | vojníc-i • војни́ц-и | bùbreg • бу̀брег | bùbrez-i • бу̀брез-и | tr̀buh • тр̀бух | tr̀bus-i • тр̀бус-и |
| G | vojník-a • војни́к-а | vojník-ā • војни́к-а̄ | bùbreg-a • бу̀брег-а | bȕbrēg-ā • бу̏бре̄г-а̄ | tr̀buh-a • тр̀бух-а | tȑbūh-ā • тр̏бӯх-а̄ |
| D | vojník-u • војни́к-у | vojníc-ima • војни́ц-има | bùbreg-u • бу̀брег-у | bùbrez-ima • бу̀брез-има | tr̀buh-u • тр̀бух-у | tr̀bus-ima • тр̀бус-има |
| A | vojník-a • војни́к-а | vojník-e • војни́к-е | bùbreg-a • бу̀брег-а | bùbreg-e • бу̀брег-е | tr̀buh-a • тр̀бух-а | tr̀buh-e • тр̀бух-е |
| V | vȍjnīč-e • во̏јнӣч-е | vojníc-i • војни́ц-и | bùbrež-e • бу̀бреж-е | bùbrez-i • бу̀брез-и | tr̀buš-e • тр̀буш-е | tr̀bus-i • тр̀бус-и |
| L | vojník-u • војни́к-у | vojníc-ima • војни́ц-има | bùbreg-u • бу̀брег-у | bùbrez-ima • бу̀брез-има | tr̀buh-u • тр̀бух-у | tr̀bus-ima • тр̀бус-има |
| I | vojník-om • војни́к-ом | vojníc-ima • војни́ц-има | bùbreg-om • бу̀брег-ом | bùbrez-ima • бу̀брез-има | tr̀buh-om • тр̀бух-ом | tr̀bus-ima • тр̀бус-имa |
| Pattern 5 - Nouns ending in -(a)k • -(а)к | ||
| Case | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| N | čvór-a-k • чво́р-а-к | čvórc-i • чво́рц-и |
| G | čvórk-a • чво́рк-а | čvȏr-ā-k-ā • чво̑р-а̄-к-а̄ |
| D | čvórk-u • чво́рк-у | čvórc-ima • чво́рц-има |
| A | čvórk-a • чво́рк-а | čvórk-e • чво́рк-е |
| V | čvȏrč-e • чво̑рч-е | čvórc-i • чво́рц-и |
| L | čvórk-u • чво́рк-у | čvórc-ima • чво́рц-има |
| I | čvórk-om • чво́рк-ом | čvórc-ima • чво́рц-има |
| Pattern 6 - Nouns ending in a palatal | ||||||
| Case | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | pȃnj • па̑њ | pánj-ev-i • па́њ-ев-и | ráž-a-nj • ра́ж-а-њ | rážnj-i • ра́жњ-и | prȋšt • при̑шт | príšt-ev-i • при́шт-ев-и |
| G | pánj-a • па́њ-а | pánj-ēv-ā • па́њ-е̄в-а̄ | rážnj-a • ра́жњ-а | ráž-ā-nj-ā • ра́ж-а̄-њ-а̄ | príšt-a • при́шт-а | príšt-ēv-ā • при́шт-е̄в-а̄ |
| D | pánj-u • па́њ-у | pánj-ev-ima • па́њ-ев-има | rážnj-u • ра́жњ-у | rážnj-ima • ра́жњ-има | príšt-u • при́шт-у | príšt-ev-ima • при́шт-ев-има |
| A | pȃnj • па̑њ | pánj-ev-e • па́њ-ев-е | ráž-a-nj • ра́ж-а-њ | rážnj-e • ра́жњ-е | prȋšt • при̑шт | príšt-ev-e • при́шт-ев-е |
| V | pȃnj-u • па̑њ-у | pánj-ev-i • па́њ-ев-и | rážnj-u • ра́жњ-у | rážnj-i • ра́жњ-и | prȋšt-u • при̑шт-у | príšt-ev-i • при́шт-ев-и |
| L | pánj-u • па́њ-у | pánj-ev-ima • па́њ-ев-има | rážnj-u • ра́жњ-у | rážnj-ima • ра́жњ-има | príšt-u • при́шт-у | príšt-ev-ima • при́шт-ев-има |
| I | pánj-em • па́њ-ем | pánj-ev-ima • па́њ-ев-има | rážnj-em • ра́жњ-ем | rážnj-ima • ра́жњ-има | príšt-em • при́шт-ем | príšt-ev-ima • при́шт-ев-има |
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Masculine nouns ending in -o • -о or -e • -е present a special case. They generally comprise personal names, hypocorisms and certain foreign-language borrowings. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neuter nouns
| singular | plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | -o/e | -a |
| Genitive | -a | -a |
| Dative/Locative | -u | -ima |
| Accusative | -o/e | -a |
| Vocative | -o/e | -a |
| Instrumental | -om/em | -ima |
Some neuter nouns add 'n' or 't' before the declension.
| singular | plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | -e | -(n/t)a |
| Genitive | -(n/t)a | -(n/t)a |
| Dative/Locative | -(n/t)u | -(n/t)ima |
| Accusative | -e | -(n/t)a |
| Vocative | -e | -(n/t)a |
| Instrumental | -(n/t)om | -(n/t)ima |
e-type nouns
This type reflects Proto-Slavic a-stems, and is characterized by the ending -a • -а in nominative singular and -ē • -е̄ in genitive singular. It contains most of the feminine nouns, and a small number of masculines.
| singular | plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | -a | -e |
| Genitive | -e | -a |
| Dative/Locative | -i | -ama |
| Accusative | -u | -e |
| Vocative | -o/a | -e |
| Instrumental | -om | -ama |
i-type nouns
This type reflects Proto-Slavic i-stems, and is characterized by the zero ending in nominative singular and -i • и in genitive singular. It contains the rest of feminine nouns, that are not contained in the e-type nouns (a-stems).
| singular | plural | |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | - | -i |
| Genitive | -i | -i |
| Dative/Locative | -i | -ima |
| Accusative | - | -i |
| Vocative | -i | -i |
| Instrumental | -i/ju | -ima |
Some nouns appear only in the plural form and do not have a singular variant (see plurale tantum). The gender of these nouns is either feminine (e.g. hlače "trousers", gaće "pants", grudi "chest") or neuter (e.g. kola "car", leđa "back", usta "mouth").[3]
Pronouns
Serbo-Croatian allows deletion of the subject pronoun (see pro-drop language).[4] Example:
- Bojim se. "I am afraid."
- Možeš reći što god hoćeš. "You can say whatever you want."
Personal pronouns
| Case | 1st sg. | 2nd sg. | 3rd sg. (m/f/n) | 1st pl. | 2nd pl. | 3rd pl. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | ja | ti | on / ona / ono | mi | vi | oni / one / ona |
| Genitive | mene | tebe | njega / nje / njega | nas | vas | njih |
| Dative | meni | tebi | njemu / njoj / njemu | nama | vama | njima |
| Accusative | mene | tebe | njega / nju / njega | nas | vas | njih |
| Vocative | -- | ti | -- | -- | vi | -- |
| Locative | (o) meni | (o) tebi | (o) njemu / njoj / njemu | (o) nama | (o) vama | (o) njima |
| Instrumental | (sa) mnom | (sa) tobom | (sa) njim / njom / njim | (sa) nama | (sa) vama | (sa) njima |
Adjectives
Some of the declensions for adjectives are the same as for nouns, and so they might rhyme: velika kuća (sing. nom.), veliku kuću (sing. acc.). Others differ: jednim klikom ("with one click", sing. masc. instrum.).
| singular | plural | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| masculine | feminine | neuter | masculine | feminine | neuter | |
| Nominative | -i | -a | -o | -i | -e | -a |
| Genitive | -og | -e | -og | -ih | -ih | -ih |
| Dative/Locative ! | -om | -oj | -om | -im | -im | -im |
| Accusative | -i/-og* | -u | -o | -e | -e | -a |
| Vocative | -i | -a | -o | -i | -e | -a |
| Instrumental | -im | -om | -im | -im | -im | -im |
* same as nominative if a word is marking inanimate object; same as genitive if a word is marking animate object.
Singular
| Case | Masculine | Feminine | Neuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | velik ("big") | velika | veliko |
| Genitive | velikog | velike | velikog |
| Dative | velikom | velikoj | velikom |
| Accusative | velik | veliku | veliko |
| Vocative | veliki | velika | veliko |
| Locative | velikom | velikoj | velikom |
| Instrumental | velikim | velikom | velikim |
Plural
| Case | Masculine | Feminine | Neuter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | veliki ("big") | velike | velika |
| Genitive | velikih | velikih | velikih |
| Dative | velikim | velikim | velikim |
| Accusative | velike | velike | velika |
| Vocative | veliki | velike | velika |
| Locative | velikim | velikim | velikim |
| Instrumental | velikim | velikim | velikim |
- Note: animate objects (people and animals) are treated differently in the singular masculine accusative. In this case, it is the same as singular masculine genitive. It is considered accusative even though it looks like the genitive. Example: Vidim velikog psa ("I see a big dog").
- Note: most adjectives ending in consonant-'a'-consonant (for example: dobar, "good"), the 'a' disappears when any letter is added. Dobar becomes, for example, dobri, dobra, dobrog, dobru, dobrim, dobrom, dobre, and dobrih, according to case and number.
Verbs
Like those of other Slavic languages, Serbo-Croatian verbs have a property of aspect: the perfective and the imperfective. Perfective indicates an action that is completed or sudden, while the imperfective denotes continuous, repeated, or habitual action. Aspect compensates for a relative lack of tenses compared with e.g. Germanic or Romance languages: the verb already contains the information whether the action is completed or lasting, so there is no general distinction between continuous and perfect tenses.
Slavic verbs in general are characterized by a relatively low number of stems, from which a wide variety of meanings is achieved by prefixation.
Tense
The indicative has seven tenses: present, past, futures I and II, pluperfect, aorist and imperfect. The latter two are not used often in daily speech (more often in Bosnia and Herzegovina than in Croatia and Serbia), especially the imperfect. The present, aorist, and imperfect are inflected, the other tenses are periphrastic:
- Past uses the present of biti ("to be") plus the perfect participle, e.g. radio sam (or sam radio, order depending on the sentence).
- Future I uses the (reduced) present of htjeti ("will" or "to want") plus the infinitive, e.g. ćemo kuhati (or kuhat ćemo, in which case the -i of the infinitive marker -ti is elided).
- Future II uses the perfective future of biti (the only verb with a simple future) plus the perfect participle, e.g. budu išli.
- Pluperfect, which is not often used, uses the composite past tense of biti plus the perfect participle, e.g. bio sam došao, or (archaic) imperfect of biti plus the participle, e.g. bijah došao
Future tense can also be formed with (reduced) present of хтети plus the conjunction да and the present of the main verb, e.g. ћеш да куваш in Serbian, but this form is incorrect in Croatian. Also, whereas in Croatian it would be "radit ćemo", in Serbian the "t" can be omitted and the verbs merged into "radićemo".
Mood
Besides the indicative, Serbo-Croatian uses the imperative, conditional, and the optative. Imperative forms vary according to the type of the verb, and is formed by adding the appropriate morpheme to a verbal stem. The conditional I (present) uses the aorist of biti plus perfect participle, while conditional II (past) consists of the perfect participle of biti, the aorist of the same verb, and the perfect participle of the main verb. Some grammars classify future II as a conditional tense, or even a mood of its own.
Optative is in its form identical to the perfect participle. It is used by speakers to express a strong wish, e.g. Živio predsjednik! 'Long live the president!', Dabogda ti se sjeme zatrlo! (an archaic and dialectal curse), etc. The optative may be translated into English by an imperative construction, with set phrases (such as the already exemplified 'long live'), or by use of the modal verb may.
Some authors suggest existence of subjunctive mood, realized as da plus the present of indicative, but most grammars treat it as present indicative.
Aspect
Verbal aspect is distinguished in English by using the simple or progressive (continuous) forms. 'He washed the dishes' indicates that the action was finished; 'He was washing the dishes' indicates that the action was ongoing (progressive). Serbo-Croatian, like all Slavic languages, has the aspect built into the verbs, rather than expressing it with different tenses.
To compare the meanings of the different aspects with verbal aspect in English, one should know three basic aspects: completed (may be called preterit, aorist, or perfect according to the language in question), progressive (on-going but not completed yet, durative), and iterative (habitual or repeated). English uses one aspect for completed and iterative and another for progressive. Serbo-Croatian uses one for completed and another for iterative and progressive.
Aspect is the most challenging part of Serbo-Croatian grammar. Although aspect exists in all other Slavic languages, learners of Serbo-Croatian who already know even one of several other Slavic languages may never learn to use aspect correctly, though they will be understood with only rare problems. While there are bi-aspectual verbs as well, primarily those derived by adding the suffix -irati or -ovati, the majority of verbs not derived in such a manner are either perfective (svršeni) or imperfective (nesvršeni). Almost all of the single aspectual verbs are part of a perfective–imperfective pair of verbs. When learning a verb, one must learn its verbal aspect, and the other verb for the opposite verbal aspect, e.g. prati ("to wash", imperfective) goes with oprati ("to wash", perfective). The pairing, however, is not always one to one: some verbs simply don't have a counterpart on a semantic level, such as izgledati ("seem") or sadržati ("contain"). In others, there are several perfective alternatives with slightly different meanings.
There are two paradigms concerning formation of verb pairs. In one paradigm, the base verb is imperfective, such as prati ("to wash"). In this case the perfective is formed by adding a prefix, in this case o, as in oprati. In the other paradigm, the root verb is perfective, and the imperfective is formed either by modifying the root: dignuti→dizati ("to lift") or adding an interfix stati→stajati ("to stop", "to stand").
A pattern which often arises can be illustrated with pisati, "to write". Pisati is imperfective, so a prefix is needed to make it perfective, in this case na-: napisati. But if other prefixes are added, modifying the meaning, the verb becomes perfective: zapisati ("to write down") or prepisati ("to copy by hand"). Since these basic verbs are perfective, an interfix is needed to make them imperfective: zapisivati and prepisivati. In some cases, this could be continued by adding a prefix: pozapisivati and isprepisivati which are again perfective.
Conjugation of verbs
There are three conjugations of verbs:
- 'a': almost all verbs that have this conjugation end in '-ati'.
- 'e': verbs ending in '-nuti' and all irregular verbs (as in the example below). Verbs ending in '-ovati', '-ivati' become 'uje' when conjugated (trovati, "to poison", is trujem, truje etc.)
- 'i': almost all verbs ending in '-jeti' or '-iti' use this conjugation.
| Person | čitati | prati (irregular) | vidjeti (-jeti or -iti) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | plural | singular | plural | singular | plural | |
| First person | čitam | čitamo | perem | peremo | vidim | vidimo |
| Second person | čitaš | čitate | pereš | perete | vidiš | vidite |
| Third person | čita | čitaju | pere | peru | vidi | vide |
Auxiliary verbs
As in most other Indo-European languages including English, the Indo-European copula ('to be') is used as an auxiliary verb. It is universally irregular, because conjugations of two proto-forms *h1es- (>English is) and *bʰuH- (>English be) merged, producing mixed paradigms: the former being used in the present, and the latter in the other tenses. In Serbo-Croatian, however, there are two present forms surviving: jesam ('I am') and budem ('I be'). Because of that dualism, some grammars (chiefly Serbian ones) treat jesam as a defective verb having only present tense. Others treat these forms as two realizations of the same irregular verb biti, jesam being imperfective and budem perfective.[5]
Jesam has the following declension in the present tense. It has long and clitic (short) forms (without leading je), while its negative form is written as one word, unlike other verbs (compare English is–isn't). The short and the negative forms are used as auxiliary, while the long form is marked.[5]
| Pronoun | Present | Present (negative forms) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long (accented) form | Short (unaccented) form | ||
| jа (I) | jesam | sam | nisam |
| ti (you) | jesi | si | nisi |
| on, ona, ono (he, she, it) | јeste | je | nije |
| mi (we) | jesmo | smo | nismo |
| vi (you pl.) | jeste | ste | niste |
| oni, one, ona (they) | јesu | su | nisu |
The copulative use of the verb јеsam matches that of the verb "to be" in English (e.g. He is a student – On је učenik), of course, in the present tense only. The 'true' forms present of the verb biti, (budem) have a limited use (in formation of the future exact tense, or in conditional clauses referring to the future, e.g. ako budem – if I am).[5]
Verb biti is conjugated as follows:
| Pronoun | Present | Future | Past tense | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | perfect | aorist | imperfect | pluperfect | ||
| jа (I) | budem | ću biti / biću | budem bio/la | sam bio/la; bio/la sam | bih | bijah / bejah / beh | bio/la sam bio/la |
| ti (you) | budeš | ćeš biti / bićeš | budeš bio/la | si bio/la; bio/la si | bi | bijaše / bejaše / beše | bio/la si bio/la |
| on, ona, ono (he, she, it) | bude | će biti / biće | bude bio/la/lo | јe bio/la/lo; bio/la/lo јe | bi | bijaše / bejaše / beše | bio/la/lo јe bio/la/lo |
| mi (we) | budemo | ćemo biti / bićemo | budemo bili/le | smo bili/le; bili/le smo | bismo | bijasmo / bejasmo / besmo | bili/le smo bili/le |
| vi (you pl.) | budete | ćete biti / bićete | budete bili/le | ste bili/le; bili/le ste | biste / beste | biјaste / bejaste / beste | bili/le ste bili/le |
| oni, one, ona (they) | budu | će biti / biće | budu bili/le | su bili/bile/bila; bili/le/la su | bi / biše | biјahu / bejahu / behu | bili/le/la su bili/le/la |
Regular verbs
The conjugation system of regular verbs is rather complex. There are several classes of verbs distinguished according to certain features verbs within a class share.
The verb is raditi (To work)
| Pronoun | Present | Future | Past tense | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | perfect | aorist | imperfect | pluperfect | ||
| ja (I) | radim | ću raditi | budem radio/la | sam radio/la; radio/la sam | rad+ah>rađah | bio/la sam radio/la | |
| ti (you) | radiš | ćeš raditi | budeš radio/la | si radio/la; radio/la si | rad+aše>rađashe | bio/la si radio/la | |
| on, ona, ono (he, she, it) | radi | će raditi | bude radio/la/lo | јe radio/la/lo; radio/la/lo јe | rad+aše>rađashe | bio/la/lo јe radio/la/lo | |
| mi (we) | radimo | ćemo raditi | budemo radili/le | smo radili/le; radili/le smo | rad+asmo>rađasmo | bili/le smo radili/le | |
| vi (you pl.) | radite | ćete raditi | budete radili/le | ste radili/le; radili/le ste | rad+aste>rađaste | bili/le ste radili/le | |
| oni, one, ona (they) | rade | će raditi | budu radili/le/la | su radili/radile/radila; radili/le/la su | rad+ahu>rađahu | bili/le/la su radili/le/la | |
This technique applies to verbs such as:
vidjeti (to see)
hodati (to walk)
pričati (to talk)
morati (must)
Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs are more complex to conjugate than regular verbs, for example the verb moći (can, to be able to)
| Pronoun | Present | Future | Past tense | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | perfect | aorist | imperfect | pluperfect | ||
| ja (I) | mogu | ću moći | budem mogao/la | sam mogao/la; mogao/la sam | mogoh | mogah | bio/la sam mogao/la |
| ti (you) | možeš | ćeš moći | budeš mogao/la | si mogao/la; mogao/la si | može | mogaše | bio/la si mogao/la |
| on, ona, ono (he, she, it) | može | će moći | bude mogao/la/lo | јe mogao/la/lo; mogao/la/lo je | može | mogaše | bio/la/lo je mogao/la/lo |
| mi (we) | možemo | ćemo moći | budemo mogli/le | smo mogli/le; mogli/le smo | mogosmo | mogasmo | bili/le smo mogli/le |
| vi (you pl.) | možete | ćete moći | budete mogli/le | ste mogli/le; mogli/le ste | mogoste | mogaste | bili/le ste mogli/le |
| oni, one, ona (they) | mogu | će moći | budu mogli/le/la | su mogli/mogle/mogla; mogli/le/la su | mogoše | mogahu | bili/le/la su mogli/le/la |
Adverbs
Adverbs in Serbo-Croatian are, unlike nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns and numbers, and like prepositions, conjunctions, exclamations and particles, immutable words. Adverbs are, thus, immutable words given to verbs to determine the time, place, manner, cause, point and the amount of the action of the verb. There are seven types of adverbs in Serbo-Croatian:
Place adverbs
Place adverbs (Serbo-Croatian: mjesni prilozi) answer the questions where? (gdje?), to where? (kamo?), which way? (kuda?), from where? (otkuda?, odakle?) and to where? (dokle?, dokud?).[6] Examples for each type are:
- gde/gdje? (where)
- ovde/ovdje (here),
- negde/negdje (somewhere),
- nigde/nigdje (nowhere),
- igde/igdje (anywhere),
- gore (up),
- doe/dolje (down),
- odpozadi/straga (from behind),
- napolju/vani (outside)
- blizu (close by);
- kuda/kamo? (to where)
- ovamo (to here)
- napred/naprijed (forwards)
- nazad (backwards);
- kuda? (which way)
- ovuda (this way),
- kojekuda (otišli su kojekuda - they dispersed),
- otkuda? (from where)
- odavde (from here),
- niotkuda (from nowhere),
- izdaleka (from far away)
- dokle? (to where):
- dotle (to here, also used as "in the mean time", dotle su oni čekali),
- donekle (up to a point).
Temporal adverbs
Temporal adverbs, or "vremenski prilozi", answer the questions when? (kada?), from when? (otkad?), until when? (dokad?). Examples are: kada (when) - sada (now), tada (then), nikada (never), ponekad (sometimes),uvijek (always), jučer (yesterday), danas (today), sutra (tomorrow), prekosutra (the day after tomorrow), lani (last year), večeras (tonight), odmah/smjesta (now/at once), zatim (then), uskoro (soon), napokon (at last); otkad (from when) - odsad (from now on), oduvijek (from always - oduvijek sam te volio - I have (from) always loved you); dokad (until when) - dosad (until now), dogodine (next year).
Syntax
Word order
Serbo-Croatian has a rich case structure that is reflected in the declension of nouns and adjectives. This makes syntax of little use and allows for a great deal of freedom in word order. In English, for example, the difference between "Man bites dog" and "Dog bites man" is shown by syntax. In Serbo-Croatian, Čovjek grize psa and Čovjeka grize pas have the same word order, but the meanings are shown by the noun endings. Any order of the three words is grammatically correct, and the meaning is clear because of the declensions. However, the usual order is subject–verb–object.
There are certain words that have no accent (enclitics) that must come in a fixed order. They are, in order,
- question word (only li),
- verbs: clitic forms of "to be" except je (sam, si, smo, ste, su, bih, bi, bismo, biste), and of "will" (ću, ćeš, će, ćemo, and ćete)
- dative pronouns (mi, ti, mu, joj, nam, vam, im, si),
- accusative pronouns (me, te, ga, je, ju, nas, vas, ih),
- the reflexive accusative pronoun (only se),
- clitic form of the third-person singular present of "to be" (je).[7]
The enclitics must almost always be at the second position of the declarative and imperative sentence. The first element may be a single word or a noun phrase, e.g. Taj se čovjek vara, "That person deceives himself", or Taj čovjek se vara. When using a combination of several enclitics in a sentence they must be at the second, third and fourth position; in some interrogative forms of sentences or in colloquial speech they can be placed even at the first position.
Relative clauses
Relative clauses are frequent in the modern Serbo-Croatian since they have expanded as attributes at the expense of the participles performing that function.[8]
Znam pacijenta koji je upravo ušao. know:PR.1.SG patient:ACC.m.SG which:NOM.m.SG be:AUX.3.SG just come in:AP.m.SG "I know the patient who has just come in."
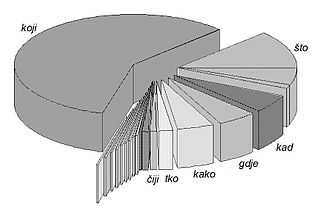
The most frequent relativizer is the relative pronoun koji. It has the greatest range of antecedents, which however are mostly nouns or personal pronouns. If we consider that in the first place nouns are the word class that takes attributes, and that the relative clause is most frequently an attributive clause, the frequency of the adjectival pronoun koji will not be surprising when compared with those relative pronouns that cannot have an antecedent noun (tko ʻwhoʼ and the declinable type of što ʻwhatʼ). Neither is it surprising that it occurs much more frequently than other adjectival relative pronouns: in comparison with their specialized semantic functions such as possessiveness (čiji ʻwhoseʼ), quality (kakav ʻwhat sort ofʼ) or quantity (koliki ʻhow largeʼ), the pronoun koji has the broadest scope of reference and identification with the referent.
See also
- Ausbausprache
- Differences between Serbo-Croatian standard varieties
- Language secessionism in Serbo-Croatian
- Mutual intelligibility
- Pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language
- Serbo-Croatian language
- Serbo-Croatian phonology
- Serbo-Croatian kinship
- Serbo-Croatian relative clauses
- Shtokavian dialect
- South Slavic dialect continuum
- Standard language
References
- ↑ Alexander, Ronelle (2000). In honor of diversity: the linguistic resources of the Balkans. Kenneth E. Naylor memorial lecture series in South Slavic linguistics ; vol. 2. Columbus, Ohio: Ohio State University, Dept. of Slavic and East European Languages and Literatures. p. 4. OCLC 47186443.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (2010). Jezik i nacionalizam [Language and Nationalism]. Rotulus Universitas (in Serbo-Croatian). Zagreb: Durieux. pp. 69–77. ISBN 978-953-188-311-5. LCCN 2011520778. OCLC 729837512. OL 15270636W. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (2005). "Gramatička kategorija broja" [Grammatical category of number]. In Tatarin, Milovan. Zavičajnik: zbornik Stanislava Marijanovića: povodom sedamdesetogodišnjice života i četrdesetpetogodišnjice znanstvenoga rada (in Serbo-Croatian). Osijek: Sveučilište Josipa Jurja Strossmayera, Filozofski fakultet. pp. 192–193. ISBN 953-6456-54-0. OCLC 68777865. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2012. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (2002). Riječi na granici punoznačnosti [Words on the Border Between Lexicon and Grammar] (in Serbo-Croatian). Zagreb: Hrvatska sveučilišna naklada. pp. 12–14. ISBN 953-169-073-1. LCCN 2009386657. OCLC 54680648. OL 2863537W. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 16 December 2014.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Mišeska Tomić, Olga (2006). Balkan Sprachbund morpho-syntactic features. Springer. p. 490. ISBN 978-1-4020-4487-8.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (2004). "Prilozi gd(j)e, kamo, kuda" [Adverbs gd(j)e, kamo, kuda]. In Okuka, Miloš; Schweier, Ulrich. Germano-Slavistische Beiträge: Festschrift für Peter Rehder zum 65. Geburtstag. Die Welt der Slaven, Sammelbände – Sborniki ; vol. 21 (in Serbo-Croatian). Munich: Otto Sagner. pp. 113–120. ISBN 3-87690-874-4. OCLC 55018584. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2013.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (2006) [1st pub. 1997]. Serbo-Croatian. Languages of the World/Materials ; 148. Munich & Newcastle: Lincom Europa. p. 46. ISBN 3-89586-161-8. OCLC 37959860. OL 2863538W. [Grammar book]. Contents. Summary.
- ↑ Kordić, Snježana (1995). Relativna rečenica [Relative Clauses]. Znanstvena biblioteka Hrvatskog filološkog društva ; 25 (in Serbo-Croatian). Zagreb: Matica hrvatska & Hrvatsko filološko društvo. pp. 277–281. ISBN 953-6050-04-8. LCCN 97154457. OCLC 37606491. OL 2863536W. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
Further reading
- Alexander, Ronelle (2006). Bosnian/Croatian/Serbian: A Grammar with Sociolinguistic Commentary. Medison: The University of Wisconsin Press. p. 464. OCLC 67384305.
- Aljović, Nadira (2002). "Long adjectival inflection and specificity in Serbo-Croatian". Recherches linguistiques de Vincennes 31: 27–42. Retrieved 7 March 2015.
- Barić, Eugenija; Lončarić, Mijo; Malić, Dragica; Znika, Marija; Zečević, Vesna; Pavešić, Slavko; Peti, Mirko (1997). Hrvatska gramatika [Croatian Grammar] (in Serbo-Croatian). Školska knjiga. p. 697. ISBN 953-0-40010-1.
- Bibović, Ljiljana (1971). "Some remarks on the factive and non-factive complements in English and Serbo-Croatian". In Filipović, Rudolf. The Yugoslav Serbo-Croatian – English contrastive project. Studies ; vol. 3. Zagreb: Institute of Linguistics, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Zagreb. pp. 37–48. OCLC 424957265.
- Browne, Wayles (1993). "Serbo-Croat". In Comrie, Bernard; Corbett, Greville G. The Slavonic Languages. Routledge language family descriptions. London & New York: Routledge. pp. 306–387. ISBN 978-0-415-28078-5. OCLC 24796613.
- Bujas, Željko (1973). "Demonstratives in Serbo-Croat to English Translational Conversion". In Filipović, Rudolf. The Yugoslav Serbo-Croatian – English contrastive project. Reports ; vol. 8. Zagreb: Institute of Linguistics, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Zagreb. pp. 21–51. OCLC 424957282.
- Dezső, László (1982). Typological Studies in Old Serbo-Croatian Syntax. Slavistische Forschungen ; vol. 38. Köln: Böhlau. p. 392. ISBN 341202581X. OCLC 239744814.
- Feleszko, Kazimierz (1970). Składnia genetiwu i wyrażeń przyimkowych z genetiwem w języku serbsko-chorwackim. Monografie slawistyczne ; vol. 21 (in Polish). Wrocław: Komitet słowianoznawstva Polskiej akademii nauk. p. 186. OCLC 63410897.
- Filipović, Luna (2010). "The importance of being a prefix : prefixal morphology and the lexicalization of motion events in Serbo-Croatian". In Hasko, Victoria & Perelmutter, Renee. New Approaches to Slavic Verbs of Motion. Studies in Language Companion Series ; vol. 115. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 247–266. ISBN 978-90-272-0582-7. OCLC 804991090. Lay summary.
- Ivir, Vladimir (1983). A contrastive analysis of English adjectives and their Serbo-Croatian correspondents. The Yugoslav Serbo-Croatian – English contrastive project. New studies ; vol. 2. Zagreb: Institute of Linguistics, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Zagreb. p. 284. OCLC 11266437.
- Kordić, Snježana (2004) [1st pub. 1997]. Kroatisch-Serbisch: ein Lehrbuch für Fortgeschrittene mit Grammatik [Serbo-Croatian: A Textbook for Advanced Students with Grammar] (in Serbo-Croatian). Hamburg: Buske. p. 196. ISBN 3-87548-382-0. OL 15270855W. [1st pub ISBN 3-87548-162-3]
- Kordić, Snježana (1997). "Neprofesionalno obavljen posao: recenzija knjige Josipa Silića, Morfologija hrvatskoga jezika" [Unprofessional results: Review of the book Josip Silić, Croatian Morphology]. Republika (in Serbo-Croatian) 53 (1–2): 190–199. ISSN 0350-1337. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 14 November 2012.
- Kordić, Snježana (1997). "Nova hrvatska gramatika: recenzija knjige Dragutina Raguža, Praktična hrvatska gramatika" [A new Croatian grammar book: Review of the book Dragutin Raguž, Practical Croatian Grammar]. Republika (in Serbo-Croatian) 53 (11–12): 212–225. ISSN 0350-1337. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 1 March 2014.
- Kordić, Snježana (1998). "Diletantski napisana gramatika: recenzija knjige Vinka Grubišića, Croatian Grammar" [An amateurish grammar book: Review of the book Vinko Grubišić, Croatian Grammar]. Republika (in Serbo-Croatian) 54 (1–2): 253–258. ISSN 0350-1337. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- Kordić, Snježana (1999). Der Relativsatz im Serbokroatischen [Relative Clauses in Serbo-Croatian]. Studies in Slavic Linguistics ; 10 (in German). Munich: Lincom Europa. p. 330. ISBN 3-89586-573-7. OCLC 42422661. OL 2863535W. Contents. Summary.
- Kordić, Snježana (2001). Wörter im Grenzbereich von Lexikon und Grammatik im Serbokroatischen [Serbo-Croatian Words on the Border Between Lexicon and Grammar]. Studies in Slavic Linguistics ; 18 (in German). Munich: Lincom Europa. p. 280. ISBN 3-89586-954-6. LCCN 2005530313. OCLC 47905097. OL 2863539W. Summary.
- Kordić, Snježana (2009). "Neprimjeren opis jezika: recenzija knjige Josipa Silića i Ive Pranjkovića, Gramatika hrvatskoga jezika" [An inappropriate description of language: Review of the book Josip Silić and Ivo Pranjković, Croatian Grammar]. Znakovi i poruke (in Serbo-Croatian) 2 (1): 93–110. ISSN 1840-3239. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 August 2012. Retrieved 5 April 2014.
- Kordić, Snježana (2009). "Komplexe Satzmuster" [Complex sentences]. In Kempgen, Sebastian; Kosta, Peter; Berger, Tilman et al. The Slavic Languages: an International Handbook of their Structure, their History and their Investigation: Band I. Handbooks of Linguistics and Communication Science ; vol. 32/1 (in German). Berlin & New York: Mouton de Gruyter. pp. 592–607. ISBN 978-3-11-015660-7. OCLC 793132320. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 August 2012. Retrieved 3 June 2013.
- Laškova, Lili (2001). Sărbo-chărvatska gramatika [Serbo-Croatian Grammar] (in Bulgarian). Sofija: Emas. p. 359. OCLC 635194865.
- Ličen, Marina; Dahl, Johannes (1981). "Die Modalpartikeln ja und doch und ihre serbo-kroatischen Entsprechungen". In Weydt, Harald. Partikeln und Deutschunterricht [The modal particles ja and doch and their Serbo-Croatian equivalents] (in German). Heidelberg: Groos. pp. 213–223. OCLC 164627155.
- Hamm, Josip (1967). Grammatik der serbokroatischen Sprache [Serbo-Croatian Grammar]. Slavistische Studienbücher ; vol. 5 (in German). Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. p. 123. OCLC 7498971.
- Kocher, Margaret (1967). "Second Person Pronouns in Serbo-Croatian". Language 43 (3): 725–741. doi:10.2307/411813. ISSN 0097-8507. OCLC 1361911.
- Magner, Thomas F. (1998). Introduction to the Croatian and Serbian Language. Pennsylvania State University Press. p. 388. OCLC 40859905.
- Mihailović, Ljiljana (1985). "Existential Sentences in English and Serbo-Croatian". In Filipović, Rudolf. The Yugoslav Serbo-Croatian – English contrastive project. Studies ; vol. 5. Zagreb: Institute of Linguistics, Faculty of Philosophy, University of Zagreb. pp. 453–492. OCLC 424957257.
- Mønnesland, Svein (1972). "Semantic factors in the syntax of nominal subordinate clauses in Serbo-Croatian". Scando-Slavica 18: 145–157. ISSN 1600-082X.
- Mørk, Henning (2000). Serbokroatisk grammatik: verbets morfologi [Serbo-Croatian Grammar: Verbal Morphology]. Arbejdspapirer ; vol. 1 (in Danish). Århus: Slavisk Institut, Århus Universitet. p. 113. OCLC 48719984.
- Mørk, Henning (2002). Serbokroatisk grammatik: substantivets morfologi [Serbo-Croatian Grammar: Noun Morphology]. Arbejdspapirer ; vol. 1 (in Danish). Århus: Slavisk Institut, Århus Universitet. p. 140. OCLC 471591123.
- Progovac, L (2005). A syntax of Serbian: Clausal architecture. Slavica Publishers.
- Rathmayr, Renate (1992). "Nominale Anrede im gesprochenen Russischen, Serbokroatischen und Tschechischen" [Nominal address in the spoken Russian, Serbo-Croatian and Czech]. In Reuther, Tilmann. Slavistische Linguistik 1991. Slavistische beiträge ; vol. 292 (in German). Munich: Otto Sagner. pp. 265–309. ISBN 3876905281. OCLC 80022463.
- Szybińska, Małgorzata (1991). "Formy adresatywne w języku polskim i serbsko-chorwackim (wybrane zagadnienia)" [Forms of address in Polish and Serbo-Croatian]. Język polski (in Polish) 71 (1): 35–41. ISSN 0021-6941.
- Thomas, George (2010). "Serbo-Croatian as a bridge between the Balkan and Central European Sprachbünde". Balkanistica 23: 371–388. ISSN 0360-2206. OCLC 2244309.
- Thomas, Paul-Louis; Osipov, Vladimir (2012). Grammaire du bosniaque, croate, monténégrin, serbe [Grammar of Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, and Serbian]. Collection de grammaires de l'Institut d'études slaves ; vol. 8 (in French). Paris: Institut d'études slaves. p. 624. ISBN 9782720404900. OCLC 805026664. Lay summary.
- Thomason, Sarah G. (1977). "A fragment of Serbocroatian declensional history". Folia Slavica 1 (1): 124–155. ISSN 0160-9394. OCLC 3262278.
| ||||||