Sequoyah
| Sequoyah | |
|---|---|
|
SE-QUO-YAH – a lithograph from History of the Indian Tribes of North America. This lithograph is from the portrait painted by Charles Bird King in 1828. | |
| Native name | ᏍᏏᏉᏯ |
| Born |
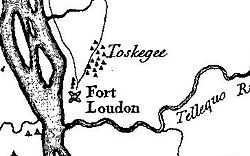
c. 1770 Tuskegee, Cherokee Nation (near present day Knoxville, Tennessee)[1] |
| Died |
August 1843 (aged 72–73) San Fernando, Tamaulipas, Mexico |
| Nationality | Cherokee |
| Other names | George Guess or Gist |
| Occupation | silversmith, blacksmith, teacher, soldier |
| Spouse(s) | 1st: Sally (maiden name unknown), 2nd: U-ti-yu |
| Children | Four with first wife, three with second |
| Parent(s) | Wut-teh and unidentified father |
Sequoyah (ᏍᏏᏉᏯ Ssiquoya, as he signed his name,[2][3] or ᏎᏉᏯ Se-quo-ya, as his name is often spelled today in Cherokee) (c. 1770–1840), named in English George Gist or George Guess, was a Cherokee silversmith. In 1821 he completed his independent creation of a Cherokee syllabary, making reading and writing in Cherokee possible. This was the only time in recorded history that a member of a pre-literate people independently created an effective writing system.[1][4] After seeing its worth, the people of the Cherokee Nation rapidly began to use his syllabary and officially adopted it in 1825. Their literacy rate quickly surpassed that of surrounding European-American settlers.[1]
Early life
Sequoyah's heroic status has led to several competing accounts of his life that are speculative, contradictory, or fabricated.[5] As noted by John B. Davis, there were very few primary documents describing facts of Sequoyah's life. Some anecdotes were passed down orally, but these often conflict or are vague about times and places.[6]
Sequoyah was born in the Cherokee town of Tuskegee circa 1770. James Mooney, a prominent anthropologist and historian of the Cherokee people, quoted a cousin as saying that as a little boy, he spent his early years with his mother. Estimates of his birth year ranged from 1760 to 1776. His name is believed to come from the Cherokee word siqua meaning 'hog'. However, Davis says the name may have been derived from sikwa (either a hog or an opossum) and vi meaning a place or an enclosure.[6] This is a reference either to a childhood deformity or to a later injury that left Sequoyah disabled.[7]
His mother, Wut-teh, was known to be Cherokee. Mooney stated that she was the niece of a Cherokee chief. McKinney and Hall noted that she was a niece of chiefs who have been identified as the brothers Old Tassel and Doublehead. Since John Watts (also known as Young Tassel) was a nephew of the two chiefs, it is likely that Wut-teh and John Watts were siblings.
Sources differ as to the identity of Sequoyah's father. Davis cites Emmet Starr's book, Early History of the Cherokees, as the source for saying that Sequoyah's father was a peddler from Swabia named Guyst, Guist, or Gist.[6] According to Goodpasture, some believe the father was an unlicensed German peddler named George Gist, who came into the Cherokee Nation in 1768, where he married and fathered a child.[8] Grant Foreman identified him as Nathaniel Gist, son of a Christopher Gist, who later became a commissioned officer with the Continental Army associated with George Washington.[9] Mooney and others suggested that he was possibly a fur trader, who would have been a man of some social status and financial backing.[10] Josiah C. Nott claimed he was the "son of a Scotchman".[11] An article in the Cherokee Phoenix, published in 1828, stated that Sequoyah's father was a half-blood and his grandfather a white man.[6][12]
The New Georgia Encyclopedia presents another version of Sequoyah's origins, from the 1971 book, Tell Them They Lie: The Sequoyah Myth, by Traveller Bird, who claims to be a Sequoyah descendant. Bird says that Sequoyah was a full-blood Cherokee who always opposed the submission and assimilation of his people into the white man's culture. The encyclopedia noted that Bird presented no documentary evidence, but has gained some credibility in academic circles.[13]
In any case the father was absent before Sequoyah was born. Various explanations have been proposed, but the reason is unknown. Wuteh did not remarry afterward (assuming she married her son's father in the first place). There were no siblings, and Sequoyah was raised by his mother alone.[6] According to Davis, Sequoyah never went to school and never learned English. He and Wuteh spoke only Cherokee.[14] As a youth, he spent much of his time tending cattle and working in their garden, while his mother ran a trading post.[6]
Sequoyah became lame early in life, though why, when and where are not known. Some reports indicate this may have been caused by injury in battle; others say the cause was a hunting accident. Davis wrote that an early issue of the Cherokee Advocate said that "...he was the victim of a hydrarthritic trouble of the knee joint, commonly called 'white swelling'." One doctor speculated that he had anascara (sic).[6] In any case, lameness prevented him from being a successful farmer or warrior.
Despite his lack of schooling, Sequoyah displayed a good deal of natural intelligence. As a child, he had devised and built milk troughs and skimmers for the dairy house that he had constructed. As he grew older and came in contact with more white men, he learned how to make jewelry. He became a noted silversmith, creating various items from the silver coins that trappers and traders carried. He never signed his pieces, so there are none that can be positively identified as his work.[6]
Sequoyah may have taken over his mother's trading post after her death, which Davis claimed occurred about the end of the 18th Century. His store became an informal meeting place for Cherokee men to socialize and, especially, drink whiskey. Sequoyah developed a great fondness for alcohol and soon spent much of his time drunk. After a few months he was rarely seen sober, neglecting his farm and trading business and spending his money buying liquor by the keg.[6]
Fortunately, he realized that he was ruining his life, and took up new interests. He began to draw. Then he took up blacksmithing, so he could repair the iron farm implements that had recently been introduced to the area. Self-taught as usual, he made his own tools, forge and bellows. He was soon doing a good business either repairing items or selling items he had created himself. His spurs and bridle bits were in great demand because he liked to decorate them with silver. Although he maintained his store, he not only stopped drinking but stopped selling alcohol.[6]
Move to Alabama
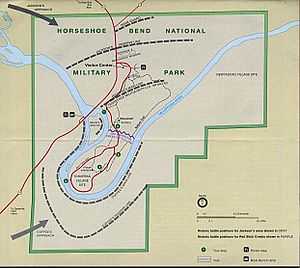
It is unclear when Sequoyah moved to Alabama from Tennessee. Some sources claim he went with his mother, though there is no confirmed date for her death. Others have stated that it was before 1809, when he started his work on the Cherokee Syllabary. Another source claims it was in 1818.[15] However, this date is too late, because he was already living in Alabama when he enlisted in the army. In 1813–14, Sequoyah served as a warrior of the Cherokee Regiment (Col. Gideon Morgan, Commander) at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend against the "Red Sticks" (Creek, or Muskogee, renegades).[16] His white comrades called him either George Guess or George Gist.[17]
The Encyclopedia of Alabama states that Sequoyah married Sally Benge in 1815.[16]
Sequoyah and Cherokee literacy
As a silversmith, Sequoyah dealt regularly with whites who had settled in the area. He was impressed by their writing, referring to their correspondence as "talking leaves." He knew that they represented a way to transmit information to other people in distant places. However, a majority of the Cherokees believed that writing was either sorcery, a special gift, or a pretense. Sequoyah accepted none of these explanations. He said that he could invent a way for Cherokees to talk on paper, even though his friends and family thought the idea ridiculous.[6]
Creation of the syllabary

Around 1809, Sequoyah began work to create a system of writing for the Cherokee language.[1] At first he sought to create a character for each word in the language. He spent a year on this effort, leaving his fields unplanted, so that his friends and neighbors thought he had lost his mind.[12][18] His wife is said to have burned his initial work, believing it to be witchcraft.[1] He realized that this approach was impractical because it would require too many pictures to be remembered. He tried making a symbol for every idea, but this also caused too many problems to be practical.[6]
Sequoyah did not succeed until he gave up trying to represent entire words and developed a symbol for each syllable in the language. After approximately a month, he had a system of 86 characters, some of which were Latin letters he obtained from a spelling book.[12] "In their present form, many of the syllabary characters resemble Roman, Cyrillic or Greek letters or Arabic numerals," says Janine Scancarelli, a scholar of Cherokee writing, "but there is no apparent relationship between their sounds in other languages and in Cherokee."[1]
Selling the product
Unable to find adults willing to learn the syllabary, he taught it to his daughter, Ayokeh (also spelled Ayoka).[1] Langguth says she was only six years old at the time.[19] He traveled to the Indian Reserves in the Arkansaw Territory where some Cherokee had settled. When he tried to convince the local leaders of the syllabary's usefulness, they doubted him, believing that the symbols were merely ad hoc reminders. Sequoyah asked each to say a word, which he wrote down, and then called his daughter in to read the words back. This demonstration convinced the leaders to let him teach the syllabary to a few more people. This took several months, during which it was rumored that he might be using the students for sorcery. After completing the lessons, Sequoyah wrote a dictated letter to each student, and read a dictated response. This test convinced the western Cherokee that he had created a practical writing system.[18]

When Sequoyah returned east, he brought a sealed envelope containing a written speech from one of the Arkansas Cherokee leaders. By reading this speech, he convinced the eastern Cherokee also to learn the system, after which it spread rapidly.[12][18] In 1825 the Cherokee Nation officially adopted the writing system. From 1828 to 1834, American missionaries assisted the Cherokee in using Sequoyah's syllabary to develop type characters and print the Cherokee Phoenix, the first newspaper of the Cherokee Nation, with text in both Cherokee and English.[4]
In 1826, the Cherokee National Council commissioned George Lowrey and David Brown to translate and print eight copies of the laws of the Cherokee Nation in the new Cherokee language using Sequoyah's system.[6]
Once Albert Gallatin saw a copy of Sequoyah's syllabary, he found the syllabary superior to the English alphabet. Even though the Cherokee student must learn 85 characters instead of 26, he can read immediately. The student could accomplish in a few weeks what students of English writing could learn in two years.[14]
In 1824, the General Council of the Eastern Cherokees awarded Sequoyah a large silver medal in honor of the syllabary. According to Davis, one side of the medal bore his image surrounded by the inscription in English, "Presented to George Gist by the General Council of the Cherokee for his ingenuity in the invention of the Cherokee Alphabet." The reverse side showed two long-stemmed pipes and the same inscription written in Cherokee. Supposedly, Sequoyah wore the medal throughout the rest of his life and it was buried with him.[6]
Life in Indian Territory

After the Nation accepted his syllabary in 1825, Sequoyah traveled to the Cherokee lands in the Arkansas Territory. There he set up a blacksmith shop and a salt works. He continued to teach the syllabary to anyone who wished.
In 1828, Sequoyah journeyed to Washington, D.C., as part of a delegation to negotiate a treaty for land in the planned Indian Territory. While in Washington, D.C., he sat for a formal portrait painted by Charles Bird King (see image at the top of this article). He holds a copy of the syllabary in his left hand and is smoking a long-stemmed pipe. During his trip, he met representatives of other Native American tribes. Inspired by these meetings, he decided to create a syllabary for universal use among Native American tribes. Sequoyah began to journey into areas of present-day Arizona and New Mexico, to meet with tribes there.
In 1829, Sequoyah moved to a location near the present city of Sallisaw, Oklahoma, where he built Sequoyah's Cabin that became his home for the rest of his life. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1965.[20]
In 1839, when the Cherokees were bitterly divided over the issue of removal to Indian Territory, Sequoyah joined with Jesse Bushyhead to try to reunite the Cherokee Nation. Sequoyah, representing the Western Cherokees, and Bushyhead representing the Eastern Cherokees, made a joint plea at a tribal council meeting at Takatoka on 20 June 1839, where they succeeded in getting a voice vote to hold a new council of all Cherokees to resolve the reunification issues.[21]
Sequoyah's last journey and death
In addition, Sequoyah dreamed of seeing the splintered Cherokee Nation reunited. In the Spring of 1842, Sequoyah began a trip to locate other Cherokee bands who were believed to have fled to Mexico and persuade them return to the Cherokee Nation in the United States. He was accompanied by his son, Teesy (Chusaleta), as well as other Cherokees identified as Co-tes-ka, Nu-wo-ta-na, Cah-ta-ta, Co-wo-si-ti, John Elijah, and The Worm.[6] Sometime between 1843 and 1845, he died during a trip to San Fernando, Tamaulipas, Mexico, when he was seeking Cherokee who migrated there at the time of Indian Removal. His resting place is believed to be in Zaragoza near the Mexico-Texas border.
- The following document gives the most circumstantial account of the death of Sequoyah:[6]
- Warren's Trading House, Red River,
- April 21st, 1845.
- "We, the undersigned Cherokees, direct from the Spanish Dominions, do hereby certify that George Guess of the Cherokee Nation, Arkansas, departed this life in the town of San-fernando in the :month of August, 1843, and his son Chusaleta is at this time on the Brasos River, Texas, about thirty miles above the falls, and he intends returning home this fall.:Given under our hands the day and date written."
- STANDING X(his mark) ROCK
- STANDING X (his mark) BOWLES
- WATCH X (his mark) JUSTICE
- WITNESSES
- Daniel G. Watson
- Jesse Chisholm.
- Austin E. Turner.
In 1938, the Cherokee Nation Principal Chief J. B. Milam funded an expedition to find Sequoyah's grave in Mexico.[22] A party of Cherokee and non-Cherokee scholars embarked from Eagle Pass, Texas, on January 1939. They found a grave site near a fresh water spring in Coahuila, Mexico, but could not conclusively determine the grave site was that of Sequoyah.[23]
In 2011, the Muskogee Phoenix published an article relating a discovery in 1903 of a gravesite in the Wichita Mountains by Hayes and Fancher which they believed was Sequoyah's. The two men said the site was in a cave and contained a human skeleton with one leg shorter than the other, a long-stemmed pipe, two silver medals, a flintlock rifle and an ax. However, the site was far north of the Mexican border.[24]
Legacy


- Oklahoma gave a statue of Sequoyah to the National Statuary Hall Collection in 1917. This was the first statue representing a native American to be placed in the hall. It is displayed in the Capitol rotunda in Washington D. C.[25]
- Sequoyah's Cabin, where he lived during 1829–1844 in Oklahoma, was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965.
- 1939, a bronze panel with a raised figure of Sequoyah, by Lee Lawrie, was erected in his honor at the Library of Congress.
- Addressing the exalted place Sequoyah holds in Cherokee imagination, the ethnographer Jack Kilpatrick wrote: "Sequoyah was always in the wilderness. He walked about, but he was not a hunter. I wonder what he was looking for."[23]
- The Sequoyah Birthplace Museum in Eastern Tennessee features his life and Cherokee culture.[26]
- On 20 December 1980 the United States Postal Service issued a 19¢ stamp in his honor in the Great Americans series.[27]

Namesake honors
- While it was long believed that the Sequoia trees were named Sequoia gigantea after him in 1847 by Austrian biologist Stephan Endlicher, this hypothesis has long been questioned.[28] A crystalline chemical compound found by distilling the needles of the trees was then named se-quoi-ene. The caterpillar of the sequoia-borer moth, a sesiid moth, was named Bembecia sequoiae.[6][29]
- The name of the district where Sequoyah lived in present-day Oklahoma was changed to the Sequoyah District in 1851. When Oklahoma was admitted to the union, that area became known as Sequoyah County.[6]
- The proposed State of Sequoyah was named in his honor.[6]
- Sequoyah Research Center is dedicated to collecting and archiving Native American writing and literature.
- Mount Sequoyah in the Great Smoky Mountains.
- Mount Sequoyah in Fayetteville, Arkansas was named in honor of him after the city donated the top of East Mountain to the Methodist Assembly for a retreat.
- The Sequoyah Hills neighborhood of Knoxville, Tennessee.
- The Tennessee Valley Authority Sequoyah Nuclear Plant bears his name.
- The Sequoyah Marina on Norris Lake in Tennessee, upstream from Norris Dam on the Clinch River.
- The USS Sequoia was a long-time yacht used by American Presidents (now privately owned).
- Sequoyah Caverns and Ellis Homestead is in Valley Head, Alabama.[30]
- Sequoyah Country Club, Oakland California[31]
- Sequoyah Council – A Boy Scouts of America Council located in Northeast Tennessee.
- The Sequoyah Book Award is chosen annually by students in Oklahoma.
- Many schools have been named for him, including
- Sequoyah High School (Georgia), Canton, Georgia
- Sequoyah High School (Oklahoma), a Native American boarding school in Tahlequah, Oklahoma
- Sequoyah High School (Tennessee), Madisonville, Tennessee
- Sequoia High School (Redwood City, California)
- Sequoya Elementary School, Tahlequah, Oklahoma
- Sequoyah Elementary School, Shawnee, Oklahoma
- Sequoyah Elementary School, Tulsa, Oklahoma
- Sequoia Elementary School, San Diego, California
- Sequoya Elementary School, Russellville, Arkansas
- Sequoya Middle School, Broken Arrow, Oklahoma
- Sequoya Elementary School, Derwood, Maryland
See also
- Bob Benge, Cherokee leader
- Hastings Shade (1941–2010), fifth-generation direct descendant of Sequoyah
- The development of writing
- John Watts (Cherokee chief)
- Tahlonteeskee
- Old Tassel
- Tenevil
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Wilford, John Noble (22 June 2009). "Carvings From Cherokee Script's Dawn". New York Times. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ↑ Morand, Ann; Kevin Smith; Daniel C. Swan; Sarah Erwin (2003). Treasures of Gilcrease: Selections from the Permanent Collection. Tulsa, OK: Gilcrease Museum. ISBN 0-9725657-1-X.
- ↑ Holmes, Ruth Bradley; Betty Sharp Smith (1976). Beginning Cherokee: Talisgo Galiquogi Dideliquasdodi Tsalagi Digoweli. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-1362-6.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Sequoyah", New Georgia Encyclopedia, accessed 3 Jan 2009
- ↑ Fogelson, Raymond D. (1974). "On the Varieties of Indian History: Sequoyah and Traveller Bird". Journal of Ethnic Studies 2.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 Davis, John B. Chronicles of Oklahoma. Vol. 8, Number 2. "The Life and Work of Sequoyah." June, 1930. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ London, 193
- ↑ Goodpasture, Albert V. Chronicles of Oklahoma Volume 1, No. 2. October, 1921. "The Paternity of Sequoya the Inventor of the Cherokee Alphabet." Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ Samuel C. Williams (March 1937). "The Father of Sequoyah: Nathaniel Gist". Volume 15, No. 1. Chronicles of Oklahoma. pp. 10–11. Retrieved 27 September 2010.
- ↑ Robert Bieder, "Sault-ste-marie-and-the-war-of-1812", Indiana Magazine of History, XCV (Mar 1999), accessed 13 Dec 2008
- ↑ Nott, Josiah C. (1849). "Two lectures on the connection between the Biblical and physical history of mankind". New York: Bartlett and Welford. p. 35
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 G. C. (1820-08-13). "Invention of the Cherokee Alphabet". Cherokee Phoenix 1 (24).
- ↑ Wadley, Ted. New Georgia Encyclopedia. "Sequoyah." 2002. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Langguth, p. 71
- ↑ Explore Southern History.com. "Wills Town Mission and Cemetery, Alabama." Retrieved 9 April 2013.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Abram, Susan M. Encyclopedia of Alabama History. "Sequoyah". Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ↑ Langguth, p. 68.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Boudinot, Elias (1832-04-01). "Invention of a New Alphabet". American Annals of Education.
- ↑ Langguth, p. 70
- ↑ Joseph Scott Mendinghall (9 December 1975). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Sequoyah's Cabin" (PDF). National Park Service. and Accompanying 4 photos from 1975. PDF (1.11 MB)
- ↑ McLoughlin, p. 14
- ↑ J. B. Milam, McFarlin Library, University of Tulsa. Libraries & Cultures: Bookplate Archive. 2001 (retrieved 23 June 2009)
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Meredith, Howard L. Bartley Milam: Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation. Muskogee, Oklahoma: Indian University Press, 1985: 47. ISBN 0-940392-17-8
- ↑ Mullins, Jonita. Muskogee Phoenix. "Sequoyah's gravesite remains unknown." 13 November 2011. Retrieved 6 April 2013.
- ↑ Architect of the Capitol. Explore Capitol Hill. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ Sequoyah Birthplace Museum
- ↑ GeorgiaInfo "Sequoyah Stamp." Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ Lowe, Gary D. 2012. Endlicher's sequence: the naming of the genus Sequoia. Fremontia 40, nos. 1 & 2: 25–35.
- ↑ Scheidt, Laurel. Hiking Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks. Guilford, CT: Globe Pequot Press, 2002: 68. ISBN 978-0-7627-1122-2 (retrieved through Google books, 23 June 2009)
- ↑ Sequoyah Caverns and Ellis Homestead
- ↑ "Welcome to Sequoyah Country Club". Retrieved 2 September 2010.
Bibliography
- Bender, Margaret. (2002) Signs of Cherokee Culture: Sequoyah's Syllabary in Eastern Cherokee Life. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- Feeling, Durbin. Cherokee-English Dictionary: Tsalagi-Yonega Didehlogwasdohdi. Tahlequah, Oklahoma: Cherokee Nation, 1975: xvii
- Holmes, Ruth Bradley; Betty Sharp Smith (1976). Beginning Cherokee: Talisgo Galiquogi Dideliquasdodi Tsalagi Digoweli. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-1362-6.
- Foreman, Grant, Sequoyah, University of Oklahoma Press, Norman,OK, 1938.
- Langguth, A. J. Driven West: Andrew Jackson and the Trail of Tears to the Civil War. New York, Simon & Schuster. 2010. ISBN 978-1-4165-4859-1.
- McKinney, Thomas and Hall, James, History of the Indian Tribes of North America. (Philadelphia,PA, 1837–1844).
- McLoughlin, William G., After the Trail of Tears: The Cherokees' Struggle for Sovereignty 1839 - 1880. University of North Carolina Press. Chapel Hill. 1993. ISBN 0-8078-2111-X.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sequoyah. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article Sequoyah. |
- "Invention of the Cherokee Alphabet", Cherokee Phoenix, 13 Aug 1828
- John B. Davis, "The Life and Work of Sequoyah", Chronicles of Oklahoma, Vol.8 (2), June 1930, Oklahoma State University
- "Sequoyah", Tiro Typeworks
- "Sequoyah (aka George Gist)", a North Georgia Notable
- The Cherokee Nation Official Website
- "The Official Cherokee Font" at the Cherokee Nation Official Website
- Sequoyah at Find a Grave
 "Guess, George". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
"Guess, George". The American Cyclopædia. 1879.
|
