Sequent calculus
Sequent calculus is, in essence, a style of formal logical argumentation where every line of a proof is a conditional tautology (called a sequent by Gerhard Gentzen) instead of an unconditional tautology. Each conditional tautology is inferred from other conditional tautologies on earlier lines in a formal argument according to rules and procedures of inference, giving a better approximation to the style of natural deduction used by mathematicians than David Hilbert's earlier style of formal logic where every line was an unconditional tautology. (This is the essence of the idea, but there are several over-simplifications here. For example, there may be non-logical axioms upon which all propositions are implicitly dependent. Then sequents signify conditional theorems in a first-order language rather than conditional tautologies.)
Sequent calculus is one of several extant styles of proof calculus for expressing line-by-line logical arguments.
- Hilbert style. Every line is an unconditional tautology (or theorem).
- Gentzen style. Every line is a conditional tautology (or theorem) with zero or more conditions on the left.
- Natural deduction. Every (conditional) line has exactly one asserted proposition on the right.
- Sequent calculus. Every (conditional) line has zero or more asserted propositions on the right.
In other words, natural deduction and sequent calculus systems are particular distinct kinds of Gentzen-style systems. Hilbert-style systems typically have a very small number of inference rules, relying more on sets of axioms. Gentzen-style systems typically have very few axioms, if any, relying more on sets of rules.
Gentzen-style systems have significant practical and theoretical advantages compared to Hilbert-style systems. For example, both natural deduction and sequent calculus systems facilitate the elimination and introduction of universal and existential quantifiers so that unquantified logical expressions can be manipulated according to the much simpler rules of propositional calculus. In a typical argument, quantifiers are eliminated, then propositional calculus is applied to unquantified expressions (which typically contain free variables), and then the quantifiers are reintroduced. This very much parallels the way in which mathematical proofs are carried out in practice by mathematicians. Predicate calculus proofs are generally much easier to discover with this approach, and are often shorter. Natural deduction systems are more suited to practical theorem-proving. Sequent calculus systems are more suited to theoretical analysis.
Introduction
In proof theory and mathematical logic, sequent calculus is a family of formal systems sharing a certain style of inference and certain formal properties. The first sequent calculi, systems LK and LJ, were introduced in 1934/1935 by Gerhard Gentzen[1] as a tool for studying natural deduction in first-order logic (in classical and intuitionistic versions, respectively). Gentzen's so-called "Main Theorem" (Hauptsatz) about LK and LJ was the cut-elimination theorem,[2][3] a result with far-reaching meta-theoretic consequences, including consistency. Gentzen further demonstrated the power and flexibility of this technique a few years later, applying a cut-elimination argument to give a (transfinite) proof of the consistency of Peano arithmetic, in surprising response to Gödel's incompleteness theorems. Since this early work, sequent calculi, also called Gentzen systems,[4][5][6][7] and the general concepts relating to them, have been widely applied in the fields of proof theory, mathematical logic, and automated deduction.
Hilbert-style deduction systems
One way to classify different styles of deduction systems is to look at the form of judgments in the system, i.e., which things may appear as the conclusion of a (sub)proof. The simplest judgment form is used in Hilbert-style deduction systems, where a judgment has the form
where 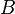 is any formula of first-order-logic (or whatever logic the deduction system applies to, e.g., propositional calculus or a higher-order logic or a modal logic). The theorems are those formulae that appear as the concluding judgment in a valid proof. A Hilbert-style system needs no distinction between formulae and judgments; we make one here solely for comparison with the cases that follow.
is any formula of first-order-logic (or whatever logic the deduction system applies to, e.g., propositional calculus or a higher-order logic or a modal logic). The theorems are those formulae that appear as the concluding judgment in a valid proof. A Hilbert-style system needs no distinction between formulae and judgments; we make one here solely for comparison with the cases that follow.
The price paid for the simple syntax of a Hilbert-style system is that complete formal proofs tend to get extremely long. Concrete arguments about proofs in such a system almost always appeal to the deduction theorem. This leads to the idea of including the deduction theorem as a formal rule in the system, which happens in natural deduction.
Natural deduction systems
In natural deduction, judgments have the shape
where the 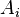 's and
's and 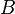 are again formulae and
are again formulae and  . Permutations of the
. Permutations of the 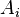 's are immaterial. In other words, a judgment consists of a list (possibly empty) of formulae on the left-hand side of a turnstile symbol "
's are immaterial. In other words, a judgment consists of a list (possibly empty) of formulae on the left-hand side of a turnstile symbol "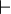 ", with a single formula on the right-hand side.[8][9][10] The theorems are those formulae
", with a single formula on the right-hand side.[8][9][10] The theorems are those formulae 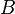 such that
such that  (with an empty left-hand side) is the conclusion of a valid proof.
(In some presentations of natural deduction, the
(with an empty left-hand side) is the conclusion of a valid proof.
(In some presentations of natural deduction, the 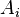 s and the turnstile are not written down explicitly; instead a two-dimensional notation from which they can be inferred is used.)
s and the turnstile are not written down explicitly; instead a two-dimensional notation from which they can be inferred is used.)
The standard semantics of a judgment in natural deduction is that it asserts that whenever[11] 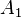 ,
, 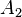 , etc., are all true,
, etc., are all true, 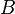 will also be true. The judgments
will also be true. The judgments
and
are equivalent in the strong sense that a proof of either one may be extended to a proof of the other.
Sequent calculus systems
Finally, sequent calculus generalizes the form of a natural deduction judgment to
a syntactic object called a sequent. The formulas on left-hand side of the turnstile are called the antecedent, and the formulas on right-hand side are called the succedent; together they are called cedents. Again, 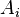 and
and 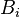 are formulae, and
are formulae, and 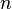 and
and 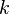 are nonnegative integers, that is, the left-hand-side or the right-hand-side (or neither or both) may be empty. As in natural deduction, theorems are those
are nonnegative integers, that is, the left-hand-side or the right-hand-side (or neither or both) may be empty. As in natural deduction, theorems are those 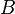 where
where  is the conclusion of a valid proof. The empty sequent, having both cedents empty, is defined to be false.[12]
is the conclusion of a valid proof. The empty sequent, having both cedents empty, is defined to be false.[12]
The standard semantics of a sequent is an assertion that whenever every 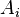 is true, at least one
is true, at least one 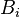 will also be true.[13] One way to express this is that a comma to the left of the turnstile should be thought of as an "and", and a comma to the right of the turnstile should be thought of as an (inclusive) "or". The sequents
will also be true.[13] One way to express this is that a comma to the left of the turnstile should be thought of as an "and", and a comma to the right of the turnstile should be thought of as an (inclusive) "or". The sequents
and
are equivalent in the strong sense that a proof of either one may be extended to a proof of the other.
At first sight, this extension of the judgment form may appear to be a strange complication — it is not motivated by an obvious shortcoming of natural deduction, and it is initially confusing that the comma seems to mean entirely different things on the two sides of the turnstile. However, in a classical context the semantics of the sequent can also (by propositional tautology) be expressed either as
(at least one of the As is false, or one of the Bs is true) or as
(it cannot be the case that all of the As are true and all of the Bs are false). In these formulations, the only difference between formulae on either side of the turnstile is that one side is negated. Thus, swapping left for right in a sequent corresponds to negating all of the constituent formulae. This means that a symmetry such as De Morgan's laws, which manifests itself as logical negation on the semantic level, translates directly into a left-right symmetry of sequents — and indeed, the inference rules in sequent calculus for dealing with conjunction (∧) are mirror images of those dealing with disjunction (∨).
Many logicians feel that this symmetric presentation offers a deeper insight in the structure of the logic than other styles of proof system, where the classical duality of negation is not as apparent in the rules.
Distinction between natural deduction and sequent calculus
Gentzen asserted a sharp distinction between his single-output natural deduction systems (NK and NJ) and his multiple-output sequent calculus systems (LK and LJ). He wrote that the intuitionistic natural deduction system NJ was somewhat ugly.[14] He said that the special role of the excluded middle in the classical natural deduction system NK is removed in the classical sequent calculus system LK.[15] He said that the sequent calculus LJ gave more symmetry than natural deduction NJ in the case of intuitionistic logic, as also in the case of classical logic (LK versus NK).[16] Then he said that in addition to these reasons, the sequent calculus with multiple succedent formulas is intended particularly for his principal theorem ("Hauptsatz").[17]
Origin of word "sequent"
The word "sequent" is taken from the word "Sequenz" in Gentzen's 1934 paper.[1] Kleene makes the following comment on the translation into English: "Gentzen says 'Sequenz', which we translate as 'sequent', because we have already used 'sequence' for any succession of objects, where the German is 'Folge'."[18]
The system LK
This section introduces the rules of the sequent calculus LK (which just stands for “klassische Prädikatenlogik”), as introduced by Gentzen in 1934.[19] A (formal) proof in this calculus is a sequence of sequents, where each of the sequents is derivable from sequents appearing earlier in the sequence by using one of the rules below.
Inference rules
The following notation will be used:
-
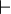 known as the turnstile, separates the assumptions on the left from the propositions on the right
known as the turnstile, separates the assumptions on the left from the propositions on the right -
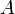 and
and 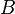 denote formulae of first-order predicate logic (one may also restrict this to propositional logic),
denote formulae of first-order predicate logic (one may also restrict this to propositional logic), -
 , and
, and 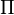 are finite (possibly empty) sequences of formulae (in fact, the order of formulae do not matter; see subsection Structural Rules), called contexts,
are finite (possibly empty) sequences of formulae (in fact, the order of formulae do not matter; see subsection Structural Rules), called contexts,
- when on the left of the
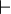 , the sequence of formulas is considered conjunctively (all assumed to hold at the same time),
, the sequence of formulas is considered conjunctively (all assumed to hold at the same time), - while on the right of the
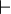 , the sequence of formulas is considered disjunctively (at least one of the formulas must hold for any assignment of variables),
, the sequence of formulas is considered disjunctively (at least one of the formulas must hold for any assignment of variables),
- when on the left of the
-
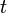 denotes an arbitrary term,
denotes an arbitrary term, -
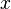 and
and 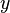 denote variables.
denote variables. - a variable is said to occur free within a formula if it occurs outside the scope of quantifiers
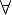 or
or 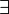 .
. -
![A[t/x]](../I/m/680216b079c29a6e9ec03b985f360a1b.png) denotes the formula that is obtained by substituting the term
denotes the formula that is obtained by substituting the term 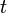 for every free occurrence of the variable
for every free occurrence of the variable 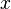 in formula
in formula 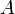 with the restriction that the term
with the restriction that the term 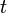 must be free for the variable
must be free for the variable 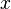 in
in 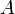 (i.e., no occurrence of any variable in
(i.e., no occurrence of any variable in 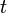 becomes bound in
becomes bound in ![A[t/x]](../I/m/680216b079c29a6e9ec03b985f360a1b.png) ).
). -
 and
and  stand for Weakening Left/Right,
stand for Weakening Left/Right, 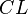 and
and  for Contraction, and
for Contraction, and  and
and  for Permutation.
for Permutation.
| Axiom: | Cut: |
|
|
|
| Left logical rules: | Right logical rules: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Left structural rules: | Right structural rules: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restrictions: In the rules  and
and  , the variable
, the variable 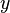 must not occur free within
must not occur free within 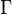 and
and 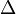 . Alternatively, the variable
. Alternatively, the variable 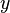 must not appear anywhere in the respective lower sequents.
must not appear anywhere in the respective lower sequents.
An intuitive explanation
The above rules can be divided into two major groups: logical and structural ones. Each of the logical rules introduces a new logical formula either on the left or on the right of the turnstile  . In contrast, the structural rules operate on the structure of the sequents, ignoring the exact shape of the formulae. The two exceptions to this general scheme are the axiom of identity (I) and the rule of (Cut).
. In contrast, the structural rules operate on the structure of the sequents, ignoring the exact shape of the formulae. The two exceptions to this general scheme are the axiom of identity (I) and the rule of (Cut).
Although stated in a formal way, the above rules allow for a very intuitive reading in terms of classical logic. Consider, for example, the rule  . It says that, whenever one can prove that
. It says that, whenever one can prove that 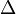 can be concluded from some sequence of formulae that contain
can be concluded from some sequence of formulae that contain 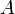 , then one can also conclude
, then one can also conclude 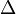 from the (stronger) assumption, that
from the (stronger) assumption, that  holds. Likewise, the rule
holds. Likewise, the rule  states that, if
states that, if 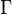 and A suffice to conclude
and A suffice to conclude 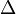 , then from Γ alone one can either still conclude
, then from Γ alone one can either still conclude 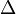 or A must be false, i.e.
or A must be false, i.e.  holds. All the rules can be interpreted in this way.
holds. All the rules can be interpreted in this way.
For an intuition about the quantifier rules, consider the rule  . Of course concluding that
. Of course concluding that  holds just from the fact that
holds just from the fact that ![A[y/x]](../I/m/b8bff5e58215db4c1196838907485685.png) is true is not in general possible. If, however, the variable y is not mentioned elsewhere (i.e. it can still be chosen freely, without influencing the other formulae), then one may assume, that
is true is not in general possible. If, however, the variable y is not mentioned elsewhere (i.e. it can still be chosen freely, without influencing the other formulae), then one may assume, that ![A[y/x]](../I/m/b8bff5e58215db4c1196838907485685.png) holds for any value of y. The other rules should then be pretty straightforward.
holds for any value of y. The other rules should then be pretty straightforward.
Instead of viewing the rules as descriptions for legal derivations in predicate logic, one may also consider them as instructions for the construction of a proof for a given statement. In this case the rules can be read bottom-up; for example,  says that, to prove that
says that, to prove that  follows from the assumptions
follows from the assumptions 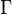 and
and 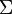 , it suffices to prove that A can be concluded from
, it suffices to prove that A can be concluded from 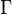 and B can be concluded from
and B can be concluded from 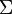 , respectively. Note that, given some antecedent, it is not clear how this is to be split into
, respectively. Note that, given some antecedent, it is not clear how this is to be split into 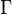 and
and 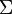 . However, there are only finitely many possibilities to be checked since the antecedent by assumption is finite. This also illustrates how proof theory can be viewed as operating on proofs in a combinatorial fashion: given proofs for both A and B, one can construct a proof for A∧B.
. However, there are only finitely many possibilities to be checked since the antecedent by assumption is finite. This also illustrates how proof theory can be viewed as operating on proofs in a combinatorial fashion: given proofs for both A and B, one can construct a proof for A∧B.
When looking for some proof, most of the rules offer more or less direct recipes of how to do this. The rule of cut is different: It states that, when a formula A can be concluded and this formula may also serve as a premise for concluding other statements, then the formula A can be "cut out" and the respective derivations are joined. When constructing a proof bottom-up, this creates the problem of guessing A (since it does not appear at all below). The cut-elimination theorem is thus crucial to the applications of sequent calculus in automated deduction: it states that all uses of the cut rule can be eliminated from a proof, implying that any provable sequent can be given a cut-free proof.
The second rule that is somewhat special is the axiom of identity (I). The intuitive reading of this is obvious: every formula proves itself. Like the cut rule, the axiom of identity is somewhat redundant: the completeness of atomic initial sequents states that the rule can be restricted to atomic formulas without any loss of provability.
Observe that all rules have mirror companions, except the ones for implication. This reflects the fact that the usual language of first-order logic does not include the "is not implied by" connective  that would be the De Morgan dual of implication. Adding such a connective with its natural rules would make the calculus completely left-right symmetric.
that would be the De Morgan dual of implication. Adding such a connective with its natural rules would make the calculus completely left-right symmetric.
Example derivations
Here is the derivation of " ", known as
the Law of excluded middle (tertium non datur in Latin).
", known as
the Law of excluded middle (tertium non datur in Latin).
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
Next is the proof of a simple fact involving quantifiers. Note that the converse is not true, and its falsity can be seen when attempting to derive it bottom-up, because an existing free variable cannot be used in substitution in the rules  and
and  .
.
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
 | ||
 |
||
For something more interesting we shall prove  . It is straightforward to find the derivation, which exemplifies the usefulness of LK in automated proving.
. It is straightforward to find the derivation, which exemplifies the usefulness of LK in automated proving.
|
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
These derivations also emphasize the strictly formal structure of the sequent calculus. For example, the logical rules as defined above always act on a formula immediately adjacent to the turnstile, such that the permutation rules are necessary. Note, however, that this is in part an artifact of the presentation, in the original style of Gentzen. A common simplification involves the use of multisets of formulas in the interpretation of the sequent, rather than sequences, eliminating the need for an explicit permutation rule. This corresponds to shifting commutativity of assumptions and derivations outside the sequent calculus, whereas LK embeds it within the system itself.
Structural rules
The structural rules deserve some additional discussion.
Weakening (W) allows the addition of arbitrary elements to a sequence. Intuitively, this is allowed in the antecedent because we can always restrict the scope of our proof (if all cars have wheels, then it's safe to say that all black cars have wheels); and in the succedent because we can always allow for alternative conclusions (if all cars have wheels, then it's safe to say that all cars have either wheels or wings).
Contraction (C) and Permutation (P) assure that neither the order (P) nor the multiplicity of occurrences (C) of elements of the sequences matters. Thus, one could instead of sequences also consider sets.
The extra effort of using sequences, however, is justified since part or all of the structural rules may be omitted. Doing so, one obtains the so-called substructural logics.
Properties of the system LK
This system of rules can be shown to be both sound and complete with respect to first-order logic, i.e. a statement 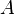 follows semantically from a set of premises
follows semantically from a set of premises 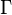
 iff the sequent
iff the sequent  can be derived by the above rules.[20]
can be derived by the above rules.[20]
In the sequent calculus, the rule of cut is admissible. This result is also referred to as Gentzen's Hauptsatz ("Main Theorem").[2][3]
Variants
The above rules can be modified in various ways:
Minor structural alternatives
There is some freedom of choice regarding the technical details of how sequents and structural rules are formalized. As long as every derivation in LK can be effectively transformed to a derivation using the new rules and vice versa, the modified rules may still be called LK.
First of all, as mentioned above, the sequents can be viewed to consist of sets or multisets. In this case, the rules for permuting and (when using sets) contracting formulae are obsolete.
The rule of weakening will become admissible, when the axiom (I) is changed, such that any sequent of the form  can be concluded. This means that
can be concluded. This means that 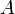 proves
proves 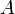 in any context. Any weakening that appears in a derivation can then be performed right at the start. This may be a convenient change when constructing proofs bottom-up.
in any context. Any weakening that appears in a derivation can then be performed right at the start. This may be a convenient change when constructing proofs bottom-up.
Independent of these one may also change the way in which contexts are split within the rules: In the cases  , and
, and  the left context is somehow split into
the left context is somehow split into 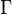 and
and 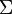 when going upwards. Since contraction allows for the duplication of these, one may assume that the full context is used in both branches of the derivation. By doing this, one assures that no important premises are lost in the wrong branch. Using weakening, the irrelevant parts of the context can be eliminated later.
when going upwards. Since contraction allows for the duplication of these, one may assume that the full context is used in both branches of the derivation. By doing this, one assures that no important premises are lost in the wrong branch. Using weakening, the irrelevant parts of the context can be eliminated later.
Absurdity
One can introduce 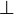 , the absurdity constant representing false, with the axiom:
, the absurdity constant representing false, with the axiom:
Or if, as described above, weakening is to be an admissible rule, then with the axiom:
With 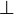 , negation can be subsumed as a special case of implication, via the definition
, negation can be subsumed as a special case of implication, via the definition  .
.
Substructural logics
Alternatively, one may restrict or forbid the use of some of the structural rules. This yields a variety of substructural logic systems. They are generally weaker than LK (i.e., they have fewer theorems), and thus not complete with respect to the standard semantics of first-order logic. However, they have other interesting properties that have led to applications in theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence.
Intuitionistic sequent calculus: System LJ
Surprisingly, some small changes in the rules of LK suffice to turn it into a proof system for intuitionistic logic.[21] To this end, one has to restrict to sequents with exactly one formula on the right-hand side, and modify the rules to maintain this invariant. For example,  is reformulated as follows (where C is an arbitrary formula):
is reformulated as follows (where C is an arbitrary formula):
The resulting system is called LJ. It is sound and complete with respect to intuitionistic logic and admits a similar cut-elimination proof. This can be used in proving disjunction and existence properties.
In fact, the only two rules in LK that need to be restricted to single-formula consequents are  and
and  [22] (and the latter can be seen as a special case of the former, via
[22] (and the latter can be seen as a special case of the former, via 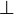 as described above). When multi-formula consequents are interpreted as disjunctions, all of the other inference rules of LK are actually derivable in LJ, while the offending rule is
as described above). When multi-formula consequents are interpreted as disjunctions, all of the other inference rules of LK are actually derivable in LJ, while the offending rule is
This amounts to the propositional formula  , a classical tautology that is not constructively valid.
, a classical tautology that is not constructively valid.
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gentzen 1934, Gentzen 1935.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Curry 1977, pp. 208–213, gives a 5-page proof of the elimination theorem. See also pages 188, 250.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kleene 2009, pp. 453, gives a very brief proof of the cut-elimination theorem.
- ↑ Curry 1977, pp. 189–244, calls Gentzen systems LC systems. Curry's emphasis is more on theory than on practical logic proofs.
- ↑ Kleene 2009, pp. 440–516. This book is much more concerned with the theoretical, metamathematical implications of Gentzen-style sequent calculus than applications to practical logic proofs.
- ↑ Kleene 2002, pp. 283–312, 331–361, defines Gentzen systems and proves various theorems within these systems, including Gödel's completeness theorem and Gentzen's theorem.
- ↑ Smullyan 1995, pp. 101–127, gives a brief theoretical presentation of Gentzen systems. He uses the tableau proof layout style.
- ↑ Curry 1977, pp. 184–244, compares natural deduction systems, denoted LA, and Gentzen systems, denoted LC. Curry's emphasis is more theoretical than practical.
- ↑ Suppes 1999, pp. 25–150, is an introductory presentation of practical natural deduction of this kind. This became the basis of System L.
- ↑ Lemmon 1965 is an elementary introduction to practical natural deduction based on the convenient abbreviated proof layout style System L based on Suppes 1999, pp. 25–150.
- ↑ Here, "whenever" is used as an informal abbreviation "for every assignment of values to the free variables in the judgment"
- ↑ Buss 1998, p. 10
- ↑ For explanations of the disjunctive semantics for the right side of sequents, see Curry 1977, pp. 189–190, Kleene 2002, pp. 290, 297, Kleene 2009, p. 441, Hilbert & Bernays 1970, p. 385, Smullyan 1995, pp. 104–105 and Gentzen 1934, p. 180.
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, p. 188. "Der Kalkül NJ hat manche formale Unschönheiten."
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, p. 191. "In dem klassischen Kalkül NK nahm der Satz vom ausgeschlossenen Dritten eine Sonderstellung unter den Schlußweisen ein [...], indem er sich der Einführungs- und Beseitigungssystematik nicht einfügte. Bei dem im folgenden anzugebenden logistischen klassichen Kalkül LK wird diese Sonderstellung aufgehoben."
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, p. 191. "Die damit erreichte Symmetrie erweist sich als für die klassische Logik angemessener."
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, p. 191. "Hiermit haben wir einige Gesichtspunkte zur Begründung der Aufstellung der folgenden Kalküle angegeben. Im wesentlichen ist ihre Form jedoch durch die Rücksicht auf den nachher zu beweisenden 'Hauptsatz' bestimmt und kann daher vorläufig nicht näher begründet werden."
- ↑ Kleene 2002, p. 441.
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, pp. 190–193.
- ↑ Kleene 2002, p. 336, wrote in 1967 that "it was a major logical discovery by Gentzen 1934–5 that, when there is any (purely logical) proof of a proposition, there is a direct proof. The implications of this discovery are in theoretical logical investigations, rather than in building collections of proved formulas."
- ↑ Gentzen 1934, p. 194, wrote: "Der Unterschied zwischen intuitionistischer und klassischer Logik ist bei den Kalkülen LJ und LK äußerlich ganz anderer Art als bei NJ und NK. Dort bestand er in Weglassung bzw. Hinzunahme des Satzes vom ausgeschlossenen Dritten, während er hier durch die Sukzedensbedingung ausgedrückt wird." English translation: "The difference between intuitionistic and classical logic is in the case of the calculi LJ and LK of an extremely, totally different kind to the case of NJ and NK. In the latter case, it consisted of the removal or addition respectively of the excluded middle rule, whereas in the former case, it is expressed through the succedent conditions."
- ↑ Structural Proof Theory (CUP, 2001), Sara Negri and Jan van Plato
References
- Buss, Samuel R. (1998). "An introduction to proof theory". In Samuel R. Buss. Handbook of proof theory. Elsevier. pp. 1–78. ISBN 0-444-89840-9.
- Curry, Haskell Brooks (1977) [1963]. Foundations of mathematical logic. New York: Dover Publications Inc. ISBN 978-0-486-63462-3.
- Gentzen, Gerhard Karl Erich (1934). "Untersuchungen über das logische Schließen. I". Mathematische Zeitschrift 39 (2): 176–210. doi:10.1007/BF01201353.
- Gentzen, Gerhard Karl Erich (1935). "Untersuchungen über das logische Schließen. II". Mathematische Zeitschrift 39 (3): 405–431. doi:10.1007/bf01201363.
- Girard, Jean-Yves; Paul Taylor; Yves Lafont (1990) [1989]. Proofs and Types. Cambridge University Press (Cambridge Tracts in Theoretical Computer Science, 7). ISBN 0-521-37181-3.
- Hilbert, David; Bernays, Paul (1970) [1939]. Grundlagen der Mathematik II (Second ed.). Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-642-86897-9.
- Kleene, Stephen Cole (2009) [1952]. Introduction to metamathematics. Ishi Press International. ISBN 978-0-923891-57-2.
- Kleene, Stephen Cole (2002) [1967]. Mathematical logic. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-42533-7.
- Lemmon, Edward John (1965). Beginning logic. Thomas Nelson. ISBN 0-17-712040-1.
- Smullyan, Raymond Merrill (1995) [1968]. First-order logic. New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-68370-6.
- Suppes, Patrick Colonel (1999) [1957]. Introduction to logic. Mineola, New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-40687-9.
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Sequent calculus", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- A Brief Diversion: Sequent Calculus
- Interactive tutorial of the Sequent Calculus





















![\cfrac{\Gamma, A[t/x] \vdash \Delta}{\Gamma, \forall x A \vdash \Delta} \quad ({\forall}L)](../I/m/ffa19488c46c30e441ed785aba819bcc.png)
![\cfrac{\Gamma \vdash A[y/x], \Delta}{\Gamma \vdash \forall x A, \Delta} \quad ({\forall}R)](../I/m/af4b8d483397f2739cdc2d2ce4fec111.png)
![\cfrac{\Gamma, A[y/x] \vdash \Delta}{\Gamma, \exists x A \vdash \Delta} \quad ({\exists}L)](../I/m/6c3e182fbbf2115770b19b854406b39a.png)
![\cfrac{\Gamma \vdash A[t/x], \Delta}{\Gamma \vdash \exists x A, \Delta} \quad ({\exists}R)](../I/m/d514d041a0d43676e4fe3f662fbf479a.png)



























