Second Battle of Kehl (1796)
Coordinates: 48°34′N 7°49′E / 48.567°N 7.817°E
| Second Battle of Kehl | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of The French Revolutionary Wars | |||||||
 The Austrians initially pushed out the French defenders, but a strong counter-attack forced them to retreat, leaving the French in possession of the village and the important bridgeheads crossing the Rhine River. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 7,000[1] | 5,000[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 1,200 killed and wounded, 800 captured[1] | 2,000 killed, wounded and missing[1][2] | ||||||
The Second Battle of Kehl occurred on 18 September 1796, when General Franz Petrasch's Austrian and Imperial troops stormed the French-held bridgehead over the Rhine river. The village of Kehl, which is now in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, was then part of Baden-Durlach. Across the river, Strasbourg, an Alsatian city, was a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition.
In the 1790s, the Rhine was wild, unpredictable, and difficult to cross. Its channels and tributaries created islands of trees and vegetation that were alternately submerged by floods or exposed during the dry seasons. A complex of bridges, gates, fortifications and barrage dams linked Kehl with Strasbourg. These had been constructed by the fortress architect Sébastien le Préstre de Vauban in the seventeenth century. The crossings had been contested before: in 1678 during the French-Dutch war, in 1703 during the War of the Spanish Succession, in 1733 during the War of the Polish Succession, and earlier in Battle of Kehl, when the French crossed into the German states on 23–24 June. Critical to French success would be the army's ability to cross the Rhine at will. The crossings at Hüningen, near the Swiss city of Basel, and at Kehl, offered access to most of southwestern Germany; from there, French armies could sweep north, south, or east, depending on their military goal.
In late summer of 1796, the Austrian force, under the command of Archduke Charles, united with the autonomous corps[Note 1] of Wilhelm von Wartensleben and pushed the French out of most of southwestern Germany. By early September, the French were in retreat across the Black Forest. On 18 September 1796, the Austrians temporarily acquired control of the tête-du-ponts (bridgeheads) joining Kehl and Strasbourg until a strong French counter-attack forced them to retreat, leaving the French in control of the bridges but the Austrians in control of the territory surrounding them. The situation remained in status quo until late October. Control of the surrounding territory there prevented the French from crossing to safety in Strasbourg, and required the French commander, Jean Victor Marie Moreau, to withdraw toward Basel. Immediately after the Battle of Schliengen (24 October 1796), while most of Moreau's army retreated south to cross the Rhine at Hüningen, Count Baillet Latour moved his Austrian force to Kehl to begin a 100-day siege.
Background: general campaign of 1796
The campaign of 1796 was part of the larger, broader French Revolutionary Wars in which republican France pitted itself against a fluid coalition of Prussians and Austrians and several other states of the Holy Roman Empire, the British, Sardinians, Dutch, and royalist French emigres. Although initially the republican French experienced several victories, the campaigns of 1793 through 1795 had been less successful. However, the Coalition partners had difficulty coordinating their war aims, and their own efforts also faltered. In 1794 and 1795, French victories in northern Italy salvaged French enthusiasm for the war, and forced the Coalition to withdraw further into Central Europe. At the end of the Rhine Campaign of 1795, the Habsburg Austrian Coalition and the French Republican called a truce between their forces that had been fighting in Germany.[3] This agreement lasted until 20 May 1796, when the Austrians announced that the truce would end on 31 May.[4]
The Austrian Coalition's Army of the Lower Rhine included 90,000 troops. The 20,000-man right wing, first under Duke Ferdinand Frederick Augustus of Württemberg, then Wilhelm von Wartensleben, stood on the east bank of the Rhine behind the Sieg River, observing the French bridgehead at Düsseldorf. The garrisons of Mainz Fortress and Ehrenbreitstein Fortress included 10,000 more. The remainder of the Imperial and Coalition army, the 80,000-strong Army of the Upper Rhine, secured the west bank behind the Nahe River. Commanded by Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser, this force anchored its right wing in Kaiserslautern on the west bank while the left wing under Anton Sztáray, Michael von Fröhlich and Louis Joseph, Prince of Condé guarded the Rhine from Mannheim to Switzerland. The original Austrian strategy was to capture Trier and to use their position on the west bank to strike at each of the French armies in turn. After news arrived in Vienna of Napoleon Bonaparte's successes, however, Wurmser was sent to Italy with 25,000 reinforcements, and the Aulic Council gave Archduke Charles command over both Austrian armies and ordered him to hold his ground.[3]
On the French side, the 80,000-man Army of Sambre-et-Meuse held the west bank of the Rhine down to the Nahe and then southwest to Sankt Wendel. On the army's left flank, Jean Baptiste Kléber had 22,000 troops in an entrenched camp at Düsseldorf. The right wing of the Army of the Rhine and Moselle was positioned behind the Rhine from Hüningen northward, centered along the Queich River near Landau, and its left wing extended west toward Saarbrücken.[3] Pierre Marie Barthélemy Ferino led Moreau's right wing at Hüningen, Louis Desaix commanded the center and Laurent Gouvion Saint-Cyr directed the left wing. Ferino's wing consisted of three infantry and cavalry divisions under François Antoine Louis Bourcier and Henri François Delaborde. Desaix's command included three divisions led by Michel de Beaupuy, Antoine Guillaume Delmas and Charles Antoine Xaintrailles. Saint-Cyr's wing had two divisions commanded by Guillaume Philibert Duhesme and Alexandre Camille Taponier.[5]
The French plan called for a springtime (April-May-June) offensive during which the two armies would press against the flanks of the northern Coalition armies in the German states while a third army approached Vienna through Italy. Specifically, Jean-Baptiste Jourdan's army would push south from Düsseldorf, hopefully drawing troops and attention toward themselves, while Moreau's army massed on the east side of the Rhine by Mannheim. According to plan, Jourdan's army feinted toward Mannheim, and Charles repositioned his troops. Once this occurred, Moreau's army endured a forced march south and attacked the bridgehead at Kehl, which was guarded by 7,000 imperial troops—troops recruited that spring from the Swabian Circle polities, inexperienced and untrained—which held the bridgehead for several hours, but then retreated toward Rastatt. Moreau reinforced the bridgehead with his forward guard, and his troops poured into Baden unhindered. In the south, by Basel, Ferino's column moved quickly across the river and advanced up the Rhine along the Swiss and German shoreline toward Lake Constance, spreading into the southern end of the Black Forest. Worried that his supply lines would be overextended or his army would be flanked, Charles began a retreat to the east.[6]
At this point, in July, the jealousies and competition between the French generals came into play. Moreau could have joined up with Jourdan's army in the north, but did not; he proceeded eastward, pushing Charles into Bavaria, while Jourdan pushed eastward, pushing Wartensleben's autonomous corps into the Ernestine duchies.[7] On either side, the union of two armies—Wartensleben's with Charles' or Jourdan's with Moreau's—could have crushed their opposition.[8]
In August, Wartensleben and Charles united first, and turned the tide against the French. With 25,000 of his best troops, the archduke crossed to the north bank of the Danube at Regensburg and moved north to join his colleague. Once their forces were reunited, they pushed the French slowly to the east. The defeat of Jourdan's army at the battles of Amberg (24 August), Würzburg (3 September) and 2nd Altenkirchen (16–19 September) allowed Charles to move more troops to the south, and effectively removed Jourdan from the remainder of the campaign.[9]
Preliminary action at Bruchsal: September 1796
While Charles and Moreau jockeyed for position on the eastern slope of the Black Forest, Franz Petrasch engaged the French at Bruchsal. The troops there, commanded by Marc Amand Élisée Scherb, included the 68th Demi-brigade and two squadrons of the 19th Dragoons; they had remained behind after the Battle of Ettlingen to observe the garrisons of Mannheim and Philippsburg. Realizing that his command was too small to withstand a concerted attack by the stronger Austrians, Scherb withdrew toward Kehl to secure the Rhine crossing to Strasburg, since Moreau, now well into a retreat across the mountains, would need the crossing for a safe passage to France.[10]
An initial Austrian attack on the French position at Bruchsal favored the French, who charged the Austrians with bayonets. Again, on 5 and 6 September, the Austrians spent most of the day skirmishing with the French at their advanced posts, masking their intention of circling around Bruchsal and marching south to secure the crossing to Strasbourg. General Scherb received intelligence of a contingent of infantry and cavalry marching against him and retired south. Scherb found the Austrians already in possession of Untergrombach, a village south of Bruchsal. After he tried to force his way through, the Austrians fell back to Weingarten at 49°3′5″N 8°31′50″E / 49.05139°N 8.53056°E.[11] Scherb found himself caught between detachments of Austrians by the Kinzig river and behind him. General Moreau deployed a demi-brigade of infantry and a regiment of cavalry from his army in the Black Forest, with instructions to proceed by forced marches to Kehl, but General Petrasch, acting on his own intelligence, sent Konstantin d'Aspré with two battalions to occupy Renchen, about 10 miles (16 km) from Kehl. This effectively prevented Moreau's reinforcements from reaching Kehl and locked Scherb in place. The undermanned garrison at Kehl was on its own.[12]
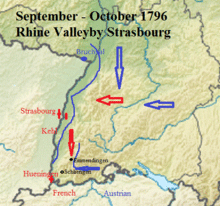
Kehl garrison status 16–17 September
The Kehl garrison consisted of one battalion of the 24th Demi-brigade and some detachments of the 104th under command of Balthazar Alexis Henri Schauenburg. This was too weak a force to defend a position of such importance, or to develop additional extensive works. Moreau reported that some of Scherb's troops had arrived, but it is unclear which ones. Furthermore, the lack of cooperation from local peasant workers and the exhaustion of troops prevented the enhancements of the fortifications from proceeding with any speed.[13] On the evening of 16 September, Petrasch and most of his column had arrived at Bischofsheim, immediately by Kehl, with three battalions and two squadrons; more troops were not far behind.[14] By 17 September, a small corps of Austrians approached the outskirts of Kehl and vigorously attacked the French sentries there; this was merely a prelude to the more significant action the following day.[13]
Action of 18 September

Before the break of dawn on 18 September (03:45), three Austrian columns attacked Kehl, while another kept Scherb pinned down by the Kinzig. The Austrian principal column, comprising the 38th Regiment, crossed the Kinzig river above the French position and proceeded toward the dykes of the Rhine above (south of) Kehl.[Note 2] This placed them between Scherb's force and Kehl.[15] Using the dykes as protection, and conducted by some peasants familiar with the fortifications, they advanced as far as the horn work on the Upper Rhine and entered a gorge which led them to the outskirts of Kehl.[16] The second column of the 38th Regiment, under command of Major Busch, proceeded via the hamlet of Sundheim toward Kehl, and obtained possession of the village itself, although not the bridge leading to Strasbourg. The third column, which included three companies of Serbians and a division of Hussars, executed a feint on the left bank of the river. One column of reserve, under the command of Franz Pongratz, approached as far as the French earthworks on the banks of the Rhine to support the columns ahead of him; another, which included a battalion of the 12th Regiment (Manfredini), moved past the hamlet by Neumuhl at 48°34′12″N 7°50′38″E / 48.57000°N 7.84389°E toward Kehl.[17]
Quickly, the Austrians acquired control of all the earthworks of the town, the village itself, and the fortress; their skirmishers reached one side of the abutment of an old bridge of palisades, and advanced to the other side, across the islands formed by branches of the Kinzig and the Rhine. There, almost within eye-shot of the French sentinels, they halted; there is some confusion about why they stopped. Possibly they mistook the abutment for the bridge itself, as Moreau seemed to think.[18] Regardless, the troops there did not burn the bridge, but started plundering and drinking.[19] The French cavalry tried to retire into Kehl via the Kinzig bridge, but the heavy Austrians fire destroyed most of them.[18]
The French executed several attempts to retake the bridges. The 68th, under command of general Jean-Baptiste de Sisce, was repulsed three times by the superior numbers of Austrians and the fearsome fire of case shot from four cannons that lined the principal road. Not until 19:00 did fortune favor the French, when Colonel d'Aspré[Note 3] and two hundred men of the Regiment Ferdinand were captured within the fort itself. The next in command, a Major Delas, was badly wounded, leaving no one in overall command of the 38th Regiment. The French general Schauenburg, who had gone to Strasbourg for troops, returned with some reinforcements, including part of the Strasbourg national guard, and led these troops over the pontoon bridges.[20] They met at once an impetuous Austrian attack,[21] but were sufficiently strong to recover. At 22:00, the Austrians still held the redoubt and the houses at the edge of the village; the arrival of a fresh battalion of the 12th Regiment led to a new attack, but it was repulsed. Ultimately, though, the Austrians had insufficient reserves to meet the fresh troops from Strasbourg. By 23:00, the French had recovered all of the Strasbourg suburbs, the village of Kehl and all of the French earthen works.[22]
According to Digby Smith and his sources, the Austrians lost 2,000 men killed, missing and wounded, and the French: 1,200 missing and captured.[23] German sources report, though, that the Austrians lost 1,500 men and 300 prisoners, and the French had 300 dead and 800 wounded.[20]
Impact of September action

Despite the limited success of Petrasch's action, the action had a broad impact on the movements of the main armies of Moreau and Archduke Charles, which still maneuvered to the east. Moreau's army would debouch through the Black Forest mountains, which lay to the east. By controlling the eastern access to the Kehl/Strasbourg crossing, Petrasch forced Moreau to march south; any retreat into France would have to occur via the bridges at Hüningen, a longer march, not at Kehl and Strasbourg. The next contact between the main armies occurred on 19 October at Emmendingen in the Elz valley, which winds through the Black Forest. The section of the valley involved in the battle runs south-west through the mountains from Elzach, through Bleibach and Waldkirch. Just to the south-west of Waldkirch, the river emerges from the mountains and flows north-west towards the Rhine, with the Black Forest to its right. This section of the river passes through Emmendingen before it reaches Riegel. Riegel sits in a narrow gap between the Black Forest and an isolated outcropping of volcanic hills known as the Kaiserstuhl.[9]
The Austrian and French armies met again at Schliengen on 24 October. Moreau had arrayed his force in a semi-circle on the heights, offering him a tactically superior position. Charles threw his army against both flanks; the French left flank fought stubbornly, but gave way under the pressure of Condé's emigre corps; the right flank withstood a day-long battering by Latour and Nauendorf, but eventually had to withdraw. The loss of access to the crossing at Kehl forced Moreau to withdraw south to Hüningen.[24]
With a strong rear guard provided by Generals Abbatucci and Lariboisière, he abandoned his position the same night and retreated part of the 9.7 miles (16 km) to Hüningen.[24] The right and left wings followed. By 3 November, he had reached Haltingen, where he organized his force to cross over the bridges into France. The Archduke then sent most of his army north to besiege Kehl.[25][26]
Orders of battle
The following troops participated in the action at Kehl.[27]
French
- 24th Demi-brigade de Ligne (one battalion)[Note 4]
- 68th Demi-brigade de Ligne (three battalions)
- 104th Demi-brigade de Ligne (remnants)
- 19th Dragoon Regiment (two squadrons)
Austrian
- Infantry Regiment Nr. 12 (three battalions)
- Infantry Regiment Nr. 15 (three battalions)
- Infantry Regiment Nr. 38 (elements)[Note 5]
Notes, citations and references
Notes
- ↑ An autonomous corps, in the Austrian or Imperial armies, was an armed force under command of an experienced field commander. They usually included two divisions, but probably not more than three, and functioned with high maneuverability and independent action, hence the name "autonomous corps." Some, called the Frei-Corps, or independent corps, were used as light infantry before the official formation of light infantry in the Habsburg Army in 1798. They provided the Army's skirmishing and scouting function; Frei-Corps were usually raised from the provinces. See Philip Haythornthwaite, Austrian Army of the Napoleonic Wars (1): Infantry. Osprey Publishing, 2012, p. 24. Military historians usually maintain that Napoleon solidified the use of the autonomous corps, armies that could function without a great deal of direction, scatter about the countryside, but reform again quickly for battle; this was actually a development that first emerged first in the French and Indian War in the Thirteen British Colonies and later in the American Revolutionary War, and became widely used in the European military as the size of armies grew in the 1790s and during the Napoleonic Wars. See David Gates, The Napoleonic Wars 1803–1815, New York, Random House, 2011, Chapter 6.
- ↑ Philippart uses both the regimental number and the name of its proprietor (38th and Ferdinand). His identification of the 12th Regiment (Manfredini) coincides with other sources: Lieutenant Field Marshal Federigo Manfredini was indeed colonel in chief (Proprietor) of the 12th line infantry regiment from 1792–1809. However, the 15th regiment's proprietor was Prince of Orange. See Stephen Millar Austrian infantry organization. Napoleon Series.org, April 2005. Accessed 21 Jan 2015.
- ↑ Luhe identifies the commander as Ocskay, but other sources place d'Aspré at the scene.
- ↑ The French Army designated two kinds of infantry: d'infanterie légère, or light infantry, to provide skirmishing cover for the troops that followed, principally d’infanterie de ligne, which fought in tight formations. Smith, p. 15.
- ↑ Philippart identifies the 38th Regiment as an active participant in this action, and later in the fighting at Kehl; Digby Smith identifies the participants as Regiment Nr. 12 and Regiment Nr. 15.
Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Digby Smith. Napoleonic Wars Data Book, NY: Greenhill Press, 1996, p. 125.
- ↑ See also John Philippart, Memoires etc. of General Moreau, London, A.J. Valpy, 1814, p. 279.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Theodore Ayrault Dodge, Warfare in the Age of Napoleon: The Revolutionary Wars Against the First Coalition in Northern Europe and the Italian Campaign, 1789–1797. Leonaur Ltd, 2011. pp. 286–287. See also Timothy Blanning, The French Revolutionary Wars, New York: Oxford University Press, 1996, ISBN 0-340-56911-5, pp. 41–59.
- ↑ Ramsay Weston Phipps,The Armies of the First French Republic: Volume II The Armées du Moselle, du Rhin, de Sambre-et-Meuse, de Rhin-et-Moselle Pickle Partners Publishing, 2011 reprint (original publication 1923–1933), p. 278.
- ↑ Digby Smith, Napoleonic Wars Data Book, Connecticut: Greenhill Press, 1996, p. 111.
- ↑ Dodge, p.290. See also (German) Charles, Archduke of Austria. Ausgewӓhlte Schriften weiland seiner Kaiserlichen Hoheit des Erzherzogs Carl von Österreich, Vienna: Braumüller, 1893–94, v. 2, pp. 72, 153–154.
- ↑ Dodge, pp. 292–293.
- ↑ Dodge, pp. 297.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 J. Rickard,Battle of Emmendingen, History of war.org. 17 February 2009, Accessed 18 November 2014.
- ↑ Philippart, pp. 66–68 and (German) Hans Eggert Willibald von der Lühe, Militair-Conversations-Lexikon:Kehl (Belagerung des Bruckenkopfes von 1796–1797), Volume 4. C. Brüggemann, 1834, pp. 259–260.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 66 and Charles, Feldzug 1796, Paris, 1796, p. 360.
- ↑ Lühe, p. 259.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Philippart, p. 69.
- ↑ Lühe, p. 260.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 73.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 71.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 72.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Philippart, p. 73.
- ↑ Phipps,II:368 and Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen, Grundsätze der Strategie: Erläutert durch die Darstellung des Feldzugs von 1796 in Deutschland, [Vienna], Strauss, 1819, p. 200.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Lühe, p. 260.
- ↑ Philippart, pp. 73–74.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 75.
- ↑ Smith, p. 125.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Thomas Graham, 1st Baron Lynedoch. The History of the Campaign of 1796 in Germany and Italy. London, (np) 1797, 18–22, 126.
- ↑ Philippart, p. 100.
- ↑ Smith, pp. 125, 131–133.
- ↑ Smith, 125.
References
- Alison, Archibald. History of Europe from the commencement of the French revolution to the restoration of the Bourbons, Volume 3. Edinburgh: W. Blackwood, 1847.
- Blanning, Timothy. The French Revolutionary Wars. New York: Oxford University Press, 1996. ISBN 978-0340569115
- Beevor, Antony. Berlin: The Downfall 1945. New York, Viking-Penguin Books, 2002. ISBN 0-670-88695-5
- Bodart, Gaston. Losses of Life in Modern Wars, Austria-Hungary. London, Clarendon Press, 1916. OCLC 1458451
- (German) Charles, Archduke of Austria (unattributed). Geschichte des Feldzuges von 1796 in Deutschland. France, 1796.
- (German) Charles, Archduke of Austria, Grundsätze der Strategie: Erläutert durch die Darstellung des Feldzugs von 1796 in Deutschland, [Vienna], Strauss, 1819
- Cuccia, Phillip. Napoleon in Italy: the sieges of Mantua, 1796–1799, Tulsa, University of Oklahoma Press, 2014.ISBN 978-0806144450
- (German) Ebert, Jens-Florian "Feldmarschall-Leutnant Fürst zu Fürstenberg," Die Österreichischen Generäle 1792–1815. Napoleon Online: Portal zu Epoch. Markus Stein, editor. Mannheim, Germany. 14 February 2010 version. Accessed 28 February 2010.
- Graham, Thomas, 1st Baron Lynedoch. The History of the Campaign of 1796 in Germany and Italy. London, (np) 1797.
- Knepper, Thomas P. The Rhine. Handbook for Environmental Chemistry Series, Part L. New York: Springer, 2006. ISBN 978-3540293934.
- (French) Lievyns, A., Jean Maurice Verdot, Pierre Bégat, Fastes de la Légion-d'honneur: biographie de tous les décorés accompagnée de l'histoire législative et réglementaire de l'ordre, Bureau de l'administration, 1844.
- (German) Lühe, Hans Eggert Willibald von der. Militär-Conversations-Lexikon:Kehl (Uberfall 1796) & (Belagerung des Bruckenkopfes von 1796–1797), Volume 4. C. Brüggemann, 1834.
- Malte-Brun, Conrad. Universal Geography, Or, a Description of All the Parts of the World, on a New Plan: Spain, Portugal, France, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Belgium, and Holland.. A. Black, 1831. OCLC 1171138
- Millar, Stephen. Austrian infantry organization. Napoleon Series.org, April 2005. Accessed 21 Jan 2015.
- Philippart, John. Memoires etc. of General Moreau. London, A. J. Valpy, 1814. OCLC 8721194
- Phipps, Ramsey Weston, The Armies of the First French Republic: Volume II The Armées du Moselle, du Rhin, de Sambre-et-Meuse, de Rhin-et-Moselle. Pickle Partners Publishing, 2011 reprint (original publication 1923–1933).
- Rickard, J (17 February 2009), Siege of Huningue, 26 October 1796 – 19 February 1797. History of war.org. Accessed 1 November 2014.
- Rickard, J. (17 February 2009), Battle of Emmendingen, History of war.org. Accessed 18 November 2014.
- Rogers, Clifford, et al. The Oxford Encyclopedia of Medieval Warfare and Military Technology. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 2010. ISBN 978-0195334036.
- Rotteck, Carl von. General History of the World, np: C. F. Stollmeyer, 1842. OCLC 653511
- Sellman, R. R. Castles and Fortresses. York (UK), Methuen, 1954. OCLC 12261230
- Smith, Digby. Napoleonic Wars Data Book, NY: Greenhill Press, 1996. ISBN 978-1853672767
- Vann, James Allen. The Swabian Kreis: Institutional Growth in the Holy Roman Empire 1648–1715. Vol. LII, Studies Presented to International Commission for the History of Representative and Parliamentary Institutions. Bruxelles, Les Éditions de la Librairie Encyclopédique, 1975. OCLC 2276157
- (German) Volk, Helmut. "Landschaftsgeschichte und Natürlichkeit der Baumarten in der Rheinaue." Waldschutzgebiete Baden-Württemberg, Band 10, pp. 159–167.
- Walker, Mack. German home towns: community, state, and general estate, 1648–1871. Ithaca, Cornell University Press, 1998. ISBN 0801406706