Saw set

Saw set is a term applied to various forms of a tool used in the tuning and sharpening of saw blades. The saw set is used to adjust the set, or distance the saw tooth is bent away from the saw blade.
Purpose

When the teeth of a saw are formed from the body, they are in line and the same thickness as the blade immediately behind them. A saw with this configuration is described as having 'no' or '0' set.
To prevent the body of the blade binding and for other enhancements to the cutting action, the teeth can be set (angled out) from the blade. Teeth can be set in several patterns: single-sided set, alternating set or a patterned set. Most Western and Asian handsaws use an alternating set, whereby a tooth is set the opposite direction from the preceding one. Specialized tools like veneer saws or flush-cut saws may be set only to one side. Some hacksaws and machine saw blades have patterned sets that may require specially designed saw sets to create.
See Saw and Sawfiler for more detailed information about set, kerf, and maintenance of saws.
A saw set makes the process of setting the teeth easier, more consistent or both.
Categories of saw set
Saw sets come in many forms: from improvised to intricate, specially designed mechanisms. The demand for a more capable saw set is clear, as from 1810 to 1925 almost 900 different saw sets were patented.[1] Saw sets can be categorized by the mechanical principle under which they operate.
Hammer

The essential components of this type of saw set are an anvil and a striking tool, often a hammer. These tools range from common blacksmith's equipment to specially designed and marketed saw sets.
This process could use any anvil with a suitable surface and any striking tool of appropriate size. The saw tooth to be set is angled over an edge of the anvil and struck in the direction the tooth is to be set.
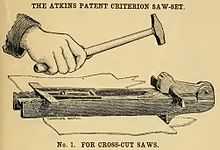
Hammering the teeth against an anvil is also used to remove set from the teeth either for maintenance or fresh setting.
Another form uses either a bevel-edged anvil or setting block so that the saw blade rests on a flat portion of the anvil and the tooth held over the bevel, to be struck until bent to the desired angle (Fig. A). Its use is described by the following:
"...lay the block, Fig. [A], in some convenient flat place and hold the tooth of saw so that the point projects over the beveled surface fully one-quarter of an inch. Give two or three strokes with a light hammer, striking the tooth always about one-quarter of an inch from the point. Regulate the set by the use of set gauge..."[2]
Following the same mechanics of operation, some designs introduced either a pin or lever aligned over the tooth that could be struck with a hammer. Rather than rely on the accuracy of the operator, such a device ensures only the portion of the saw under the pin is bent (Fig. B).
Lever and plate
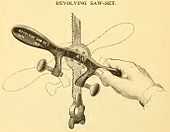
This type of saw set can be called lever, plate, wrest, spring or comb.[3][4] The plate that forms the body of the tool is fitted over the saw and levered perpendicular to the saw blade which springs or bends the tooth to an angle. The name comb likely refers to versions with many slots which bears resemblance to a comb for hair.
The simplest form of a lever saw set is a plate, usually of metal, thick enough to only fit over one tooth at a time and notched to a depth less than that of the tooth. To more easily create a consistent set, a stop of some form is added to the design ensuring the tool be levered to the same angle on each tooth. These stops (also, stop blocks) can be adjustable as in the case of the thumbscrews on the saw set in Fig. C.
One advantage of this design is that many lever saw sets can bend the tooth either direction. An alternating set can be made without turning the saw or saw set around as is generally necessary with Hammer or Pliers style saw sets.
Pliers

Regular pliers with small jaws could be used to set a tooth. Designers added to this to make pliers with a built in stop (Fig. D). The stop is usually adjustable and rests against the saw blade as the jaws bend the tooth. The goal of the stop is to make a consistent set and prevent tooth breakage. Depending on the style, the tooth is either gripped first in the jaws and then bent or the saw set is aligned to the tooth and the jaws closed.
Two-handled

Two-handled, or pistol-grip saw sets use the action of two handles closing to move cams or plungers. A pistol-grip style tool is most often what is thought of as a saw set in contemporary discussions of saw maintenance, especially amongst hand tool enthusiasts.[3]
The inventor Charles Morrill introduced a saw set with a plunger based on his patent.[5] This design, as well as improvements added to it, came into prolific use and in the United States are frequently found with woodworking tools. An image of a Morrill design saw set is found at the introduction of the article. The plunger (also, pin) pushes against the saw tooth when the handles are squeezed together. The other face of the saw tooth rests against an anvil and the whole saw blade is held at the desired angle to the anvil by a stop or rest. On most designs both the anvil and the rest are adjustable.
Another milestone was the introduction of the Taintor "positive" saw set. It utilizes a multi-position anvil and a special cam that clamps to the blade before the plunger pushes against the tooth. The cam was designed to prevent the saw set moving once aligned with a tooth.
Using the same mechanical design as the Morrill or Taintor saw sets, several manufacturers repositioned the handles to be held parallel to the blade, rather than perpendicular as with the original Morrill design. This is the form referred to as pistol-grip, due to its mild resemblance to the profile of a pistol. This form includes the 42 series from Stanley (X,W and 442), an E. C. Stearns design, as well as some contemporary saw sets.
Automated
Automated saw sets use machine automation rather than the user to move the setting mechanism between teeth. The mechanized nature should also apply the same pressure to each tooth.
Some of these machines were designed by manufacturers, such as US Pat. 29,772 and 47,806 by various members of the Disston family. Others were made for sharpening shops (either independent or a department of a company) to increase efficiency. Foley is known to have produced saw-setting machines targeted at saw sharpening shops.
References
- ↑ Friberg, Todd. Patent American Saw Sets. Osage Press.
- ↑ Disston & Sons, Henry (1902). Handbook for Lumbermen.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Fridberg, Todd (September 1995). "Collecting Saw Sets". The Tool Shed 88. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ↑ Conley, Mark. "What is a saw set?". The Saw Set Collector's Resource. Retrieved 25 July 2012.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 375,088
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Saw sets. |