Saveri
| Carnatic music |
|---|
| Concepts |
| Compositions |
| Instruments |
|
Saveri (pronounced sāvēri) is a Carnatic music ragam. This raga is a janya of the 15th Melakarta raga Mayamalavagowla. This raga brings out karuna rasa, i.e. it brings mood of pity.[1]
Structure and Lakshana
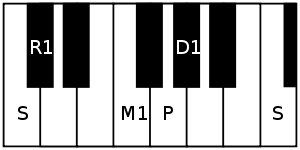
Ascending scale with Shadjam at C

Descending scale with Shadjam at C
This ragam is an Audava-Sampurna ragam (five notes in the ascending scale and seven notes in the descending scale).
The notes are shuddha rishabham, shuddha madhyamam and shuddha dhaivatam in ascending scale and kakali nishadam, shuddha dhaivatam, shuddha madhyamam, antara gandharam and shuddha rishabham in descent. The two swaras which give the raga such a characteristic are R (Rishabham) and D (Dhaivatham).
Select compositions
- Sarasuda, a varnam composed by Kotavasal Venkatarama Iyer, set to Adi tala
- Sankari Sankuru and Durusuga and Janani natajana composed by Shyama Sastri
- Bhavayaami Raghuraamam Anjaneya Raghuraamam Pari Pahi ganadipaha and Devi Pavane by Maharaja Swathi Thirunal
- Rama Bana and Daridapu leka – Adi Tala composed by Thyagaraja
- Kari Kalabha Mukham in Tisra Ekam composed by Muthuswamy Dikshitar
- Sri Rajagopala in Adi composed by Muthuswamy Dikshitar
- Velayya Daya composed by Koteeswara Iyer
- Murugu muruga by Periyasaamy Thooran
- Parakumadade by Purandaradasa
- janakasutha a Geetham
- amdukonavamma by Bhakta Gnanananda Teertha(Sri Ogirala Veera Raghava Sarma)
- Nee sevaku by Bhakta Gnanananda Teertha(Sri Ogirala Veera Raghava Sarma)
- Verri nammikato by Bhakta Gnanananda Teertha(Sri Ogirala Veera Raghava Sarma)
Related rāgams
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Scale similarities
- Karnataka Shuddha Saveri is a pentatonic scale which has a symmetric descending scale as the ascending scale, which is same as the ascending scale of Saveri, while Saveri has a sampurna descending scale. Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is S R1 G3 P D1 S : S D1 P G3 R1 S
- Malahari is a audava-shadava scale (5 notes in ascending and 6 in descending scale) that resembles Saveri.[2] Its ascending scale has shuddha madhyamam in place of antara gandharam, while the nishadham is dropped in descending scale. Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure is S R1 M1 P D1 S : S D1 P M1 G3 R1 S
References
- ↑ Ragas in Carnatic music by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications
- ↑ Raganidhi by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||