San Lazzaro degli Armeni
|
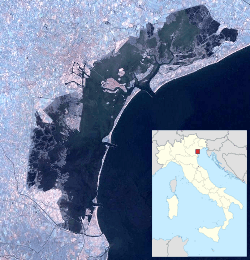
Aerial view of the island in 2013 | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 45°24′43″N 12°21′41″E / 45.411979°N 12.361422°ECoordinates: 45°24′43″N 12°21′41″E / 45.411979°N 12.361422°E |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Venetian Lagoon |
| Area | 30,000 m2 (320,000 sq ft)[1] |
| Country | |
| Region | Veneto |
| Province | Province of Venice |
| Commune | Venice |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 35 [2] |
| Ethnic groups | Armenians |
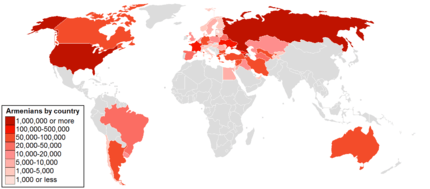
San Lazzaro degli Armeni (Italian pronunciation: [ˈsan laːdzarɔ deʎi armeni]; Venetian: San Làzaro dei Armeni, lit. "Saint Lazarus of the Armenians",[3][4] Armenian: Սուրբ Ղազար, Surb Ghazar)[lower-alpha 1] is a small island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy. It lies to the southeast of Venice and immediately west of the Lido.
A leper colony during the Middle Ages, since 1717[5] the island has been home to the Armenian Catholic Monastery of San Lazzaro.[lower-alpha 2] It is the headquarters of the Mechitarist Order and, as such, one of the world's prominent centers of Armenian culture[7] and Armenian studies.[8]
From 1789 until the early 20th century it was a major center of Armenian printing. The island is one of the best known historic sites of the Armenian diaspora.[9] The monastery has a large collection of books, journals, artifacts and the third largest collection of Armenian manuscripts.
History
Middle Ages
In 810 the Republic of Venice allocated the island to the abbot of the Benedictine Monastery of St. Ilario of Fusina.[10] In 1182 a leper colony (hospital for people with leprosy) was established at the island.[10] It was chosen for a leper colony since the island is relatively far away from the principal islands forming the city of Venice. It received its name from St. Lazarus, the patron saint of lepers.[11] In 1348 the leper colony was renovated and a church dedicated to San Lazzaro was built.[10] The hospital was moved to Venice in 1595 and the island was gradually abandoned.[12] In the 17th century the island was leased to various religious groups.[12] By the early 18th century only a "few crumbling ruins" remained in the isle.[11]
Armenian period
18th-19th centuries


In 1701 Mkhitar Sebastatsi (Mechitar or Mekhitar), an Armenian Catholic monk, founded a Catholic order in Constantinople that would later be called after him.[13] The order moved to Modon (Methoni) in Peloponnese in 1703,[14] after repressions by the Ottoman government and the Armenian Apostolic Church. In 1711 the order received recognition by Pope Clement XI.[13] In April 1715, a group of twelve Armenian Catholic monks led by Mkhitar Sebastatsi arrived in Venice from Morea (Peloponnese), following its invasion by the Ottoman Empire.[15] The Venetian Admiral Mocenigo and Governor of Morea, Angelo Emo "sympathizing deeply with the fearful distress of the unfortunate community, yielded to their earnest entreaties for permission to embark on a government vessels which was about to leave for Venice."[14]
On September 8, 1717, the Venetian Senate ceded the island of St. Lazarus to the Mechitarist order. "The Armenian Monks at once hastened to occupy the ruins on the Island... and the Abbot ordered the most necessary repairs to be at once made on the crumbling and dilapidated buildings which still remained."[16] The Armenian monks were required not to rename the island.[12] Upon acquisition the construction of a two-storey Armenian monastery began. The preexisting church of St. Lazarus was renovated. Gardens, residency buildings, a seminary and other structures were constructed.[12] The construction of the monastery was completed by 1740.[17] Mkhitar Sebastatsi died in 1749[18] and was succeeded by Stepanos Melkonian of Constantinople whose tenure as abbot ended 1799.[19]
The Venetian Republic was disestablished by Napoleon in 1797, however, the Mechitarist congregation was "left in peace",[20] allegedly because of the "presence of an indispensable Armenian official in Naopleon's secretariat."[21] In 1810 Napoleon signed a decree, which declared the congregation may continue to exist as an "Academy of learning".[19]
The island has been enlarged several times. In 1815 by the permission of the Austrian Empire the island's size doubled from around 7,200 m2 (77,500 sq ft) to 14,400 m2 (155,000 sq ft).[12]
During the 1848 revolutions in the Italian states a small garrison was stationed at the island.[22]
William Dean Howells described the island and the monastery in 1866 as follows: "As a seat of learning, San Lazzaro is famed throughout the Armenian world, and gathers under its roofs the best scholars and poets of that nation. In the press of the convent books are printed in some thirty different languages; and a number of the fathers employ themselves constantly in works of transition."[23]

20th century and beyond
The island was enlarged twice in the first half of the twentieth century. First, in 1912 the old canal was filled in and the shoreline was straightened. Following the Second World War, between 1947 and 1949 significant land was reclaimed in the southeastern and southwestern sides of the island. Furthermore, a wall was built around the shore. A fire broke out in 1975, which partially destroyed the library and damaged the church, and destroyed two Gaspare Diziani paintings. Between 2002 and 2004, an extensive restoration of the monastery's structures was carried out by the funding of the Italian government.[10]
Currently, over thirty people reside at the island, including monks, seminarians and students.[2][24][25] The island may be reached by a vaporetto from the San Zaccaria station. There is one guided tour a day, starting at around 3:30 pm.[26] There are tours in several different languages.[24][25]
The monastery


The island currently contains a church with a neo-Gothic interior, a tall onion-shaped campanile (bell tower), residential quarters, library, museum, picture gallery, manuscript repository, printing plant, and sundry teaching and research facilities.[13] The gardens of the monastery have been admired by many visitors.[27][28][29][30] An Armenian Genocide memorial was erected in the 1960s.[31]
Collections
The monastery library has over 150,000 printed books and periodicals,[32] 3,000[33]–4,000 Armenian manuscripts,[24][25][34] Oriental artifacts,[35] and an Egyptian mummy.[25][32] The Egyptian mummy is attributed to Namenkhet Amun, a priest at the Amon Temple in Karnak, Egypt. It was sent to San Lazzaro in 1825 by Boghos Bey Yusufian, an Egyptian minister of Armenian origin. Radiocarbon dating revealed that it dates to 450-430 BC (Late Period of ancient Egypt).[36]
San Lazzaro holds the third largest[30][33] collection of Armenian manuscripts after Matenadaran in Yerevan, Armenia (11,000 in the strict sense[33] to 17,000 in total)[37] and the Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem (3,890).[33] According to a contemporaneous source, in 1836, the library had 10,000 books and 400 (mostly Armenian) manuscripts.[38] The earliest manuscripts preserved at the library of manuscripts at San Lazzaro date to the eighth century.[39][34] The library holds one of the ten[40] extant copies of Urbatagirk, the first-ever Armenian book printed by Hakob Meghapart in Venice in 1512.[41] The monastery also preserves 44 Armenian prayer scrolls (hmayil).[42] In the mid-19th century an English publication wrote that "the convent may be regarded as a species of metropolis of Armenian literature."[43] The ceiling of the library of manuscripts was painted by Giovanni Battista Tiepolo.[39]
Publishing house
A publishing house was established at the monastery in 1789. In the early 19th century, a number of important publications were made on the island,[44] including a seminal two-volume dictionary of Classical Armenian (Նոր Բառգիրք Հայկազեան Լեզուի, 1836-7), which remains "unsurpassed".[44] Beginning in 1800 a periodical journal has been published at the island. Bazmavep, established in 1843, continues to be published to this day. The printing press at San Lazzaro is the oldest continuously operating Armenian publishing house in the world.[45]
Significance
The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church calls the convent of San Lazzaro and the order of the Mechitarists "especially remarkable" of the religious orders based in Venice.[46] San Lazzaro is "one of the Armenian diaspora's richest enclaves of culture".[47] It has sometimes been called "little Armenia"[48][49] (including by Catholicos Karekin II).[50] The New York Times wrote in 1919: "For more than two centuries this island has been an Armenian oasis transplanted to the Venetian lagoon."[51] Mary M. Tarzian suggests that Armenian nationalism among Armenians in the Ottoman Empire emerged from the educational vision of the Mechitarists in San Lazzaro.[52] Charles Yriarte wrote in 1877 that the Armenians "look with justice upon the island of San Lazzaro as the torch which shall one day illuminate Armenia, when the hour comes for her to live again in history and to take her place once more among free nations."[53]
According to Robert H. Hewsen the monastery of San lazzaro "for a full century was the only center of intensive Armenian cultural activity that the Armenians possessed" and until the establishment of the Lazarev Institute in Moscow in 1815 "the heritage of the Armenian people lay almost entirely in the hands of the Mekhitarists" in San Lazzaro.[54]
The prominent Armenian poet Hovhannes Shiraz wrote a poem about the island:[55]
| Օտար ջրերում հայացեալ Կղզի Հայոց հին լույսն է քեզնով նորանում... Հայրենիքից դուրս՝ հայրենեաց համար: |
An Armenian island in the foreign waters, You rekindle the old light of Armenia... Outside the homeland, for the sake of the homeland. |
Rose jam
The Mechitarist monks at San Lazzaro are known for making jam from rose petal around May, when the roses are in full bloom. Besides rose petal, it contains white caster sugar, water, and lemon juice.[56] It is called Vartanush[57][58] (Western Armenian pronunciation of վարդանուշ, vardanush literally translating to "sweet rose"; also a female given name). Around five thousand jars of jam are made and sold in the gift shop in the island. Monks also eat it for breakfast.[59]
Notable residents and students
- Mkhitar Sebastatsi (Mekhitar or Mechitar), the founder of the Mechitarist Order lived in the island from 1717 until his death in 1749.
- Mikayel Chamchian, Armenian historian
- Arpiar Arpiarian, Armenian writer
- Gabriel Aivazovsky, Armenian Archbishop, scientist, historian
- Pietro Kuciukian, Italian Armenian surgeon and writer
- Ohannés Gurekian, Armenian architect, engineer, and alpinist
- Kurken Alemshah, Armenian composer and conductor
- Mihran Damadian, Armenian freedom fighter, political activist, writer and teacher
- Daniel Varoujan, Armenian poet
- Ariel Agemian, Armenian painter
- Edgar Manas, Armenian composer, conductor and musicologist
- Tovmas Terzian, Armenian poet and playwright
- Yervand Lalayan, Armenian ethnographer, archaeologist, folklorist. He worked at the island for around six months in 1894.[60]
- Ghevont Alishan, a prominent historian, was a member of the Mechitarist Order since 1838. In 1849-51 he edited the journal Bazmavep and taught at the monastic seminary in 1866-72.[61] He lived in the island permanently from 1872 until his death in 1901.[62]
Notable visitors
.jpg)
- Pope Pius VII (May 9, 1800)[19]
- Lord Byron, a prominent English Romantic poet, lived in the island from late 1816 to early 1817. He signed his name in a book first time on November 27, 1816.[63] By early 1817 Byron had acquired enough Armenian to translate passages from Classical Armenian into English.[64] He co-authored English Grammar and Armenian in 1817, and Armenian Grammar and English in 1819, where he included quotations from classical and modern Armenian.[65] Byron is considered the most prominent of all visitors of the island.[32] The room where Byron studied now bears his name and is cherished by the monks.[29][32] There is also a plaque commemorating Byron's visit.[30][66]
- Julius Heinrich Petermann, German orientalist (1833)[12]
- Friedrich Windischmann, German orientalist (1833)[67]
- Alfred de Musset, French writer (1834)[68]
- George Sand, French novelist (July 1834)[69]
- Ivan Aivazovsky, Russian-Armenian painter (1840). He met his older brother, Gabriel, who was working at the monastery at that time. At the monastery library and the art gallery, Aivazovsky familiarized himself with Armenian manuscripts and Armenian art in general.[70]
- John Ruskin, British art critic (early 1850s)[71]
- Richard Wagner, German composer (1859)[72]
- Vardges Sureniants, Armenian painter (1881)[73]
- Eleonora Duse, Italian actress (1886)[12]
- Komitas, Armenian musicologist (July 1907). He lectured on Armenian folk and sacred music and researched the Armenian music notation (khaz) system in the monastery library.[47]
- Yeghishe Charents, Armenian poet (1924)[74]
- Avetik Isahakyan, Armenian writer (1924)[74]
- Aram Khachaturian, Soviet Armenian composer (1963)[75]
- Victor Ambartsumian, Soviet Armenian astrophysicist (1969)[76]
- Robert Kocharyan, 2nd President of Armenia (2005)[77]
- Prince Charles Philippe, Duke of Anjou (2005)[78]
- Karekin II, Catholicos of All Armenians (2008)[79]
- Serzh Sargsyan, 3rd President of Armenia (2011)[80]
Cultural depictions
Numerous artists have painted the island. Among them Gevorg Bashinjaghian (1892),[81] Ivan Aivazovsky (1899),[82] Joseph Pennell (1905),[83] Hovhannes Zardaryan (1958).[84]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to San Lazzaro degli Armeni (Venice). |
References
- Notes
- ↑ Also romanized Surb Łazar. Usually referred to as Վենետիկի Սուրբ Ղազար կղզի, Venetiki Surb Ghazar kghzi, Western Armenian: Venedigi Surp Ghazar gghzi which literally translates to "Saint Lazarus island of Venice".
- ↑ Armenian: Մխիթարեան Մայրավանք Սուրբ Ղազար, Mkhitarian Mayravank' Surb Ghazar; Italian: Monastero Mechitarista di San Lazzaro degli Armeni[6]
- Citations
- ↑ "Venezia - Ponte con l'Oriente. Venezia visitare.". ciaocacao.it (in Italian).
A pochi chilometri da Venezia si trova l'isola di San Lazzaro degli armeni, dove anche ai nostri giorni, si trova un seminario funzionante armeno. Da diversi secoli l'isola e' di proprieta' della chiesa armena ed ha la superficie di 30.000 mq.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Imboden, Durant. "San Lazzaro degli Armeni". Europe for Visitors. Archived from the original on 24 May 2014.
Its residents include 10 monks, 10 seminarians, and 15 Armenian students...
- ↑ Valcanover, Francesco (1965). "Collection of the Armenian Mekhitarist Fathers, Island of St. Lazarus of the Armenians". Museums and Galleries of Venice. Milan: Moneta Editore. p. 149.
- ↑ "Island of Saint Lazarus of the Armenians". Michelin Guide.
- ↑ Doody, Margaret (2007). Tropic of Venice. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 272. ISBN 978-0-8122-3984-3.
- ↑ "Monastero Mechitarista di San Lazzaro degli Armeni". veneziasi.it (in Italian).
- ↑ Murphy, Christopher (2011). Shadows of Forever: The Annals of Forever. Trafford Publishing. p. 311. ISBN 9781426946011.
...had transformed San Lazzaro into a world-renowned center of Armenian culture and learning.
- ↑ Dursteler, Eric R. (2013). A Companion to Venetian History, 1400-1797. BRILL. p. 459. ISBN 9004252517.
...the island of San Lazzaro on which he established a monastery that became a center for Armenian studies and led to a revival of Armenian consciousness.
- ↑ Bakalian, Anny (1993). Armenian Americans: From Being to Feeling Armenian. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers. pp. 345–346. ISBN 1-56000-025-2.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Bambakian, Vartuhi. "The Island of San Lazzaro". mechitar.com. The Armenian Mekhitarist Congregation. Archived from the original on 21 January 2015.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Langlois 1874, pp. 12-13.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 "Սուրբ Ղազար [Surb Ghazar]". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia Volume 11 (in Armenian). Yerevan: Armenian Encyclopedia. 1985. pp. 203–204.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Adalian, Rouben Paul (2010). Historical Dictionary of Armenia. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press. pp. 426–427. ISBN 978-0-8108-7450-3.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Langlois 1874, p. 20.
- ↑ Langlois 1874, p. 13.
- ↑ Langlois 1874, p. 21.
- ↑ Langlois 1874, p. 23.
- ↑ Langlois 1874, p. 24.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 "From the Fall of the Venetian Republic to the Napoleonic Decree Recognizing the Congregation". mechitar.com. The Armenian Mekhitarist Congregation. Archived from the original on 27 February 2015.
- ↑ von Voss, Huberta, ed. (2007). Portraits of Hope: Armenians in the Contemporary World (1st English ed.). New York: Berghahn Books. p. 137. ISBN 9781845452575.
- ↑ Buckley, Jonathan (2010). The Rough Guide to Venice & the Veneto (8th ed.). London: Rough Guides. p. 226. ISBN 9781848368705.
- ↑ Keates, Jonathan (2005). The Siege Of Venice. Chatto & Windus. p. 411.
- ↑ Howells, William Dean (1907) [1866]. Venetian Life. Boston and New York: Houghton, Mifflin & Company. p. 180.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 "The Island of San Lazzaro degli Armeni where the roses are red…and sweet". The Venice Times. 4 January 2014.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 Toth, Susan Allen (19 April 1998). "Hidden Venice". Los Angeles Times. p. 3.
- ↑ Belford, Ros; Dunford, Martin; Woolfrey, Celia (2003). Italy. Rough Guides. p. 332.
- ↑ Robertson, Alexander (1905). The Roman Catholic Church in Italy. Morgan and Scott. p. 186.
The island, too, with its flower and fruit gardens, is so well kept that an excursion to San Lazzaro is a favourite one with all visitors to Venice.
- ↑ Macfarlane, Charles (1830). The Armenians: A Tale of Constantinople, Volume 1. Philadelphia: Carey and Lea. p. 254.
San Lazaro is about the middle size, and adorned with a pretty garden...
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Garrett, Martin (2001). Venice: A Cultural and Literary Companion. New York: Interlink Books. p. 166.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 Carswell, John (2001). Kahn, Robert, ed. Florence, Venice & the Towns of Italy. New York Review of Books. p. 143.
- ↑ "Memorial on Saint Lazarus Island, Venice, Italy". Armenian National Institute.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 Saryan, Levon A. (July–August 2011). "A Visit to San Lazzaro: An Armenian Island in the Heart of Europe Part I, Part II, Part III". Armenian Weekly.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 Coulie, Bernard (2014). "Collections and Catalogues of Armenian Manuscripts". In Calzolari, Valentina. Armenian Philology in the Modern Era: From Manuscript to Digital Text. Brill Publishers. pp. 23–26. ISBN 9789004259942.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 Fodor's Venice & the Venetian Arc. Fodor's Travel Publications. 2006. p. 68.
- ↑ "Guided visits to Isola di San Lazzaro degli Armeni". Città di Venezia.
- ↑ Huchet, Jean-Bernard (2010). "Archaeoentomological study of the insect remains found within the mummy of Namenkhet Amun (San Lazzaro Armenian Monastery, Venice/Italy)" (PDF). Advances in Egyptology (Armenian Egyptology Centre) (1): 59–80.
- ↑ "Mesrop Mashtots Matenadaran". armenianheritage.org. Armenian Monuments Awareness Project.
- ↑ Valery, M. (1836). "Italy and the Italians". The Foreign Quarterly Review (London: Adolphus Richter & Co.) 13 (32): 269.
The island of San Lazzaro, inhabited by the Armenian monks, and which is at the same time a monastery, a college, a library, and a printing establishment, deserves especial notice. The library contains 10,000 volumes, and 400 MSS. chiefly Armenian.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Mesrobian 1973, p. 33.
- ↑ Trvnats, Anush (28 April 2012). "Թուեր Եւ Փաստեր` Հայ Գրատպութեան Պատմութիւնից". Aztag (in Armenian).
«Ուրբաթագրքի» առաջին հրատարակութիւնից աշխարհում պահպանուել է 10 օրինակ
- ↑ Yapoudjian, Hagop (14 October 2013). "Մտորումներ Սուրբ Ղազար Այցելութեան Մը Առիթով". Aztag (in Armenian).
- ↑ Ghazaryan, Davit (2014). "Կիպրիանոս հայրապետը և Հուստիանե կույսը 15-16-րդ դարերի ժապավենաձև հմայիլների գեղարվեստական հարդարանքում" (PDF). Banber Matenadarani (in Armenian): 244.
- ↑ Venice: Past and Present. London: Religious Tract Society. 1853. p. 168.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Mathews, Jr., Edward G. (2000). "Armenia". In Johnston, Will M. Encyclopedia of Monasticism: A-L. Chicago and London: Fitzroy Dearborn. pp. 86–87.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, the monastery in Venice produced hundreds of editions of Armenian texts, a number of important studies, and a dictionary of classical Armenian that is still unsurpassed.
- ↑ Mouradyan, Anahit (2012). "Հայ տպագրության 500-ամյակը [The 500th Anniversary of the Armenian Book-Printing]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (1): 58–59.
- ↑ Cross, F. L.; Livingstone, E. A., eds. (2005). "Venice". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (3 rev. ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 1699. ISBN 9780192802903.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 Soulahian Kuyumjian, Rita (2001). Archeology of Madness: Komitas, Portrait of an Armenian Icon. Princeton, New Jersey: Gomidas Institute. p. 59. ISBN 1-903656-10-9.
- ↑ "5th Annual Conference of the Forum of Armenian Associations of Europe Venice, Italy". faaeurope.ofirme.sk. Forum of Armenian Associations of Europe. 6–9 June 2003.
The city, which covers more than 200 islands, has a little Armenia in it; Armenian cultural and educational center Saint Ghazar
- ↑ Hamalian, Leo (1980). As others see us: the Armenian image in literature. New York: Ararat Press. p. 71.
...the Abbot Peter Mekhitar, who founded "a little Armenia with Venetian overtones...
- ↑ "Ն.Ս.Օ.Տ.Տ. Գարեգին Բ Ամենայն Հայոց Կաթողիկոսի խոսքը Մխիթարյան միաբանությանը Սուրբ Ղազար կղզում" (PDF). Etchmiadzin (in Armenian) (Mother See of Holy Etchmiadzin) (5): 28. May 2008.
Սուրբ Ղազարը Հայաստանից հազարավոր կիլոմետրեր հեռու մի փոքր Հայաստան է
- ↑ The New York Times Current History: The European war, Volume 19 (April−May−June 1919). New York: The New York Times Company. p. 72.
- ↑ Terzian, Shelley (2014). "Central effects of religious education in Armenia from Ancient Times to Post-Soviet Armenia". In Wolhuter, Charl; de Wet, Corene. International Comparative Perspectives on Religion and Education. SUN MeDIA. p. 37.
- ↑ Yriarte 1880, p. 302.
- ↑ Hewsen, Robert H. (2001). Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 12, 158. ISBN 0-226-33228-4.
- ↑ "Հայերն Իտալիայում [Armenians in Italy]". italy.mfa.am (in Armenian). Embassy of Armenia to Italy.
- ↑ Davies, Emiko (10 May 2011). "Rose petal Jam from a Venetian monastery". emikodavies.com.
- ↑ "Maggio: le rose". la Repubblica (in Italian). 11 May 2012.
Mentre di origine armena è la “vartanush”, la marmellata di rose che in Italia viene prodotta a Venezia, nell’Isola di San Lazzaro degli Armeni dai monaci Mechitaristi.
- ↑ "Isola di San Lazzaro degli Armeni" (in Italian). Italian Botanical Heritage.
Una tecnica secolare ne imprigiona i profumi nella Vartanush, la marmellata di petali di rose che, tradizionalmente, vengono colti al sorgere del sole.
- ↑ Gora, Sasha (8 March 2013). "San Lazzaro degli Armeni – Where Monks Make Rose Petal Jam in Venice, Italy". Honest Cooking.
- ↑ Melik-Pashayan, K. (1978). "Լալայան Երվանդ [Lalayan Yervand]". Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia Volume 4 (in Armenian). p. 475.
- ↑ Asmarian, H. A. (2003). "Ղևոնդ Ալիշանի ճանապարհորդական նոթերից [From Ghevond Alishan’s travel notes]". Lraber Hasarakakan Gitutyunneri (in Armenian) (2): 127.
- ↑ Shtikian, S. A. (1970). "Ղևոնդ Ալիշան [Ghevond Alishan]". Patma-Banasirakan Handes (in Armenian) (2): 13.
- ↑ Mesrobian 1973, p. 27.
- ↑ Mesrobian 1973, p. 31.
- ↑ Elze, Karl (1872). Lord Byron, a biography, with a critical essay on his place in literature. London: J. Murray. pp. 217–218.
- ↑ Vangelista, Massimo (4 September 2013). "Lord Byron in the Armenian Monastery in Venice". byronico.com.
- ↑ Schmitt-Garibian, Wolfgang (October 2014). "The Armenian Holdings of the Bavarian State Library" (UNPUBLISHED). Third International Conference of Armenian Libraries: 3.
- ↑ de Musset, Alfred (1867). Oeuvres, Volume 7 (in French). Paris: Charpentier. p. 246.
Après le repas, ils montaient en gondole, et s'en allaient voguer autour de l'île des Arméniens...
- ↑ Sand, George (1844). "Venise, juillet 1834.". Œuvres de George Sand: Un hiver au midi de l'Europe (in French). Paris: Perrotin. p. 95.
Nous arrivâmes à l'île de Saint-Lazare, où nous avions une visite à faire aux moines arméniens.
- ↑ Khachatrian, Shahen. ""Поэт моря" ["The Sea Poet"]" (in Russian). Center of Spiritual Culture, Leading and National Research Samara State Aerospace University.
- ↑ Cook, Edward Tyas (1912). Homes and Haunts of John Ruskin. New York: Macmillan. pp. 111–112.
- ↑ Barker, John W. (2008). Wagner and Venice. University of Rochester Press. p. 111. ISBN 9781580462884.
- ↑ Adamyan, A. (2012), Վարդգես Սուրենյանց [Vardges Sureniants] (PDF) (in Armenian), National Library of Armenia, p. 7
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 "Իսահակյանի և Չարենցի առաջին հանդիպումը Վենետիկում". magaghat.am (in Armenian).
Մեծատաղանդ բանաստեղծ Եղիշե Չարենցին առաջին անգամ տեսա Վենետիկում, 1924 թվականին: [...] Գնում էինք ծովափ, հետո գնում էինք Մխիթարյանների վանքը` Սուրբ Ղազար:
- ↑ "Ֆոտոալբոմ [Photo gallery]". akhic.am (in Armenian). Aram Khachaturian International Competition.
Ա.Խաչատրյանը Մխիթարյան միաբանությունում Սուրբ Ղազար կղզի 1963
- ↑ Rosino, Leonida (1988). "Encounters with Victor Ambartsumian one afternoon at the San Lazzaro Degli Armeni island at Venice". Astrophysics 29 (1): 412–414. doi:10.1007/BF01005854.
- ↑ ՀՀ նախագահ Ռոբերտ Քոչարյանը պաշտոնական այցով կմեկնի Իտալիա (in Armenian). Armenpress. 25 January 2005.
- ↑ "Island of San Lazzaro degli Armeni, Venice". oslj.org.uk. Order of Saint Lazarus of Jerusalem. 11 March 2011.
- ↑ "Catholicos Concludes Vatican Visit". Asbarez. 13 May 2008.
- ↑ "President Serzh Sargsyan visited the Mkhitarian Congregation at the St. Lazarus Island in Venice". president.am (Office to the President of the Republic of Armenia). 14 December 2011.
- ↑ "Սբ. Ղազար կղզին գիշերով (1892)" (in Armenian). National Gallery of Armenia.
- ↑ "Բայրոնի այցը Մխիթարյաններին Սբ. Ղազար կղզում (1899)" (in Armenian). National Gallery of Armenia.
- ↑ Pennell, Joseph. "The Armenian convent". Library of Congress.
- ↑ "Սբ Ղազարի կղզին. Վենետիկ (1958)" (in Armenian). National Gallery of Armenia.
Bibliography
- Langlois, Victor (1874). The Armenian Monastery of St. Lazarus-Venice. Venice: Typography of St. Lazarus.
- Mesrobian, Arpena (1973). "Lord Byron at the Armenian Monastery on San Lazzaro". The Courier (Syracuse University) 11 (1): 27–37.
- Yriarte, Charles (1880) [1877]. Venice: its history, art, industries and modern life [Venise: l'histoire, l'art, l'industrie, la ville et la vie]. Sitwell, F. J. (translator). New York: Scribner and Welford. pp. 301–306.
- Issaverdenz, James (1890). The Island of San Lazzaro, Or, The Armenian Monastery Near Venice. Armenian typography of San Lazzaro.
- Gordan, Lucy (February 2012). "The Venetian Island of St. Lazarus: Where Armenian Culture Survived the Diaspora". Inside the Vatican: 38–40. PDF version
Further reading
- Maguolo, Michela; Bandera, Massimiliano (1999). San Lazzaro degli Armeni: l'isola, il monastero, il restauro (in Italian). Venezia: Marsilio. ISBN 9788831774222. OCLC 247889977.
- Bolton, Claire (1982). A visit to San Lazzaro. Oxford, England: Alembic Press. OCLC 46689623.
- Richardson, Nigel (13 February 2011). "Oasis in the bedlam of Venice". The Times (London).
- Hacikyan, Agop Jack; Basmajian, Gabriel; Franchuk, Edward S.; Ouzounian, Nourhan (2005). The Heritage of Armenian Literature: From the eighteenth century to modern times. Detroit: Wayne State University Press. pp. 50–55. ISBN 9780814332214.
- Pasquin Valery, Antoine Claude (1839) [1838]. Historical, literary, and artistical travels in Italy, a completer and methodical guide for travellers and artists [Voyage en Italie, guide du voyageur et de l'artiste]. Paris: Baudry. pp. 191–192.
- Fell, Cicely (31 December 2014). "Out of Armenia, Venice". BBC Radio 4.
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

.jpg)