Salar de Arizaro
 The dry lakebeds and yardangs in Salar de Arizaro, imaged by NASA's Earth Observing-1 satellite. In the upper left corner, small rounded bumps in the landscape are yardangs, dusty hills formed when soft rocks are weathered and abraded by winds. The yardangs are aligned precisely with the northwesterly winds. On the right, bulbous hills have sharps edges, a formation typical of salt weathering around the base. During salt weathering, rocks are eroded by repeated salt crystal growth. The eroded material has been blown away by the strong winds of the high desert, leaving the sharp edge.[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
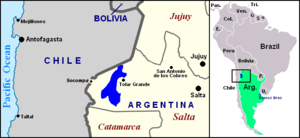
Salar de Arizaro is a large salt flat of the Andes in north-western Argentina, bordering with Chile. It is located between the villages of Tolar Grande and Caipe and near Mina La Casualidad,[1] in Los Andes Department, Salta Province.
Overview
.jpg)
Located in the central-western area of the Puna de Atacama, it covers an area of 1,600 km².[3] Per extension, the Salar de Arizaro is the 6th largest salt flat in the World and the 2nd largest in Argentina after the Salinas Grandes.[4][5]
The salar area is mined for metallic and non-metallic resources, as is it rich in salt, marble, iron, copper and onyx.[6]
The nearest salt flats are the ones of Antofalla, Hombre Muerto (both in north of Catamarca Province), Pocitos (in the east) and the Salinas Grandes of Jujuy and Salta provinces.
The Salar de Arizaro is crossed in the middle by the Salta–Antofagasta railway and by the Provincial Route 27[1] (part of the former RN 59). A particular characteristic of it is a conical hill named Cerro Cono (or Cono de Arita),[7] a sandstone-formation.[8]
Gallery
-

Cono de Arita
-
.jpg)
Cono de Arita
See also
Literature
- Gonzalo Monterroso: Touring Argentina - Salta. 1999, ISBN 9879821645
- R. N. Alonso, J. G. Viramonte: Geología y Metalogenia de la Puna. Estudios geol. 43:393-407 (1987)
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 (Spanish) An article about the Salar de Arizaro
- ↑ Salar de Arizaro at NASA Earth Observatory
- ↑ (Spanish) SEGEMAR (Sistema Geológico Minero Argentino) “Sales”. Publicación técnica SEGEMAR – UNSAM Nº 9 – Diciembre 2003 – ISSN 0329-5230 – Dic. 2003.
- ↑ (Spanish) List of greatest Salares at es.wp
- ↑ Salar de Arizaro at mindat.org
- ↑ Salar de Arizaro Earth Snapshot
- ↑ (Spanish) A picture of the Cerro Cono with a brief description
- ↑ (Spanish) Noticiero Salta: ¿El Cono de Arita es natural o un monumento milenario?
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Salar de Arizaro. |