Saddle joint
| Saddle joint | |
|---|---|
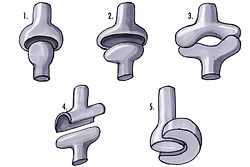 1: Ball and socket joint; 2: Condyloid joint (Ellipsoid); 3: Saddle joint; 4 Hinge joint; 5: Pivot joint; | |
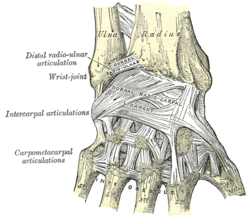 Ligaments of wrist. Posterior view. | |
| Details | |
| Latin | articulatio sellaris |
| Identifiers | |
| Gray's | p.286 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | a_64zPzhtm#/12161531 |
| TA | A03.0.00.048 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In a saddle joint (sellar joint, articulation by reciprocal reception) the opposing surfaces are reciprocally concave-convex.
Movements
The movements are as same as in the condyloid joint; that is to say, flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction are allowed; but no axial rotation. Saddle joints are said to be biaxial, allowing movement in the sagittal and frontal planes.
Examples
The best example of saddle joints are the base of the thumb and wrist. Sternoclavicular joint
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Saddle joints. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||