SRRM2
| Serine/arginine repetitive matrix 2 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | SRRM2 ; 300-KD; CWF21; Cwc21; SRL300; SRm300 | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 606032 MGI: 1923206 HomoloGene: 130678 GeneCards: SRRM2 Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
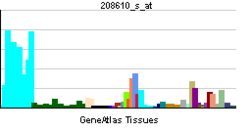 | |||||||||||||
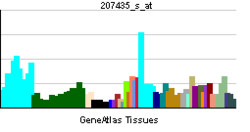 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 23524 | 75956 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000167978 | ENSMUSG00000039218 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q9UQ35 | Q8BTI8 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_016333 | NM_175229 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_057417 | NP_780438 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 16: 2.8 – 2.82 Mb | Chr 17: 23.8 – 23.82 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRRM2 gene.[1][2][3]
Interactions
SRRM2 has been shown to interact with Pinin.[4]
References
- ↑ Blencowe BJ, Baurén G, Eldridge AG, Issner R, Nickerson JA, Rosonina E et al. (Feb 2000). "The SRm160/300 splicing coactivator subunits". RNA 6 (1): 111–20. doi:10.1017/S1355838200991982. PMC 1369899. PMID 10668804. Vancouver style error (help)
- ↑ Sawada Y, Miura Y, Umeki K, Tamaoki T, Fujinaga K, Ohtaki S (Sep 2000). "Cloning and characterization of a novel RNA-binding protein SRL300 with RS domains". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1492 (1): 191–5. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(00)00065-8. PMID 11004489.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: SRRM2 serine/arginine repetitive matrix 2".
- ↑ Zimowska G, Shi J, Munguba G, Jackson MR, Alpatov R, Simmons MN et al. (Nov 2003). "Pinin/DRS/memA interacts with SRp75, SRm300 and SRrp130 in corneal epithelial cells". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44 (11): 4715–23. doi:10.1167/iovs.03-0240. PMID 14578391.
Further reading
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nakajima D, Ohira M, Seki N, Miyajima N et al. (1997). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 4 (2): 141–50. doi:10.1093/dnares/4.2.141. PMID 9205841.
- Blencowe BJ, Issner R, Nickerson JA, Sharp PA (1998). "A coactivator of pre-mRNA splicing". Genes Dev. 12 (7): 996–1009. doi:10.1101/gad.12.7.996. PMC 316672. PMID 9531537.
- McGarvey T, Rosonina E, McCracken S, Li Q, Arnaout R, Mientjes E et al. (2000). "The acute myeloid leukemia-associated protein, DEK, forms a splicing-dependent interaction with exon-product complexes". J. Cell Biol. 150 (2): 309–20. doi:10.1083/jcb.150.2.309. PMC 2180225. PMID 10908574.
- Jurica MS, Licklider LJ, Gygi SR, Grigorieff N, Moore MJ (2002). "Purification and characterization of native spliceosomes suitable for three-dimensional structural analysis". RNA 8 (4): 426–39. doi:10.1017/S1355838202021088. PMC 1370266. PMID 11991638.
- Zimowska G, Shi J, Munguba G, Jackson MR, Alpatov R, Simmons MN et al. (2003). "Pinin/DRS/memA interacts with SRp75, SRm300 and SRrp130 in corneal epithelial cells". Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 44 (11): 4715–23. doi:10.1167/iovs.03-0240. PMID 14578391.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Mukherji M, Stettler-Gill M, Peters EC (2004). "Robust phosphoproteomic profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation sites from human T cells using immobilized metal affinity chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry". Anal. Chem. 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935. Vancouver style error (help)
- Jin J, Smith FD, Stark C, Wells CD, Fawcett JP, Kulkarni S et al. (2004). "Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization". Curr. Biol. 14 (16): 1436–50. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.07.051. PMID 15324660.
- Ballif BA, Villén J, Beausoleil SA, Schwartz D, Gygi SP (2004). "Phosphoproteomic analysis of the developing mouse brain". Mol. Cell Proteomics 3 (11): 1093–101. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400085-MCP200. PMID 15345747. Vancouver style error (help)
- Benzinger A, Muster N, Koch HB, Yates JR, Hermeking H (2005). "Targeted proteomic analysis of 14-3-3 sigma, a p53 effector commonly silenced in cancer". Mol. Cell Proteomics 4 (6): 785–95. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500021-MCP200. PMID 15778465.
- Kim JE, Tannenbaum SR, White FM (2005). "Global phosphoproteome of HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma cells". J. Proteome Res. 4 (4): 1339–46. doi:10.1021/pr050048h. PMID 16083285.
- Nousiainen M, Silljé HH, Sauer G, Nigg EA, Körner R (2006). "Phosphoproteome analysis of the human mitotic spindle". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103 (14): 5391–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507066103. PMC 1459365. PMID 16565220. Vancouver style error (help)
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, Rush J, Gygi SP (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–92. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243. Vancouver style error (help)
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.