SNAP23
| Synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PDB rendering based on 1nhl. | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | SNAP23 ; HsT17016; SNAP-23; SNAP23A; SNAP23B | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 602534 MGI: 109356 HomoloGene: 37857 GeneCards: SNAP23 Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
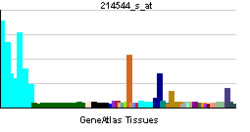 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 8773 | 20619 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000092531 | ENSMUSG00000027287 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | O00161 | O09044 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_003825 | NM_001177792 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_003816 | NP_001171263 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 15: 42.78 – 42.84 Mb | Chr 2: 120.57 – 120.6 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Synaptosomal-associated protein 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNAP23 gene.[1][2] Two alternative transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been described for this gene.
Function
Specificity of vesicular transport is regulated, in part, by the interaction of a vesicle-associated membrane protein termed synaptobrevin/VAMP with a target compartment membrane protein termed syntaxin. These proteins, together with SNAP25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa), form a complex which serves as a binding site for the general membrane fusion machinery. Synaptobrevin/VAMP and syntaxin are believed to be involved in vesicular transport in most, if not all cells, while SNAP25 is present almost exclusively in the brain, suggesting that a ubiquitously expressed homolog of SNAP25 exists to facilitate transport vesicle/target membrane fusion in other tissues.
SNAP23 is structurally and functionally similar to SNAP25 and binds tightly to multiple syntaxins and synaptobrevins/VAMPs. It is an essential component of the high affinity receptor for the general membrane fusion machinery and is an important regulator of transport vesicle docking and fusion.[3]
Clinical significance
In individuals with insulin resistance, SNAP23 is found to be translocated from the plasma membrane to the cytosol where it becomes associated with lipid droplets and is therefore unable to translocate GLUT-4 to the membrane, hindering glucose transport.
Interactions
SNAP23 has been shown to interact with STX2,[2][4][5][6] NAPA,[7] KIF5B,[8] STX6,[9] SYBL1,[10][11] VAMP2,[4][12][13] Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator,[14] STX4,[2][4][5][6][12][13][15][16] Syntaxin 3,[2][4][6][15] STX1A,[2][4][5][6][15] Vesicle-associated membrane protein 8,[4][12] STX11,[7][17] VAMP3[4][12][16] and SNAPAP.[18]
References
- ↑ Mollinedo F, Lazo PA (April 1997). "Identification of two isoforms of the vesicle-membrane fusion protein SNAP-23 in human neutrophils and HL-60 cells". Biochem Biophys Res Commun 231 (3): 808–12. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6196. PMID 9070898.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Ravichandran V, Chawla A, Roche PA (August 1996). "Identification of a novel syntaxin- and synaptobrevin/VAMP-binding protein, SNAP-23, expressed in non-neuronal tissues". J Biol Chem 271 (23): 13300–3. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.23.13300. PMID 8663154.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: SNAP23 synaptosomal-associated protein, 23kDa".
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Imai, Akane; Nashida Tomoko; Yoshie Sumio; Shimomura Hiromi (August 2003). "Intracellular localisation of SNARE proteins in rat parotid acinar cells: SNARE complexes on the apical plasma membrane". Arch. Oral Biol. (England) 48 (8): 597–604. doi:10.1016/S0003-9969(03)00116-X. ISSN 0003-9969. PMID 12828989.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Li, Guangmu; Alexander Edward A; Schwartz John H (May 2003). "Syntaxin isoform specificity in the regulation of renal H+-ATPase exocytosis". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (22): 19791–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212250200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12651853.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Araki, S; Tamori Y; Kawanishi M; Shinoda H; Masugi J; Mori H; Niki T; Okazawa H; Kubota T; Kasuga M (May 1997). "Inhibition of the binding of SNAP-23 to syntaxin 4 by Munc18c". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (UNITED STATES) 234 (1): 257–62. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6560. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 9168999.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Rual, Jean-François; Venkatesan Kavitha, Hao Tong, Hirozane-Kishikawa Tomoko, Dricot Amélie, Li Ning, Berriz Gabriel F, Gibbons Francis D, Dreze Matija, Ayivi-Guedehoussou Nono, Klitgord Niels, Simon Christophe, Boxem Mike, Milstein Stuart, Rosenberg Jennifer, Goldberg Debra S, Zhang Lan V, Wong Sharyl L, Franklin Giovanni, Li Siming, Albala Joanna S, Lim Janghoo, Fraughton Carlene, Llamosas Estelle, Cevik Sebiha, Bex Camille, Lamesch Philippe, Sikorski Robert S, Vandenhaute Jean, Zoghbi Huda Y, Smolyar Alex, Bosak Stephanie, Sequerra Reynaldo, Doucette-Stamm Lynn, Cusick Michael E, Hill David E, Roth Frederick P, Vidal Marc (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature (England) 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- ↑ Diefenbach, Russell J; Diefenbach Eve; Douglas Mark W; Cunningham Anthony L (December 2002). "The heavy chain of conventional kinesin interacts with the SNARE proteins SNAP25 and SNAP23". Biochemistry (United States) 41 (50): 14906–15. doi:10.1021/bi026417u. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 12475239.
- ↑ Martín-Martín, B; Nabokina S M; Blasi J; Lazo P A; Mollinedo F (October 2000). "Involvement of SNAP-23 and syntaxin 6 in human neutrophil exocytosis". Blood (UNITED STATES) 96 (7): 2574–83. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 11001914.
- ↑ Martinez-Arca, Sonia; Rudge Rachel, Vacca Marcella, Raposo Graça, Camonis Jacques, Proux-Gillardeaux Véronique, Daviet Laurent, Formstecher Etienne, Hamburger Alexandre, Filippini Francesco, D'Esposito Maurizio, Galli Thierry (July 2003). "A dual mechanism controlling the localization and function of exocytic v-SNAREs". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (United States) 100 (15): 9011–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.1431910100. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 166429. PMID 12853575.
- ↑ Galli, T; Zahraoui A; Vaidyanathan V V; Raposo G; Tian J M; Karin M; Niemann H; Louvard D (June 1998). "A Novel Tetanus Neurotoxin-insensitive Vesicle-associated Membrane Protein in SNARE Complexes of the Apical Plasma Membrane of Epithelial Cells". Mol. Biol. Cell (UNITED STATES) 9 (6): 1437–48. doi:10.1091/mbc.9.6.1437. ISSN 1059-1524. PMC 25366. PMID 9614185.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Paumet, F; Le Mao J; Martin S; Galli T; David B; Blank U; Roa M (June 2000). "Soluble NSF attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) in RBL-2H3 mast cells: functional role of syntaxin 4 in exocytosis and identification of a vesicle-associated membrane protein 8-containing secretory compartment". J. Immunol. (UNITED STATES) 164 (11): 5850–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5850. ISSN 0022-1767. PMID 10820264.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Kawanishi, M; Tamori Y; Okazawa H; Araki S; Shinoda H; Kasuga M (March 2000). "Role of SNAP23 in insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mediation of complex formation between syntaxin4 and VAMP2". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (11): 8240–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.11.8240. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10713150.
- ↑ Cormet-Boyaka, Estelle; Di Anke; Chang Steven Y; Naren Anjaparavanda P; Tousson Albert; Nelson Deborah J; Kirk Kevin L (September 2002). "CFTR chloride channels are regulated by a SNAP-23/syntaxin 1A complex". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (United States) 99 (19): 12477–82. doi:10.1073/pnas.192203899. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 129470. PMID 12209004.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Steegmaier, M; Yang B; Yoo J S; Huang B; Shen M; Yu S; Luo Y; Scheller R H (December 1998). "Three novel proteins of the syntaxin/SNAP-25 family". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 273 (51): 34171–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.51.34171. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9852078.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Freedman, Steven J; Song Hyun Kyu, Xu Yingwu, Sun Zhen-Yu J, Eck Michael J (April 2003). "Homotetrameric structure of the SNAP-23 N-terminal coiled-coil domain". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 278 (15): 13462–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210483200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12556468.
- ↑ Valdez, A C; Cabaniols J P; Brown M J; Roche P A (March 1999). "Syntaxin 11 is associated with SNAP-23 on late endosomes and the trans-Golgi network". J. Cell. Sci. (ENGLAND) 112 (6): 845–54. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 10036234.
- ↑ Buxton, Penelope; Zhang Xiang-Ming; Walsh Bong; Sriratana Absorn; Schenberg Irina; Manickam Elizabeth; Rowe Tony (October 2003). "Identification and characterization of Snapin as a ubiquitously expressed SNARE-binding protein that interacts with SNAP23 in non-neuronal cells". Biochem. J. (England) 375 (Pt 2): 433–40. doi:10.1042/BJ20030427. PMC 1223698. PMID 12877659.
Further reading
- Araki S; Tamori Y; Kawanishi M et al. (1997). "Inhibition of the binding of SNAP-23 to syntaxin 4 by Munc18c". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 234 (1): 257–62. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6560. PMID 9168999.
- Tang BL; Tan AE; Lim LK et al. (1998). "Syntaxin 12, a member of the syntaxin family localized to the endosome". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (12): 6944–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.12.6944. PMID 9507000.
- Galli T; Zahraoui A; Vaidyanathan VV et al. (1998). "A Novel Tetanus Neurotoxin-insensitive Vesicle-associated Membrane Protein in SNARE Complexes of the Apical Plasma Membrane of Epithelial Cells". Mol. Biol. Cell 9 (6): 1437–48. doi:10.1091/mbc.9.6.1437. PMC 25366. PMID 9614185.
- Foster LJ; Yeung B; Mohtashami M et al. (1998). "Binary interactions of the SNARE proteins syntaxin-4, SNAP23, and VAMP-2 and their regulation by phosphorylation". Biochemistry 37 (31): 11089–96. doi:10.1021/bi980253t. PMID 9693005.
- Riento K; Galli T; Jansson S et al. (1999). "Interaction of Munc-18-2 with syntaxin 3 controls the association of apical SNAREs in epithelial cells". J. Cell. Sci. 111 (17): 2681–8. PMID 9701566.
- Guo Z, Turner C, Castle D (1998). "Relocation of the t-SNARE SNAP-23 from lamellipodia-like cell surface projections regulates compound exocytosis in mast cells". Cell 94 (4): 537–48. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81594-9. PMID 9727496.
- Inoue T; Nielsen S; Mandon B et al. (1998). "SNAP-23 in rat kidney: colocalization with aquaporin-2 in collecting duct vesicles". Am. J. Physiol. 275 (5 Pt 2): F752–60. PMID 9815132.
- Valdez AC, Cabaniols JP, Brown MJ, Roche PA (1999). "Syntaxin 11 is associated with SNAP-23 on late endosomes and the trans-Golgi network". J. Cell. Sci. 112 (6): 845–54. PMID 10036234.
- Okamoto M, Schoch S, Südhof TC (1999). "EHSH1/intersectin, a protein that contains EH and SH3 domains and binds to dynamin and SNAP-25. A protein connection between exocytosis and endocytosis?". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (26): 18446–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.26.18446. PMID 10373452.
- Cabaniols JP, Ravichandran V, Roche PA (2000). "Phosphorylation of SNAP-23 by the Novel Kinase SNAK Regulates t-SNARE Complex Assembly". Mol. Biol. Cell 10 (12): 4033–41. doi:10.1091/mbc.10.12.4033. PMC 25741. PMID 10588641.
- Kawanishi M; Tamori Y; Okazawa H et al. (2000). "Role of SNAP23 in insulin-induced translocation of GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mediation of complex formation between syntaxin4 and VAMP2". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (11): 8240–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.11.8240. PMID 10713150.
- Paumet F; Le Mao J; Martin S et al. (2000). "Soluble NSF attachment protein receptors (SNAREs) in RBL-2H3 mast cells: functional role of syntaxin 4 in exocytosis and identification of a vesicle-associated membrane protein 8-containing secretory compartment". J. Immunol. 164 (11): 5850–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5850. PMID 10820264.
- Scales SJ; Chen YA; Yoo BY et al. (2000). "SNAREs contribute to the specificity of membrane fusion". Neuron 26 (2): 457–64. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81177-0. PMID 10839363.
- Martín-Martín B; Nabokina SM; Blasi J et al. (2000). "Involvement of SNAP-23 and syntaxin 6 in human neutrophil exocytosis". Blood 96 (7): 2574–83. PMID 11001914.
- Faigle W; Colucci-Guyon E; Louvard D et al. (2000). "Vimentin Filaments in Fibroblasts Are a Reservoir for SNAP23, a Component of the Membrane Fusion Machinery". Mol. Biol. Cell 11 (10): 3485–94. doi:10.1091/mbc.11.10.3485. PMC 15008. PMID 11029050.
- Lazo PA; Nadal M; Ferrer M et al. (2001). "Genomic organization, chromosomal localization, alternative splicing, and isoforms of the human synaptosome-associated protein-23 gene implicated in vesicle-membrane fusion processes". Hum. Genet. 108 (3): 211–5. doi:10.1007/s004390100480. PMID 11354632.
- Shukla A; Corydon TJ; Nielsen S et al. (2001). "Identification of three new splice variants of the SNARE protein SNAP-23". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 285 (2): 320–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5144. PMID 11444845.
- Logan MR, Lacy P, Bablitz B, Moqbel R (2002). "Expression of eosinophil target SNAREs as potential cognate receptors for vesicle-associated membrane protein-2 in exocytosis". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 109 (2): 299–306. doi:10.1067/mai.2002.121453. PMID 11842301.
| |||||||||
